Stars - MrCrabtreesScience
... • Pressure from the core balance pressure from above layers, particles don’t move. • Energy bounces around inside this layer for an average of 170,000 years. • 7-2,000,000 K ...
... • Pressure from the core balance pressure from above layers, particles don’t move. • Energy bounces around inside this layer for an average of 170,000 years. • 7-2,000,000 K ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... About the Groups Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger ...
... About the Groups Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger ...
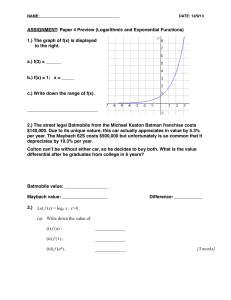
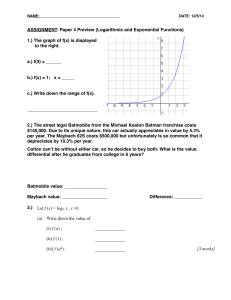
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... Answer: ________!! ...
... Answer: ________!! ...
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... Answer: ________!! ...
... Answer: ________!! ...
Star- large ball of gas held together by large ball of gas held
... Stars originate from clouds of gas and dust molecules that clump up due to gravity. When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, a ...
... Stars originate from clouds of gas and dust molecules that clump up due to gravity. When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, a ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19) The basics: GRAVITY vs. PRESSURE
... are very distant (~ 1,000 to 100,000 pc), and are not distributed in the disk of the Milky Way ⇒ they form a spherical “halo” around the Milky Way. H-R diagrams: MS includes low mass stars, but NO stars with mass > about 0.8 solar masses ⇒ all are old! Ages ~ 12-17 billion years. These were almost c ...
... are very distant (~ 1,000 to 100,000 pc), and are not distributed in the disk of the Milky Way ⇒ they form a spherical “halo” around the Milky Way. H-R diagrams: MS includes low mass stars, but NO stars with mass > about 0.8 solar masses ⇒ all are old! Ages ~ 12-17 billion years. These were almost c ...
c - Fsusd
... a) absolute brightness & temperature b) apparent brightness & absolute brightness c) distance & absolute brightness d) diameter & apparent brightness ...
... a) absolute brightness & temperature b) apparent brightness & absolute brightness c) distance & absolute brightness d) diameter & apparent brightness ...
Stars - PAMS-Doyle
... • The nearest galaxy to ours is called the "Sagittarius Dwarf" and it is about 60 000 light years away from our own galaxy (the Milky Way). Assuming we can get a vehicle to reach the speed of light, it would take 60 000 years for a vehicle to travel to this galaxy. • Given current technology, it is ...
... • The nearest galaxy to ours is called the "Sagittarius Dwarf" and it is about 60 000 light years away from our own galaxy (the Milky Way). Assuming we can get a vehicle to reach the speed of light, it would take 60 000 years for a vehicle to travel to this galaxy. • Given current technology, it is ...
presentation source
... • Protostar - collapsing core of molecular cloud. Pressure builds till nuclear fusion ignites in centre, becoming a star. • Associated with disks (planetary systems), outflows and jets. • Disperse their cocoon to become visible. • Typically form in clusters, dominated by light from 1-2 brightest mem ...
... • Protostar - collapsing core of molecular cloud. Pressure builds till nuclear fusion ignites in centre, becoming a star. • Associated with disks (planetary systems), outflows and jets. • Disperse their cocoon to become visible. • Typically form in clusters, dominated by light from 1-2 brightest mem ...
Stellar Evolution: After the Main Sequence
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of Population II stars, then ejected into space and incorporated into a later ste ...
... • Relatively young Population I stars are metal rich; ancient Population II stars are metal poor • The metals (heavy elements) in Population I stars were manufactured by thermonuclear reactions in an earlier generation of Population II stars, then ejected into space and incorporated into a later ste ...
File
... The explosion called a supernova occurs after a large star has become a red supergiant. When the star stops expanding because it can no longer create enough energy to support its own mass, it collapses completely and makes a giant explosion. A supernova is brighter than all the stars in the galaxy c ...
... The explosion called a supernova occurs after a large star has become a red supergiant. When the star stops expanding because it can no longer create enough energy to support its own mass, it collapses completely and makes a giant explosion. A supernova is brighter than all the stars in the galaxy c ...
Where is the Sun in the Milk Way?
... • This equaDon shows the effect of the geometrical diluDon of the flux as a funcDon of distance from a star. • It’s also called the “Inverse-‐Square Law” ...
... • This equaDon shows the effect of the geometrical diluDon of the flux as a funcDon of distance from a star. • It’s also called the “Inverse-‐Square Law” ...
Universe ppt - Killeen ISD
... Moving Galaxies - Astronomers use information about how galaxies are moving as one way to develop ideas about how the universe formed. By examining the visible light spectrum of a galaxy, astronomers can tell how fast the galaxy is moving toward or away from our galaxy (the Milky Way). Only a few of ...
... Moving Galaxies - Astronomers use information about how galaxies are moving as one way to develop ideas about how the universe formed. By examining the visible light spectrum of a galaxy, astronomers can tell how fast the galaxy is moving toward or away from our galaxy (the Milky Way). Only a few of ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... A star has a high luminosity (100 solar luminosities) and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? ...
... A star has a high luminosity (100 solar luminosities) and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? ...
HERE
... Spectral class O, B stars (rare, but very interesting): Giant, hot, bright, blue stars burn up quickly and die violently. Lifetime is only 1-10 million years. Spectral class A,F,G,K stars (like the Sun): Middle of the road habits. Orange, yellow or white in color. Typically will live for 1-20 bi ...
... Spectral class O, B stars (rare, but very interesting): Giant, hot, bright, blue stars burn up quickly and die violently. Lifetime is only 1-10 million years. Spectral class A,F,G,K stars (like the Sun): Middle of the road habits. Orange, yellow or white in color. Typically will live for 1-20 bi ...
Sections F and G
... objects are hotter than those around larger, less dense objects. Accretion discs around white dwarfs lead to optical emission (novae), while those around neutron stars (or black holes) result in X-ray emission (X-ray binaries). Novae A nova (short for stella nova, or new star) is a star which underg ...
... objects are hotter than those around larger, less dense objects. Accretion discs around white dwarfs lead to optical emission (novae), while those around neutron stars (or black holes) result in X-ray emission (X-ray binaries). Novae A nova (short for stella nova, or new star) is a star which underg ...
The Temperatures of Stars
... A stellar spectrum is produced by taking starlight and spreading it out into its constituent colors, such as: ...
... A stellar spectrum is produced by taking starlight and spreading it out into its constituent colors, such as: ...
How many stars are visible to the naked eye in the night sky?
... Since the Canadian Astronaut Program was established in 1983, twelve Canadians have been selected to become astronauts. Currently there are two active Canadian Astronauts. They are: LieutenantColonel Jeremy Hansen and Dr. David SaintJacques. ...
... Since the Canadian Astronaut Program was established in 1983, twelve Canadians have been selected to become astronauts. Currently there are two active Canadian Astronauts. They are: LieutenantColonel Jeremy Hansen and Dr. David SaintJacques. ...
Stars - Lauer Science
... ▪ Gravity pulls the gas and dust together to form a protostar. ▪ Protostar is the earliest stage of a star’s life. ...
... ▪ Gravity pulls the gas and dust together to form a protostar. ▪ Protostar is the earliest stage of a star’s life. ...
Absolute Magnitudes of Supernovae
... Figure 1: Six views of a distance galaxy with a supernova to the lower left of the galaxy. Notice the decreasing brightness and changing color of the supernova with time. (Hubble Space Telescope) ...
... Figure 1: Six views of a distance galaxy with a supernova to the lower left of the galaxy. Notice the decreasing brightness and changing color of the supernova with time. (Hubble Space Telescope) ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.