September Globular Clusters - Salisbury Plain Observing Group
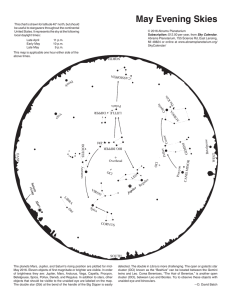
... M15 lies around 30,000 light years away, a diameter of 200 light years, and like M13 contains many red giant stars, but with its greater distance appears fainter and more compact. It’s also noted as one of the few globulars to contain a planetary nebula, Pease 1, which at magnitude 14, can be locate ...
... M15 lies around 30,000 light years away, a diameter of 200 light years, and like M13 contains many red giant stars, but with its greater distance appears fainter and more compact. It’s also noted as one of the few globulars to contain a planetary nebula, Pease 1, which at magnitude 14, can be locate ...
Review2
... c. Why gravity dominates the motion of celestial objects although it is the weakest. 2. Astronomical Instruments – collecting electromagnetic radiation a. Basic telescope design – refracting vs. reflecting telescopes, and the reasons why the refracting telescopes are no longer the design of choice. ...
... c. Why gravity dominates the motion of celestial objects although it is the weakest. 2. Astronomical Instruments – collecting electromagnetic radiation a. Basic telescope design – refracting vs. reflecting telescopes, and the reasons why the refracting telescopes are no longer the design of choice. ...
Stellar Evolution
... again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse heavier and heavier elements until they reach iron. When this occurs the star doesn’t have enough energy to further fuse iron so gravity quickly crushes the star, causing the protons and electrons to combine and become neutrons. At this moment, th ...
... again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse heavier and heavier elements until they reach iron. When this occurs the star doesn’t have enough energy to further fuse iron so gravity quickly crushes the star, causing the protons and electrons to combine and become neutrons. At this moment, th ...
Branches of Earth Science Tools Used to Study Stars Constellations
... o SPECTRUM: the band of colors that forms as light passes through a prism o Used to see if galaxies are moving away or toward the earth Telescopes: device that makes distant objects appear closer Types of Telescopes o Optical o Radio o X-Ray o U-V o Infrared ...
... o SPECTRUM: the band of colors that forms as light passes through a prism o Used to see if galaxies are moving away or toward the earth Telescopes: device that makes distant objects appear closer Types of Telescopes o Optical o Radio o X-Ray o U-V o Infrared ...
Test #3
... a. the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars. b. the distance to the binary and its radial velocity. c. the semi major axis and period of the orbit. d. the radial velocities of the two stars. 15. Blue stars are _____ than red stars a. hotter b. cooler c. larger ...
... a. the ratio of the angular separation from the center of mass of each of the stars. b. the distance to the binary and its radial velocity. c. the semi major axis and period of the orbit. d. the radial velocities of the two stars. 15. Blue stars are _____ than red stars a. hotter b. cooler c. larger ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... the star ages. 4. Explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
... the star ages. 4. Explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
Space Test: Practice Questions and Answers 1. Who discovered
... The Steady State Theory believed that the universe doesn’t change with time. However, more matter is added as it expands. It also stated that the universe had not beginning or end. In Big Bang the ...
... The Steady State Theory believed that the universe doesn’t change with time. However, more matter is added as it expands. It also stated that the universe had not beginning or end. In Big Bang the ...
Lesson 3 Power Notes Outline
... Giant stars shine brightly because of their large surface areas. ...
... Giant stars shine brightly because of their large surface areas. ...
Chapter 12
... when a large nebula condensed and was collected together by gravity. 2. Our solar system formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. 3. Inner or terrestrial planets and outer or Jovian planets. ...
... when a large nebula condensed and was collected together by gravity. 2. Our solar system formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. 3. Inner or terrestrial planets and outer or Jovian planets. ...
Photometry
... main sequence on your paper graph. Keep the y axes precisely parallel and over top one another. Seek a best fit for the central portion of the combined patterns. (The cool red stars in the lower right of your paper graph are quite scattered and may not fit very well.) Each star of the main sequence ...
... main sequence on your paper graph. Keep the y axes precisely parallel and over top one another. Seek a best fit for the central portion of the combined patterns. (The cool red stars in the lower right of your paper graph are quite scattered and may not fit very well.) Each star of the main sequence ...
May Evening Skies
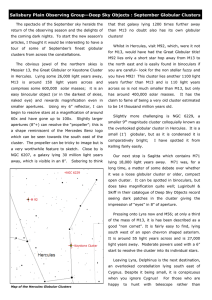
... The planets Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn's rising position are plotted for midMay 2016. Eleven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Mars, Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Procyon, Betelgeuse, Spica, Pollux, Deneb, and Regulus. In addition to stars, other ...
... The planets Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn's rising position are plotted for midMay 2016. Eleven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Mars, Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Procyon, Betelgeuse, Spica, Pollux, Deneb, and Regulus. In addition to stars, other ...
Lecture 6
... the naked eye responds. Also, faintest were about 100x fainter than brightest. Break the factor of 100 into 5 equal factors: Start with Vega Polaris 2.51x fainter 2.5x fainter than Polaris 2.5x fainter than that ...
... the naked eye responds. Also, faintest were about 100x fainter than brightest. Break the factor of 100 into 5 equal factors: Start with Vega Polaris 2.51x fainter 2.5x fainter than Polaris 2.5x fainter than that ...
E5 stellar processes and stellar evolution (HL only)
... • Neutron stars with masses substantially more than the Oppenheimer-Volkoff limit continue to collapse as the neutron pressure is insufficient. They become Black holes • At the centre of the black hole is a singularity • The boundary around the singularity where even light does not have sufficient e ...
... • Neutron stars with masses substantially more than the Oppenheimer-Volkoff limit continue to collapse as the neutron pressure is insufficient. They become Black holes • At the centre of the black hole is a singularity • The boundary around the singularity where even light does not have sufficient e ...
Spectral Variations of Several RV Tauri Type Stars Patrick Durant
... Light curve fits by Nesmith and Cash (adjacent poster, this conference) were used to convert the Julian Dates of our spectral observations to the appropriate phase of the ...
... Light curve fits by Nesmith and Cash (adjacent poster, this conference) were used to convert the Julian Dates of our spectral observations to the appropriate phase of the ...
6. 1 Star Distances 6. 2 Apparent Brightness, Intrinsic Brightness
... surface area on stellar luminosity and is commonly plotted as absolute magnitude versus spectral type but also as luminosity versus surface temperature or color. ...
... surface area on stellar luminosity and is commonly plotted as absolute magnitude versus spectral type but also as luminosity versus surface temperature or color. ...
Astrophysics
... point mass. Point mass singularity, and this breaks the laws of Physics. The strength of gravity inside a black hole is so massive that nothing can escape, not even light (which is why they are not visible). The perimeter at which light can/cannot escape is called the Event Horizon, but far away f ...
... point mass. Point mass singularity, and this breaks the laws of Physics. The strength of gravity inside a black hole is so massive that nothing can escape, not even light (which is why they are not visible). The perimeter at which light can/cannot escape is called the Event Horizon, but far away f ...
Assessment Star Characteristics and Life Cycle
... According to the diagram, which type of star has both the highest temperature and the greatest luminosity (brightness)? A) Blue Giants C) White Dwarfs B) Red Supergiants D) Red Giants 2. According to the H-R Diagram from question number 1, what color are the coolest stars on the main sequence? A) bl ...
... According to the diagram, which type of star has both the highest temperature and the greatest luminosity (brightness)? A) Blue Giants C) White Dwarfs B) Red Supergiants D) Red Giants 2. According to the H-R Diagram from question number 1, what color are the coolest stars on the main sequence? A) bl ...
NOVAE and SUPERNOVAE
... Occur only in stars whose masses are greater than 8 M. At the end of its life, massive stars form an iron core by fusing silicon. The iron core forms in a few days. Fusion ends at this point. The core has a mass of about 2 M. The iron core cannot support itself and collapses, from a size of ...
... Occur only in stars whose masses are greater than 8 M. At the end of its life, massive stars form an iron core by fusing silicon. The iron core forms in a few days. Fusion ends at this point. The core has a mass of about 2 M. The iron core cannot support itself and collapses, from a size of ...
Due: January 14, 2014 Name: White dwarfs are “has been
... b. Star formation is independent of the temperature of the cloud. c. Higher temperatures help star formation. d. Star formation is so complicated that it is not possible to say how one quantity, such as temperature, affects it. ...
... b. Star formation is independent of the temperature of the cloud. c. Higher temperatures help star formation. d. Star formation is so complicated that it is not possible to say how one quantity, such as temperature, affects it. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.