Edited_Lecture_Transcripts_05_06 - 05 - astronomo
... above it against the, the force of gravity, and so, as you go down into the earth, pressures become very, very high. Densities become very high. We have density so, pressure so high at the center of the Earth that despite the fact that as we'll see, temperatures are very high. The center of the Ear ...
... above it against the, the force of gravity, and so, as you go down into the earth, pressures become very, very high. Densities become very high. We have density so, pressure so high at the center of the Earth that despite the fact that as we'll see, temperatures are very high. The center of the Ear ...
Unpublished draft available in format
... If it does consult the process and property facet, and repeat the procedure described in 3.41. 3.43 Does it prefer to a particular method of observation or study? This procedure continues until all facets have been reviewed in the sequence of the citation order given in 3.1. ...
... If it does consult the process and property facet, and repeat the procedure described in 3.41. 3.43 Does it prefer to a particular method of observation or study? This procedure continues until all facets have been reviewed in the sequence of the citation order given in 3.1. ...
Seasons What causes the seasons?
... Between the Spring equinox and the Summer solstice, days in the Northern Hemisphere grow longer as it is tilted towards the sun, and hence this hemisphere gets more energy The opposite is true in the Southern Hemisphere. ...
... Between the Spring equinox and the Summer solstice, days in the Northern Hemisphere grow longer as it is tilted towards the sun, and hence this hemisphere gets more energy The opposite is true in the Southern Hemisphere. ...
sample text - Highereducationresources
... Mercurial year only 88 Earth days long. In contrast, one rotation around its axis—or a single day—takes almost 59 Earth days. Geology (Heading level 2) Mariner 10 gave us a wealth of information about Mercury when it approached the planet in 1974 and 1975. Because Mercury has no water and barely any ...
... Mercurial year only 88 Earth days long. In contrast, one rotation around its axis—or a single day—takes almost 59 Earth days. Geology (Heading level 2) Mariner 10 gave us a wealth of information about Mercury when it approached the planet in 1974 and 1975. Because Mercury has no water and barely any ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... m = constant – 2.5 log10F , choosing constant to make scale consistent with Hipparchus. Absolute magnitude M is defined as the apparent magnitude a star ...
... m = constant – 2.5 log10F , choosing constant to make scale consistent with Hipparchus. Absolute magnitude M is defined as the apparent magnitude a star ...
The Sun, Our Star
... will flow outward from the Sun’s center Near the Sun’s center, energy is moved outward by photon radiation – a region surrounding the core known as the radiative zone Photons created in the Sun’s interior do not travel very far before being reabsorbed – energy created in the Sun center will take ...
... will flow outward from the Sun’s center Near the Sun’s center, energy is moved outward by photon radiation – a region surrounding the core known as the radiative zone Photons created in the Sun’s interior do not travel very far before being reabsorbed – energy created in the Sun center will take ...
Lecture 12
... Measure the energy flux from the star (integrated over all wavelengths): inverse square law, L F= 4pd 2 …gives the bolometric luminosity if the distance d is known. Can determine the distance directly if we can measure the ...
... Measure the energy flux from the star (integrated over all wavelengths): inverse square law, L F= 4pd 2 …gives the bolometric luminosity if the distance d is known. Can determine the distance directly if we can measure the ...
Right Ascension
... A star at a distance of 1 parsec would have a parallax of one arcsecond – this is the definition of parsec, which is short for parallax arcsecond. A star at a distance of 2 parsecs would have a parallax of 0.5 arcsecond. So, measure the parallax, and you know the distance. The closest star, Proxima ...
... A star at a distance of 1 parsec would have a parallax of one arcsecond – this is the definition of parsec, which is short for parallax arcsecond. A star at a distance of 2 parsecs would have a parallax of 0.5 arcsecond. So, measure the parallax, and you know the distance. The closest star, Proxima ...
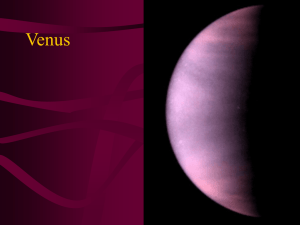
Venus - University of Chicago Math
... • an infrared radiometer to measure IR emissions from the Venus atmosphere • an airglow ultraviolet spectrometer to measure scattered and emitted UV light • a neutral mass spectrometer to determine the composition of the upper atmosphere ...
... • an infrared radiometer to measure IR emissions from the Venus atmosphere • an airglow ultraviolet spectrometer to measure scattered and emitted UV light • a neutral mass spectrometer to determine the composition of the upper atmosphere ...
NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... and Sun cause the Moon to appear in phases. The Moon goes through four main phases as it travels from west to east in its monthly orbit of the earth. Try observing the moon at the same time each night and its eastward movement will be revealed. The phases are caused by the angle of sunlight reflecte ...
... and Sun cause the Moon to appear in phases. The Moon goes through four main phases as it travels from west to east in its monthly orbit of the earth. Try observing the moon at the same time each night and its eastward movement will be revealed. The phases are caused by the angle of sunlight reflecte ...
Homework #3, AST 203, Spring 2010
... And this list doesn’t yet include the massive moons of the Earth, Jupiter, and Saturn (the largest of which are considerably larger than Pluto), or the planets discovered around other stars. The term “planet” is now too broad to allow a single, all-encompassing clean definition, and our field has be ...
... And this list doesn’t yet include the massive moons of the Earth, Jupiter, and Saturn (the largest of which are considerably larger than Pluto), or the planets discovered around other stars. The term “planet” is now too broad to allow a single, all-encompassing clean definition, and our field has be ...
The Sky Viewed from Earth - Beck-Shop
... which stars in the different constellations were labeled in order of descending brightness, but using the Greek symbols and letter order in the alphabet. For example, the star Alpha (the Greek letter α) Centauri, our closest stellar neighbor, is the brightest star in the constellation Centaurus (Q. ...
... which stars in the different constellations were labeled in order of descending brightness, but using the Greek symbols and letter order in the alphabet. For example, the star Alpha (the Greek letter α) Centauri, our closest stellar neighbor, is the brightest star in the constellation Centaurus (Q. ...
Chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... paper towel in a microwave. At the wavelength of the oven, the paper does not react, the bun heats up slightly (from moisture in the bread heating up) and the hot dog gets very hot and could, if left in too long, even explode. The same wavelength affects each item differently, just as atmospheric ga ...
... paper towel in a microwave. At the wavelength of the oven, the paper does not react, the bun heats up slightly (from moisture in the bread heating up) and the hot dog gets very hot and could, if left in too long, even explode. The same wavelength affects each item differently, just as atmospheric ga ...
16. Gravity and Space - Mr. Brick's Web Page
... In order for humans to survive long term in space, sustainable artificial environments need to be built. The International Space Station is home to a crew of at least two astronauts. They conduct research and perform experiments about the long-term effects of living in space. The results of these ex ...
... In order for humans to survive long term in space, sustainable artificial environments need to be built. The International Space Station is home to a crew of at least two astronauts. They conduct research and perform experiments about the long-term effects of living in space. The results of these ex ...
THE ROTATION OF THE SUN
... “greatest western elongation” when Venus is observed as a “morning star”. For example, what is the date of the greatest elongation using the data of Figure 1? Sometimes between 12 and 31 August 2002 (exactly on August 22). Be careful, it is a “greatest eastern elongation” at that time. So the image ...
... “greatest western elongation” when Venus is observed as a “morning star”. For example, what is the date of the greatest elongation using the data of Figure 1? Sometimes between 12 and 31 August 2002 (exactly on August 22). Be careful, it is a “greatest eastern elongation” at that time. So the image ...
Lesson 6 - Magnitudes of Stars
... These are often referred to as apparent magnitudes because the value depends on Distance from Earth Luminosity ...
... These are often referred to as apparent magnitudes because the value depends on Distance from Earth Luminosity ...
Planetary Orbit Simulator – Pretest
... Question 8: At which point or points is the planet slowing down? (planets shown here are assumed to be orbiting counter-clockwise) a) A, E b) B,C,D c) D d) A, B, C, D, E e) none of the points (the planet is moving at constant speed) Question 9: The speed of a planet in orbit is a) constant. b) alway ...
... Question 8: At which point or points is the planet slowing down? (planets shown here are assumed to be orbiting counter-clockwise) a) A, E b) B,C,D c) D d) A, B, C, D, E e) none of the points (the planet is moving at constant speed) Question 9: The speed of a planet in orbit is a) constant. b) alway ...
Advancing Physics A2
... Some or all of the following activities may be used: Activity 110P Presentation 'Changes in velocity and rotation' Also uses File 50L Launchable File 'Doppler seen and heard' Many objects in the Universe spin on their axis or orbit around a more massive body. Typically this will result in component ...
... Some or all of the following activities may be used: Activity 110P Presentation 'Changes in velocity and rotation' Also uses File 50L Launchable File 'Doppler seen and heard' Many objects in the Universe spin on their axis or orbit around a more massive body. Typically this will result in component ...
the solar system - HMXEarthScience
... degree of tilt of the planet’s axis distance between the planet and the Sun planet’s period of rotation amount of insolation given off by the Sun ...
... degree of tilt of the planet’s axis distance between the planet and the Sun planet’s period of rotation amount of insolation given off by the Sun ...