How to Build an Astrolabe - St John`s College, Cambridge
... the brightest stars in the sky. Its name is derived from Arabic, and means "the follower", as it appears to follow the cluster of stars known as The Pleiades across the sky. Altair (α Aquilae): the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila, the Eagle. Arcturus (α Boötis): part of the constellati ...
... the brightest stars in the sky. Its name is derived from Arabic, and means "the follower", as it appears to follow the cluster of stars known as The Pleiades across the sky. Altair (α Aquilae): the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila, the Eagle. Arcturus (α Boötis): part of the constellati ...
Rotational Doppler beaming in eclipsing binaries
... orbital Doppler beaming has been included in the simulations, but, for clarity and simplicity, additional effects such as ellipsoidal variations, the reflection effect and gravitational lensing have not been included. For illustration purposes all binaries are assumed to be seen exactly edge-on (i=9 ...
... orbital Doppler beaming has been included in the simulations, but, for clarity and simplicity, additional effects such as ellipsoidal variations, the reflection effect and gravitational lensing have not been included. For illustration purposes all binaries are assumed to be seen exactly edge-on (i=9 ...
Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and lithium abundances of six
... whereas the Sc abundance has been determined from other lines (Paper I). The oxygen abundance was then derived by fitting the observed [OI] line with the line computed with different oxygen abundance values; let us note that the [OI] and the nearby ScII lines form roughly in the same atmospheric lay ...
... whereas the Sc abundance has been determined from other lines (Paper I). The oxygen abundance was then derived by fitting the observed [OI] line with the line computed with different oxygen abundance values; let us note that the [OI] and the nearby ScII lines form roughly in the same atmospheric lay ...
Hot Horizontal Branch Stars in the Galactic Bulge. I
... on PSF-subtracted images and added to the list of trial positions). The resulting lists of magnitudes and positions were then transformed to a common coordinate system, defined by the positions on one of the V frames. The correction included terms for pixel scale (identical in x and y) and for rotat ...
... on PSF-subtracted images and added to the list of trial positions). The resulting lists of magnitudes and positions were then transformed to a common coordinate system, defined by the positions on one of the V frames. The correction included terms for pixel scale (identical in x and y) and for rotat ...
astro-ph/0303282 PDF
... annuli, scaled to the size of our photometric apertures and compared to an estimate of the flux in the core of the AO PSF from the photometric calibration discussed above. The resulting 5-sigma limiting magnitude is shown in Figure 3. Except for the large diffraction spikes (which are partially rem ...
... annuli, scaled to the size of our photometric apertures and compared to an estimate of the flux in the core of the AO PSF from the photometric calibration discussed above. The resulting 5-sigma limiting magnitude is shown in Figure 3. Except for the large diffraction spikes (which are partially rem ...
Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi and his book of the fixed stars: a journey of
... sky. Al-Ṣūfī’s contribution to astronomy was not only limited to writing this book but he was also instrumental in developing the science of astronomy for a very long time. He also contributed to the building of an important observatory in the city of Shiraz as well as constructing many astronomical ...
... sky. Al-Ṣūfī’s contribution to astronomy was not only limited to writing this book but he was also instrumental in developing the science of astronomy for a very long time. He also contributed to the building of an important observatory in the city of Shiraz as well as constructing many astronomical ...
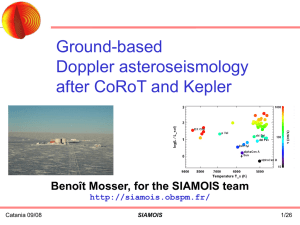
targets - siamois
... F6V star, mV = 4, vsini = 5 km/s, 90-day long run Modelling: stochastic excitation + intrinsic damping + SIAMOIS characteristics and performance Catania 09/08 ...
... F6V star, mV = 4, vsini = 5 km/s, 90-day long run Modelling: stochastic excitation + intrinsic damping + SIAMOIS characteristics and performance Catania 09/08 ...
Binarity in carbon-enhanced metal-poor stars
... theoretically expected from massive AGB stars with hot dredge-up, terminating the AGB process before the star had time to develop s-process elements (Herwig 2004), or some rotating AGB companions (Herwig, Langer & Lugaro 2003; Siess, Goriely & Langer 2004). However, this result is dependent on the p ...
... theoretically expected from massive AGB stars with hot dredge-up, terminating the AGB process before the star had time to develop s-process elements (Herwig 2004), or some rotating AGB companions (Herwig, Langer & Lugaro 2003; Siess, Goriely & Langer 2004). However, this result is dependent on the p ...
Do We Know of Any Maunder Minimum Stars?
... log RHK < −5.1, the latter of which they considered Maunder minimum candidates. Baliunas & Jastrow (1990) suggested that the activity level of the sun during the Maunder Minimum corresponded to that of these low-activity stars, S = 0.1451. Zhang et al. (1994) applied this value to an analysis of the ...
... log RHK < −5.1, the latter of which they considered Maunder minimum candidates. Baliunas & Jastrow (1990) suggested that the activity level of the sun during the Maunder Minimum corresponded to that of these low-activity stars, S = 0.1451. Zhang et al. (1994) applied this value to an analysis of the ...
Evidence for the Tidal Destruction of Hot Jupiters by Subgiant Stars
... Figure 2. Galactic U V W kinematics of subgiant stars that host exoplanets discovered with the radial-velocity technique. In each panel, we plot the U V W space motions of the subgiant sample as blue points and the density of points in a control sample selected from the Hipparcos catalog as the back ...
... Figure 2. Galactic U V W kinematics of subgiant stars that host exoplanets discovered with the radial-velocity technique. In each panel, we plot the U V W space motions of the subgiant sample as blue points and the density of points in a control sample selected from the Hipparcos catalog as the back ...
Stars: Intro & Classification Astronomy 1 — Elementary Astronomy LA Mission College
... • Infer relative sizes of stars, when possible, from differences in their blackbody curves Pre-activity Question 1) The graph at right shows the blackbody spectra for three different stars. Which of the stars is at the highest temperature? a) Star A b) Star B c) Star C ...
... • Infer relative sizes of stars, when possible, from differences in their blackbody curves Pre-activity Question 1) The graph at right shows the blackbody spectra for three different stars. Which of the stars is at the highest temperature? a) Star A b) Star B c) Star C ...
Radial Velocity - Yale Exoplanet
... and provided a precise wavelength solution spanning about 50 Å. The spectrum was recorded with a photon-counting Reticon photodiode array. Working from 1980 to 1992, they monitored 17 main sequence stars and 4 subgiant stars and achieved the unprecedented precision of 15 m s−1 . Unfortunately, beca ...
... and provided a precise wavelength solution spanning about 50 Å. The spectrum was recorded with a photon-counting Reticon photodiode array. Working from 1980 to 1992, they monitored 17 main sequence stars and 4 subgiant stars and achieved the unprecedented precision of 15 m s−1 . Unfortunately, beca ...
Astronomy Astrophysics
... near dawn, he considered the emission spike as an artefact from residual night sky emission. We inspected Reid’s spectrum but could not find any other residual night sky emission throughout the entire spectrum. We noticed, however, that the line core of Hβ displays a slight asymmetry. The Hα profile ...
... near dawn, he considered the emission spike as an artefact from residual night sky emission. We inspected Reid’s spectrum but could not find any other residual night sky emission throughout the entire spectrum. We noticed, however, that the line core of Hβ displays a slight asymmetry. The Hα profile ...
The ages of pre-main-sequence stars
... The position of pre-main-sequence or protostars in the Hertzsprung±Russell diagram is often used to determine their mass and age by comparison with pre-main-sequence evolution tracks. On the assumption that the stellar models are accurate, we demonstrate that, if the metallicity is known, the mass o ...
... The position of pre-main-sequence or protostars in the Hertzsprung±Russell diagram is often used to determine their mass and age by comparison with pre-main-sequence evolution tracks. On the assumption that the stellar models are accurate, we demonstrate that, if the metallicity is known, the mass o ...
Learn to write, compare, and order decimals using place value and
... Additional Example 1A & B: Reading and Writing Decimals Write each decimal in standard form, expanded form, and words. ...
... Additional Example 1A & B: Reading and Writing Decimals Write each decimal in standard form, expanded form, and words. ...
Chapter 17--Star Stuff
... to the birth of a main-sequence star depends on the star’s mass. Massive stars do everything faster. The contraction of a high-mass protostar into a main-sequence star may take only a million years or less. A star like our Sun takes about 50 million years to go from the beginning of the protostellar ...
... to the birth of a main-sequence star depends on the star’s mass. Massive stars do everything faster. The contraction of a high-mass protostar into a main-sequence star may take only a million years or less. A star like our Sun takes about 50 million years to go from the beginning of the protostellar ...
POSTERS SESSION I: Atmospheres of Massive Stars
... We demonstrate that it is possible to have clumping occur close to the star while still achieving an excellent fit to Hα by consistently treating the wind’s rotation in the spectral modeling. An excellent agreement to other important optical lines such as HeII 4686 Å and NIII 4634–4640 Å is also o ...
... We demonstrate that it is possible to have clumping occur close to the star while still achieving an excellent fit to Hα by consistently treating the wind’s rotation in the spectral modeling. An excellent agreement to other important optical lines such as HeII 4686 Å and NIII 4634–4640 Å is also o ...
Metal-poor Stars
... surface composition has not yet been significantly altered by any such mixing processes. The main indicator used to determine stellar metallicity is the iron abundance, [Fe/H], which is defined as [A/B]= log10 (NA/NB )? −log10(NA /NB ) for the number N of atoms of elements A and B, and refers to ...
... surface composition has not yet been significantly altered by any such mixing processes. The main indicator used to determine stellar metallicity is the iron abundance, [Fe/H], which is defined as [A/B]= log10 (NA/NB )? −log10(NA /NB ) for the number N of atoms of elements A and B, and refers to ...
Seminar Outburst of Comet 17P/Holmes
... ∼ 4 AU1 ) the activity of comets is very weak or none at all2 and only their nuclei are seen. Comet nucleus is a conglomerat of frozen gases, ice, dust and rocky particles that are bound together. Nuclei are irregularly shaped and their typical dimension (effective diameter) is a few tenths to a few ...
... ∼ 4 AU1 ) the activity of comets is very weak or none at all2 and only their nuclei are seen. Comet nucleus is a conglomerat of frozen gases, ice, dust and rocky particles that are bound together. Nuclei are irregularly shaped and their typical dimension (effective diameter) is a few tenths to a few ...
Document
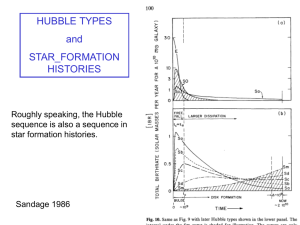
... passive evolution of stellar populations formed at z>2-3. Slope is primarily driven by mass-metallicity relation. Morphologically (HST)-selected Es and S0s (Bower et al. 1992, Aragon-Salamanca et al. 1993, Rakos et al. 1995, Stanford et al. 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, Schade et al. 1996, 1997, Ellis et ...
... passive evolution of stellar populations formed at z>2-3. Slope is primarily driven by mass-metallicity relation. Morphologically (HST)-selected Es and S0s (Bower et al. 1992, Aragon-Salamanca et al. 1993, Rakos et al. 1995, Stanford et al. 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, Schade et al. 1996, 1997, Ellis et ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.