Interpolation of Magnitude.
... We are now going to make two estimates of a semi- regular star called W Cygni (W Cyg). You should have its chart in front of you. Click and it will be the next picture. ...
... We are now going to make two estimates of a semi- regular star called W Cygni (W Cyg). You should have its chart in front of you. Click and it will be the next picture. ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... high mass stars and low mass stars, pre-main-sequence and post-main-sequence stages, core sizes, SchönbergChandrasekhar limit, isothermal cores, changing from static, spherically-symmetric models to realist models, ...
... high mass stars and low mass stars, pre-main-sequence and post-main-sequence stages, core sizes, SchönbergChandrasekhar limit, isothermal cores, changing from static, spherically-symmetric models to realist models, ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... high mass stars and low mass stars, pre-main-sequence and post-main-sequence stages, core sizes, SchönbergChandrasekhar limit, isothermal cores, changing from static, spherically-symmetric models to realist models, ...
... high mass stars and low mass stars, pre-main-sequence and post-main-sequence stages, core sizes, SchönbergChandrasekhar limit, isothermal cores, changing from static, spherically-symmetric models to realist models, ...
Star Formation in Our Galaxy - Wiley-VCH
... their diameters (about 0.1 µm) and reradiate this energy into the infrared. Regions where the dust effectively blocks the light from background stars are traditionally known as dark clouds. Generally, these represent higher-density subunits within a flocculent cloud complex, although they can also b ...
... their diameters (about 0.1 µm) and reradiate this energy into the infrared. Regions where the dust effectively blocks the light from background stars are traditionally known as dark clouds. Generally, these represent higher-density subunits within a flocculent cloud complex, although they can also b ...
Research Papers-Cosmology/Download/5936
... it assumed that star is rotating with a large number of revolutions n = 645 r/s. In this case, there is a danger that it will be broken by centrifugal forces. The force of gravity is opposes to the centrifugal forces. In order to prevent the destruction of stars, we have to assume that a radius of ...
... it assumed that star is rotating with a large number of revolutions n = 645 r/s. In this case, there is a danger that it will be broken by centrifugal forces. The force of gravity is opposes to the centrifugal forces. In order to prevent the destruction of stars, we have to assume that a radius of ...
ANTARES - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... post-starburst galaxies (French et al., 2016), but it is not clear why that is the case. This use case demonstrates another element of the antares architecture, namely multiwavelength association. It is likely that all galaxies contain a massive black hole at their center, but they are only detectab ...
... post-starburst galaxies (French et al., 2016), but it is not clear why that is the case. This use case demonstrates another element of the antares architecture, namely multiwavelength association. It is likely that all galaxies contain a massive black hole at their center, but they are only detectab ...
Neutron stars and quark stars - Goethe
... • first order phase transition to exotic matter in dense QCD likely! • → generates a new, stable solution for compact stars! (besides white dwarfs and neutron stars) • not constraint by mass-radius data yet! • impacts on supernovae, proto-neutron star evolution, neutron star properties, pulsars, . . ...
... • first order phase transition to exotic matter in dense QCD likely! • → generates a new, stable solution for compact stars! (besides white dwarfs and neutron stars) • not constraint by mass-radius data yet! • impacts on supernovae, proto-neutron star evolution, neutron star properties, pulsars, . . ...
Chapter 15, Galaxies
... Use independent measurements to check the luminosity of the standard candle. For example, we can use parallax measurements of the distance to main sequence stars to check measurements of distance using main-sequence fitting. If we do this for a few of them, then we can verify the assumption that the ...
... Use independent measurements to check the luminosity of the standard candle. For example, we can use parallax measurements of the distance to main sequence stars to check measurements of distance using main-sequence fitting. If we do this for a few of them, then we can verify the assumption that the ...
Pulsating variable stars and the Hertzsprung
... Stellar spectral classification: a brief story of early steps While Isaac Newton (1643 – 1727) observed the continuous spectrum of the Sun, he missed the discovery of absorption lines. In 1802, William Hyde Wollaston (1766-1828) reported dark gaps between colors in the continuous spectrum. Later, Jo ...
... Stellar spectral classification: a brief story of early steps While Isaac Newton (1643 – 1727) observed the continuous spectrum of the Sun, he missed the discovery of absorption lines. In 1802, William Hyde Wollaston (1766-1828) reported dark gaps between colors in the continuous spectrum. Later, Jo ...
the iconography of ancient astronomy
... the ancient Egyptians - a useful shorthand term we will also use) had glamour quality in ancient man's mind due to the group of very bright stars lying near each other that in the earliest years of calendar regulation as they began to rise in the night sky were associated with the onset of the New Y ...
... the ancient Egyptians - a useful shorthand term we will also use) had glamour quality in ancient man's mind due to the group of very bright stars lying near each other that in the earliest years of calendar regulation as they began to rise in the night sky were associated with the onset of the New Y ...
Chapter 31 Galaxies & the Universe
... Astronomers have determined the shape of the Milky Way by using radio waves because they penetrate the interstellar gas and dust without being scattered or absorbed. ...
... Astronomers have determined the shape of the Milky Way by using radio waves because they penetrate the interstellar gas and dust without being scattered or absorbed. ...
Constellation Detection
... missing or out of frame; we set the matching threshold NUM_MATCH to be half of the total star numbers in the constellation template. If the matching number is above the threshold, we decide the constellation is detected in the test image. Finding the proper scale of the template improves the accurac ...
... missing or out of frame; we set the matching threshold NUM_MATCH to be half of the total star numbers in the constellation template. If the matching number is above the threshold, we decide the constellation is detected in the test image. Finding the proper scale of the template improves the accurac ...
CHP 13
... 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star. b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can ...
... 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star. b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can ...
CloudsToSolarSystems_EXES
... But just remember that unless you are willing to share information with other groups, they will not share with you! You can’t show other teams your briefing papers, but must explain and to them what is on it verbally. ...
... But just remember that unless you are willing to share information with other groups, they will not share with you! You can’t show other teams your briefing papers, but must explain and to them what is on it verbally. ...
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
... In particular, since the original classification more population types have appeared, such as an intermediate type II population, corresponding to the thick disk stars. ...
... In particular, since the original classification more population types have appeared, such as an intermediate type II population, corresponding to the thick disk stars. ...
The Star Finder Book - Starpath School of Navigation
... recurring questions. We especially appreciate questions and comments of former students after they navigate their first ocean crossing. Comments from new navigators are invaluable to the development of teaching methods and course materials. This booklet is one example. Most discoveries of new naviga ...
... recurring questions. We especially appreciate questions and comments of former students after they navigate their first ocean crossing. Comments from new navigators are invaluable to the development of teaching methods and course materials. This booklet is one example. Most discoveries of new naviga ...
TWO DIFFERENT ALTITUDES
... 3. These stars lead directly to Polaris, and are called the ______________. 4. The North Star and the Pole Star are names for ___________. 5. The imaginary line that runs through Earth's north and south poles points to _______. 6. Like the sun and the moon, the stars appear to "rise" and "set.” Howe ...
... 3. These stars lead directly to Polaris, and are called the ______________. 4. The North Star and the Pole Star are names for ___________. 5. The imaginary line that runs through Earth's north and south poles points to _______. 6. Like the sun and the moon, the stars appear to "rise" and "set.” Howe ...
Sidereal Time and Celestial Coordinates
... Comet Machholz C/2004 Q2 • Discovered byDonald Machholz, Jr. on August 27, 2004 • Period of about 120,000 years • Just up to naked eye visibility now, but much easier to see in binoculars ...
... Comet Machholz C/2004 Q2 • Discovered byDonald Machholz, Jr. on August 27, 2004 • Period of about 120,000 years • Just up to naked eye visibility now, but much easier to see in binoculars ...
Astronomy 160: Frontiers and Controversies in Astrophysics
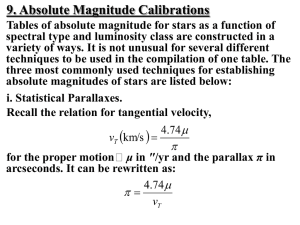
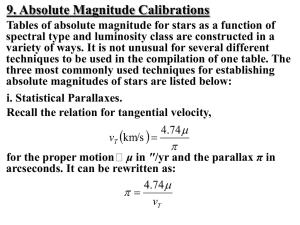
... If the definition of the numerator on the right hand side of that equation changes, the denominator must also change by the same amount (to keep the parallax angle on the left hand side of the equation the same). A larger unit means that the numerical value measured is smaller (for example, 24 inche ...
... If the definition of the numerator on the right hand side of that equation changes, the denominator must also change by the same amount (to keep the parallax angle on the left hand side of the equation the same). A larger unit means that the numerical value measured is smaller (for example, 24 inche ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.