Stellar Masses
... stably. Objects with masses slightly below this limit are called brown dwarfs, and are ‘star like’ in the sense that nuclear burning of deuterium occurs in their core. Below a mass of 0.015M⊙ (roughly 16 times the mass of Jupiter) not even deuterium burning can occur, and these objects are perhaps b ...
... stably. Objects with masses slightly below this limit are called brown dwarfs, and are ‘star like’ in the sense that nuclear burning of deuterium occurs in their core. Below a mass of 0.015M⊙ (roughly 16 times the mass of Jupiter) not even deuterium burning can occur, and these objects are perhaps b ...
Archaeoastronomy, Astronomy of Celts, A. Gaspani
... phenomena, such as the eclipses or the visibility of the planets, has strengthened the belief in the magic power of the members of this class, the Druids. It is well known that the role of this class was not just consultative, it also dominated the local political life among the Celtic community. An ...
... phenomena, such as the eclipses or the visibility of the planets, has strengthened the belief in the magic power of the members of this class, the Druids. It is well known that the role of this class was not just consultative, it also dominated the local political life among the Celtic community. An ...
Module 5 Modelling the universe - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... another way, an atom in space has 1036 times more space to move in than an atom has in a solid. However, the density of space is not constant; there are some regions where the density is larger, and these regions therefore have a greater gravitational attraction towards themselves than the regions w ...
... another way, an atom in space has 1036 times more space to move in than an atom has in a solid. However, the density of space is not constant; there are some regions where the density is larger, and these regions therefore have a greater gravitational attraction towards themselves than the regions w ...
An introduce of the spectrograph of the GALEX
... functions of red and blue galaxies to z~1. (...) After z~1, M*B has dimmed by 1.2-1.3 mag for all colors of galaxies, φ* for blue galaxies has hardly changed, and φ* for red galaxies has at least doubled (our formal value is ~0.5 dex). Luminosity density jB has fallen by 0.6 dex for blue galaxies bu ...
... functions of red and blue galaxies to z~1. (...) After z~1, M*B has dimmed by 1.2-1.3 mag for all colors of galaxies, φ* for blue galaxies has hardly changed, and φ* for red galaxies has at least doubled (our formal value is ~0.5 dex). Luminosity density jB has fallen by 0.6 dex for blue galaxies bu ...
FREE Sample Here
... Answer: E 24) Which of the following statements about the Milky Way Galaxy is not true? A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of ...
... Answer: E 24) Which of the following statements about the Milky Way Galaxy is not true? A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of ...
Activity III: Calibrating Images
... that has traveled vast distances. Amazingly, the light remains virtually unaffected by the first 99.999999999999% or so of its journey. However, in the trip through the Earth’s atmosphere, and even through the optics of the telescope, the light may finally be affected causing the brightness of the s ...
... that has traveled vast distances. Amazingly, the light remains virtually unaffected by the first 99.999999999999% or so of its journey. However, in the trip through the Earth’s atmosphere, and even through the optics of the telescope, the light may finally be affected causing the brightness of the s ...
Sky Watcher - Boise Astronomical Society
... Venus is the bright "Morning Star", blazing low in the east before and during dawn. The planet loses a little of its altitude in May, but at magnitude -4 around mid-month you will not have any trouble distinguishing it. The Red Planet reached opposition and peak visibility in April, and remains impr ...
... Venus is the bright "Morning Star", blazing low in the east before and during dawn. The planet loses a little of its altitude in May, but at magnitude -4 around mid-month you will not have any trouble distinguishing it. The Red Planet reached opposition and peak visibility in April, and remains impr ...
Red supergiants around the obscured open cluster Stephenson 2
... moderate K magnitudes, and membership of individual stars is difficult to assess. D07 found a large population of field stars with KS magnitudes comparable to the supergiants. Indeed, down to their limiting magnitude KS = 8, there are many more field stars than RSG members in the r = 7′ circle analy ...
... moderate K magnitudes, and membership of individual stars is difficult to assess. D07 found a large population of field stars with KS magnitudes comparable to the supergiants. Indeed, down to their limiting magnitude KS = 8, there are many more field stars than RSG members in the r = 7′ circle analy ...
Lectures 19-20 The Milky Way Galaxy
... (~2 micron) to help see through the dust. This is helpful because there are large number of K and M giant stars (T ~ 4000 K) in the central part of the galaxy, and these are brightest in at 2-micron. Note that the nearest star to the Sun is ~1 pc away. The density of stars is much higher in the Gala ...
... (~2 micron) to help see through the dust. This is helpful because there are large number of K and M giant stars (T ~ 4000 K) in the central part of the galaxy, and these are brightest in at 2-micron. Note that the nearest star to the Sun is ~1 pc away. The density of stars is much higher in the Gala ...
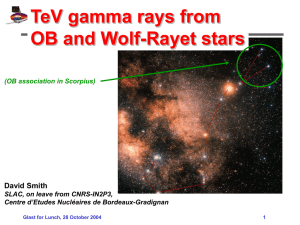
ppt - SLAC
... 2. Atmospheric pressure depends on the star's surface gravity and so, roughly, on its size —a giant, dwarf, or in between. The size and surface brightness yield the star's luminosity and often its evolutionary status (young, middle-aged, or nearing death). Apparent brightness then gives an idea of t ...
... 2. Atmospheric pressure depends on the star's surface gravity and so, roughly, on its size —a giant, dwarf, or in between. The size and surface brightness yield the star's luminosity and often its evolutionary status (young, middle-aged, or nearing death). Apparent brightness then gives an idea of t ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... as afflicted the Earth for its first 0.7 Gy. We have established to which of these categories each of the known exoplanetary systems belongs. In order to map the outward movement of the HZs around these known exoplanetary systems during their stars’ main sequence lifetimes, our first step was to mod ...
... as afflicted the Earth for its first 0.7 Gy. We have established to which of these categories each of the known exoplanetary systems belongs. In order to map the outward movement of the HZs around these known exoplanetary systems during their stars’ main sequence lifetimes, our first step was to mod ...
Stellar Evolution Task
... Red giants are sooo large that we can actually 'see' their size. Sadly we have to use very special techniques and can't just look through a very large telescope. Many bright red stars we see in the sky are red giants. ...
... Red giants are sooo large that we can actually 'see' their size. Sadly we have to use very special techniques and can't just look through a very large telescope. Many bright red stars we see in the sky are red giants. ...
Stars Stars All Around - Columbus City Schools
... Discovery Dome with class or 2. Have students complete Exploring the Constellation Webquest activity using the internet. Evaluation: A teacher-created short cycle assessment will be administered at the end of the unit to assess all clear learning targets. KWL chart, pre-assessment, video quiz, class ...
... Discovery Dome with class or 2. Have students complete Exploring the Constellation Webquest activity using the internet. Evaluation: A teacher-created short cycle assessment will be administered at the end of the unit to assess all clear learning targets. KWL chart, pre-assessment, video quiz, class ...
Impact on stellar properties of changing physics SAC Summer
... absorbed by the overlying layers of the envelope, which in the end causes some mass loss. This short-lived phase of evolution of low mass stars is referred to as the helium core flash. In more massive stars, the collapsing core will reach 108 K before it is dense enough to be degenerate. Then, heliu ...
... absorbed by the overlying layers of the envelope, which in the end causes some mass loss. This short-lived phase of evolution of low mass stars is referred to as the helium core flash. In more massive stars, the collapsing core will reach 108 K before it is dense enough to be degenerate. Then, heliu ...
ppt file - Universitat de Barcelona
... packed rather than in isolation? Nobody knows (up to now) the answer, but we can gain insight by: ...
... packed rather than in isolation? Nobody knows (up to now) the answer, but we can gain insight by: ...
Lecture18
... “Luminosity class” used to distinguish a red main sequence (e.g. M5V) from a red supergiant (M5I). Sizes of stars vary tremendously: White Dwarfs tiny (size of Earth), Supergiants larger than the entire solar system! Thursday, November 4, 2010 ...
... “Luminosity class” used to distinguish a red main sequence (e.g. M5V) from a red supergiant (M5I). Sizes of stars vary tremendously: White Dwarfs tiny (size of Earth), Supergiants larger than the entire solar system! Thursday, November 4, 2010 ...
Chapter 1 - Pearson Education
... More recently, the development of space travel and the computer revolution have helped fuel tremendous progress in astronomy. We've learned a lot about our solar system by sending probes to the planets, and many of our most powerful observatories, including the Hubble Space Telescope, reside in spac ...
... More recently, the development of space travel and the computer revolution have helped fuel tremendous progress in astronomy. We've learned a lot about our solar system by sending probes to the planets, and many of our most powerful observatories, including the Hubble Space Telescope, reside in spac ...
Lecture-25 Notes - Georgia Southern University Astrophysics
... what John Herschel saw. The Virgo Cluster & hints of filaments are visible. Even in 1878 there was strong evidence that galaxies tend to cluster together in gigantic (millions of parsecs) structures. ...
... what John Herschel saw. The Virgo Cluster & hints of filaments are visible. Even in 1878 there was strong evidence that galaxies tend to cluster together in gigantic (millions of parsecs) structures. ...
Galaxy Powerpoint Notes
... III. Irregular and dwarf galaxies Irregular galaxies do not have a regular shape, hence the name ‘irregular’. They are very uncommon within our universe though they are believed to once be spiral or elliptical galaxies that were altered by a gravitational pull. Irregular galaxies contain an abundant ...
... III. Irregular and dwarf galaxies Irregular galaxies do not have a regular shape, hence the name ‘irregular’. They are very uncommon within our universe though they are believed to once be spiral or elliptical galaxies that were altered by a gravitational pull. Irregular galaxies contain an abundant ...
Star 1 A star is a massive, luminous ball of plasma held together by
... For at least a portion of its life, a star shines due to thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen in its core releasing energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer space. Almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium were created by stars, either via stellar nucleosy ...
... For at least a portion of its life, a star shines due to thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen in its core releasing energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer space. Almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium were created by stars, either via stellar nucleosy ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.