Extragalactic Distances from Planetary Nebulae
... To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such stars come from M > 2 M progenitors. ...
... To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such stars come from M > 2 M progenitors. ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... mass. Stars with greater mass have a greater gravitational attraction – causing the core temperature to be greater, which in turn increases the rate of nuclear fusion and decreases the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of tim ...
... mass. Stars with greater mass have a greater gravitational attraction – causing the core temperature to be greater, which in turn increases the rate of nuclear fusion and decreases the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of tim ...
More on Stars and the Sky
... objects appear stationary. Why? What is the typical parallax of a nearby star? Why is it not possible to measure the parallax better than 0.01” from ground based instruments, but can be done from space? What is the precession of the Earth. Which of the following would change due to precession celest ...
... objects appear stationary. Why? What is the typical parallax of a nearby star? Why is it not possible to measure the parallax better than 0.01” from ground based instruments, but can be done from space? What is the precession of the Earth. Which of the following would change due to precession celest ...
Star formation, feedback and the role of SNe II and SNe Ia in the
... most of the gas in dwarf galaxies with halo circular velocities lower than 30 km s-1. Mayer et at 2006 simulated the interaction of dwarf spheroidal galaxies with the Milky Way halo and found that a galaxy similar to Draco can be stripped completely of its gas in a time scale 2-3 Gyr if the gas is m ...
... most of the gas in dwarf galaxies with halo circular velocities lower than 30 km s-1. Mayer et at 2006 simulated the interaction of dwarf spheroidal galaxies with the Milky Way halo and found that a galaxy similar to Draco can be stripped completely of its gas in a time scale 2-3 Gyr if the gas is m ...
In the icy near-vacuum of interstellar space are seething
... And yet these tiny grains—of uncertain composition, though graphite, silicon, carbide, and iron are possible constituents—contribute less than one percent to a cloud's total mass. Their effect becomes appreciable only because of the great size of the clouds—some of them up to 100 light-years across. ...
... And yet these tiny grains—of uncertain composition, though graphite, silicon, carbide, and iron are possible constituents—contribute less than one percent to a cloud's total mass. Their effect becomes appreciable only because of the great size of the clouds—some of them up to 100 light-years across. ...
Table of Contents - Imiloa Astronomy Center
... was, is purported to have asked Job if he (Job) was able to “loose the bands of Orion” (Job ...
... was, is purported to have asked Job if he (Job) was able to “loose the bands of Orion” (Job ...
Powerpoint
... These are Brown Dwarfs or failed stars. Very difficult to detect because so faint. First seen in 1994 with Palomar 200”. How many are there? ...
... These are Brown Dwarfs or failed stars. Very difficult to detect because so faint. First seen in 1994 with Palomar 200”. How many are there? ...
The star Epsilon UMa, or more commonly known as Alioth
... way to remember these classes in order is by remembering that “Only Bored Astronomers Find Gratification Knowing Mnemonics”. Alioth’s spectral type is A in which for these stars the color of the light emitted ranges from a very light blue to white and the approximate surface temperature ranges from ...
... way to remember these classes in order is by remembering that “Only Bored Astronomers Find Gratification Knowing Mnemonics”. Alioth’s spectral type is A in which for these stars the color of the light emitted ranges from a very light blue to white and the approximate surface temperature ranges from ...
Hitomi Observation of the Highly Obscured High-Mass X-ray
... of continuum and line components significantly decreased in this ten years while the equivalent widths increased. Unabsorbed luminosity in 2 to 10 keV is 5.8×1035 ergs/s, which is far below the Eddington limit of 1.8×1038 ergs/s for a neutron star of 1.4 M⊙ and hence permits moderate accretion. The ...
... of continuum and line components significantly decreased in this ten years while the equivalent widths increased. Unabsorbed luminosity in 2 to 10 keV is 5.8×1035 ergs/s, which is far below the Eddington limit of 1.8×1038 ergs/s for a neutron star of 1.4 M⊙ and hence permits moderate accretion. The ...
My power point presentation on spectroscopy of stars (ppt file)
... • We can hardly see any surface details from the solar system, except for our own Sun • The interior of a star is even more hidden than the surface layers • Essentially the only information a star sends to us is its electromagnetic radiation • Can we dissect the radiation from a star to find out any ...
... • We can hardly see any surface details from the solar system, except for our own Sun • The interior of a star is even more hidden than the surface layers • Essentially the only information a star sends to us is its electromagnetic radiation • Can we dissect the radiation from a star to find out any ...
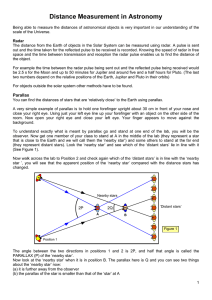
The Astronomical Unit and Parallax Laboratory Worksheet
... The first page on the graphs handout shows observations of the spectrum of another star, similar to the Sun but far more distant, over the course of a year, as seen from the Earth. The wave ...
... The first page on the graphs handout shows observations of the spectrum of another star, similar to the Sun but far more distant, over the course of a year, as seen from the Earth. The wave ...
Chapter 15: The Deaths of Massive Stars
... (b) Shock waves are sent outward that throw off the outer layers of the supergiant. These shock waves may be further heated by neutrinos escaping the collapsed core. 5. Elements heavier than iron cannot be formed without some source of energy. Heavy elements found here on Earth can be produced in tw ...
... (b) Shock waves are sent outward that throw off the outer layers of the supergiant. These shock waves may be further heated by neutrinos escaping the collapsed core. 5. Elements heavier than iron cannot be formed without some source of energy. Heavy elements found here on Earth can be produced in tw ...
UniverseofGalaxies
... divided into SBa, SBb, SBc, with similar characteristics to regular spirals, except for a centrallyoriented bar ...
... divided into SBa, SBb, SBc, with similar characteristics to regular spirals, except for a centrallyoriented bar ...
PROBLEM SET #9 SOLUTIONS AST142 1. Quasar luminosity
... is accreting at the Eddington rate, and show that these two findings are consistent with one another. ...
... is accreting at the Eddington rate, and show that these two findings are consistent with one another. ...
An interesting nebular object in LDN 288
... (b in Fig.5b). There is another star with a jet in its vicinity (object c in the Fig.5b). c. SNO 69 [3] (see Fig.5c). This looks like a trapezium-like system, consisting of four stars. There are spiral jets, at the ends of which there are condensations. It seems that not only the jets, but also the ...
... (b in Fig.5b). There is another star with a jet in its vicinity (object c in the Fig.5b). c. SNO 69 [3] (see Fig.5c). This looks like a trapezium-like system, consisting of four stars. There are spiral jets, at the ends of which there are condensations. It seems that not only the jets, but also the ...
Lab 1: The Celestial Sphere
... will disassemble the globe. One full clockwise turn represents one day. (If you wished to, you could hold the Earth still and turn the celestial sphere. Hence, the daily rotation of the Earth and the apparent rotation of the stars around the Earth are equivalent for this lab.) 5. You can make the Su ...
... will disassemble the globe. One full clockwise turn represents one day. (If you wished to, you could hold the Earth still and turn the celestial sphere. Hence, the daily rotation of the Earth and the apparent rotation of the stars around the Earth are equivalent for this lab.) 5. You can make the Su ...
Fulltext PDF
... The stars of a galaxy distribute themselves into broadly three components, viz. – disc, halo, and bulge (Figure 1). The halo is made up of an older population of stars that constitute globular clusters. Globular clusters are made up of low metallicity, dense aggregates of 50,000–100,000 stars, gravi ...
... The stars of a galaxy distribute themselves into broadly three components, viz. – disc, halo, and bulge (Figure 1). The halo is made up of an older population of stars that constitute globular clusters. Globular clusters are made up of low metallicity, dense aggregates of 50,000–100,000 stars, gravi ...
Solutions
... 2. Right now the Sun is a main-sequence star. Later in its life, it will become a red giant: it’s luminosity will go up hundreds or thousands of times, it will be many (between ten and a hundred) times larger, and it will be a bit cooler. (a) Will the rate at which the Sun converts some of its mass ...
... 2. Right now the Sun is a main-sequence star. Later in its life, it will become a red giant: it’s luminosity will go up hundreds or thousands of times, it will be many (between ten and a hundred) times larger, and it will be a bit cooler. (a) Will the rate at which the Sun converts some of its mass ...
Astronomy 15 - Homework 3 - Due Wed. April 24 1) As we`ll see
... Suppose the planet absorbs all this power and reflects none of it, that it radiates as a blackbody over its whole surface with a single temperature (the planet might be a small, rapidly spinning, blackened copper ball, for example – in that case heat would quickly conduct through the whole body. Obv ...
... Suppose the planet absorbs all this power and reflects none of it, that it radiates as a blackbody over its whole surface with a single temperature (the planet might be a small, rapidly spinning, blackened copper ball, for example – in that case heat would quickly conduct through the whole body. Obv ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.