Astronomy Exam #2 for the 10
... The hot main sequence stars appear to be mostly B and A spectral type with an absolute magnitude between +2 and -5. This range in absolute magnitudes corresponds to a range in luminosity of between 16 and 10,000 solar luminosities. These stars will have a short main sequence lifetime compared to the ...
... The hot main sequence stars appear to be mostly B and A spectral type with an absolute magnitude between +2 and -5. This range in absolute magnitudes corresponds to a range in luminosity of between 16 and 10,000 solar luminosities. These stars will have a short main sequence lifetime compared to the ...
18 are exactly the same ones as for galactic star clusters of early
... the observations to fainter limits and this will be done, despite the photometric difficulties associated with the bright nebulosity. In the analogous but more distant cluster, NGC 6611, Walker (1961) found many very faint variables at 20 to 21 magnitude. Nine years ago one faint variable of about v ...
... the observations to fainter limits and this will be done, despite the photometric difficulties associated with the bright nebulosity. In the analogous but more distant cluster, NGC 6611, Walker (1961) found many very faint variables at 20 to 21 magnitude. Nine years ago one faint variable of about v ...
Wien`s law - Uplift Education
... • Perhaps the Universe is not infinite. But current model of the Universe is that it is infinite. • Perhaps the light is absorbed before it gets to us. But then Universe would warm up and eventually reradiate energy. Real help: the Big Bang model leads to the idea that the observable universe is not ...
... • Perhaps the Universe is not infinite. But current model of the Universe is that it is infinite. • Perhaps the light is absorbed before it gets to us. But then Universe would warm up and eventually reradiate energy. Real help: the Big Bang model leads to the idea that the observable universe is not ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... Are you familiar with the properties of the Interstellar Medium (ISM)? Do you understand how the star formation process begins? How well you understand what processes are going on during the proto-star stage of a star’s life? What needs to happen for a proto-star to become a main sequence star? What ...
... Are you familiar with the properties of the Interstellar Medium (ISM)? Do you understand how the star formation process begins? How well you understand what processes are going on during the proto-star stage of a star’s life? What needs to happen for a proto-star to become a main sequence star? What ...
34ReviewNuclear
... You look at a star cluster and see two red stars: one (A) is much brighter than the other (B). What can you conclude? A. Star A is hotter than star B B. Star A is farther away than star B C. Star A is bigger than star B D. Star A is smaller than star B E. The stars are the same size ...
... You look at a star cluster and see two red stars: one (A) is much brighter than the other (B). What can you conclude? A. Star A is hotter than star B B. Star A is farther away than star B C. Star A is bigger than star B D. Star A is smaller than star B E. The stars are the same size ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... • V: Main-sequence stars – The full classification of a star includes both a spectral type and a luminosity class: • The Sun is a G2 V • Proxima Centauri is M5 V • Betelgeuse is M2 I • Sirius A: A1 V • Sirius B: DA2 V ...
... • V: Main-sequence stars – The full classification of a star includes both a spectral type and a luminosity class: • The Sun is a G2 V • Proxima Centauri is M5 V • Betelgeuse is M2 I • Sirius A: A1 V • Sirius B: DA2 V ...
The Helix Nebula • NGC 7293
... In this detailed view, a forest of thousands of gaseous tentacles embedded along the inner rim of the nebula points back toward the central, dying star, a small but super-hot white dwarf that seems to float in a sea of blue gas [white dot in center of nebula]. These tentacles, which superficially re ...
... In this detailed view, a forest of thousands of gaseous tentacles embedded along the inner rim of the nebula points back toward the central, dying star, a small but super-hot white dwarf that seems to float in a sea of blue gas [white dot in center of nebula]. These tentacles, which superficially re ...
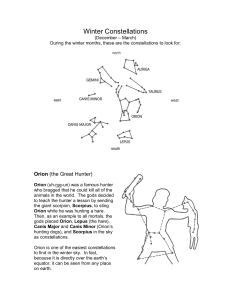
seven winter constellations
... gods rewarded him for this important invention with a place of honor in the sky. Auriga holds the reins to his chariot in his right hand. In his left arm he carries a small goat, marked by one bright star known as “the Mother Goat.” Just below “the Mother Goat” is a triangle of three smaller stars c ...
... gods rewarded him for this important invention with a place of honor in the sky. Auriga holds the reins to his chariot in his right hand. In his left arm he carries a small goat, marked by one bright star known as “the Mother Goat.” Just below “the Mother Goat” is a triangle of three smaller stars c ...
White Dwarfs
... • Sun will expand to a Red giant in ~ 5 billion years • Expands to ~ Earth’s radius • Earth will then be incinerated (焚化)! • Sun may form a planetary nebula (but uncertain) • Sun’s C,O core will become a white dwarf ...
... • Sun will expand to a Red giant in ~ 5 billion years • Expands to ~ Earth’s radius • Earth will then be incinerated (焚化)! • Sun may form a planetary nebula (but uncertain) • Sun’s C,O core will become a white dwarf ...
Properties of Supernovae
... Supernova explosions are the most powerful events in the Universe. In less than a second, about 1044 Joules of energy are released---about the same as the Sun has released in its entire lifetime! The explosion results from the death of a massive star which has consumed its entire fuel supply. The ap ...
... Supernova explosions are the most powerful events in the Universe. In less than a second, about 1044 Joules of energy are released---about the same as the Sun has released in its entire lifetime! The explosion results from the death of a massive star which has consumed its entire fuel supply. The ap ...
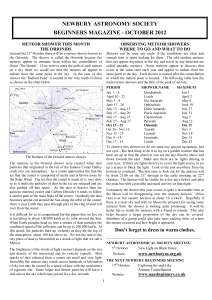
October 2012 - astronomy for beginners
... better fun to watch for meteors with a friend or friends. This also helps because a larger proportion of the sky can be covered. Members of a group could also take turns making notes of where the meteor occurred and how bright it appeared. ...
... better fun to watch for meteors with a friend or friends. This also helps because a larger proportion of the sky can be covered. Members of a group could also take turns making notes of where the meteor occurred and how bright it appeared. ...
the printable Observing Olympics Object Info Sheet in pdf
... nebula has been expanding at a constant rate of 10 milli-arcseconds a year, then it would take 1000 ± 260 years to reach a diameter of 20 arcseconds. This may be an upper limit to the age, because ejected material will be slowed when it encounters material ejected from the star at earlier stages of ...
... nebula has been expanding at a constant rate of 10 milli-arcseconds a year, then it would take 1000 ± 260 years to reach a diameter of 20 arcseconds. This may be an upper limit to the age, because ejected material will be slowed when it encounters material ejected from the star at earlier stages of ...
Measuring Stellar Distances
... Furthermore, the volume defined by r = 20 parsecs is only one ten-millionth of the total volume of the disk of our Galaxy. How can we be sure that this tiny volume contains a representative sample of stars? Fortunately, a theoretical argument involving stellar lifetimes serves as a consistency check ...
... Furthermore, the volume defined by r = 20 parsecs is only one ten-millionth of the total volume of the disk of our Galaxy. How can we be sure that this tiny volume contains a representative sample of stars? Fortunately, a theoretical argument involving stellar lifetimes serves as a consistency check ...
File
... In this unit we will learn about: • How we measure stars’ distances using parallax • Why a star’s color indicates temperature & how to use Wien’s law to determine temperature • The difference between luminosity and brightness • How we can measure radius using temperature • The magnitude system of s ...
... In this unit we will learn about: • How we measure stars’ distances using parallax • Why a star’s color indicates temperature & how to use Wien’s law to determine temperature • The difference between luminosity and brightness • How we can measure radius using temperature • The magnitude system of s ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • the core of a red giant star, revealed when the outer layers are shed during the planetary nebula phase. • a white dwarf star that has cooled to a low temperature over its long lifetime. Stars with masses less that 8% of that of the Sun remain as long-lived, dim brown objects, never brightening li ...
... • the core of a red giant star, revealed when the outer layers are shed during the planetary nebula phase. • a white dwarf star that has cooled to a low temperature over its long lifetime. Stars with masses less that 8% of that of the Sun remain as long-lived, dim brown objects, never brightening li ...
1 Astronomical Measurements and Quantities 2 Astronomical Objects
... Photometric concepts, Magnitudes and Colors: intensity, flux density and luminosity; apparent magnitudes and Pogson formula; filters and systems of magnitudes; colors; distance modulus and absolute magnitudes; magnitude corrections; absolute energy distributions and bolometric magnitudes; luminosity ...
... Photometric concepts, Magnitudes and Colors: intensity, flux density and luminosity; apparent magnitudes and Pogson formula; filters and systems of magnitudes; colors; distance modulus and absolute magnitudes; magnitude corrections; absolute energy distributions and bolometric magnitudes; luminosity ...
Lecture 4: Telescopes Web site Stuff from last time Naked eye and magnitudes
... for "seeing faraway things as though nearby." Most practical applications were maritime use; spotting ships or land from far off. ...
... for "seeing faraway things as though nearby." Most practical applications were maritime use; spotting ships or land from far off. ...
Chapter 24
... Other galaxies • Four basic types of galaxies • Barred spiral galaxy • Stars arranged in the shape of a bar • Generally quite large • About 10% of all galaxies • Elliptical galaxy • Ellipsoidal shape • About 60% of all galaxies • Most are smaller than spiral galaxies; however, they are also the lar ...
... Other galaxies • Four basic types of galaxies • Barred spiral galaxy • Stars arranged in the shape of a bar • Generally quite large • About 10% of all galaxies • Elliptical galaxy • Ellipsoidal shape • About 60% of all galaxies • Most are smaller than spiral galaxies; however, they are also the lar ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.