KASD Gr 8 Science Curriculum
... 3.3.10.A7 Interpret and create models of the Earth’s physical features in various mapping representations. Scale: apply an appropriate scale to illustrate major events throughout geologic time. 3.3.8.A.3 Explain how matter on earth is ...
... 3.3.10.A7 Interpret and create models of the Earth’s physical features in various mapping representations. Scale: apply an appropriate scale to illustrate major events throughout geologic time. 3.3.8.A.3 Explain how matter on earth is ...
Topic 6-1 Gravitational Force and Field
... strength) on a planet 10 times as massive as the earth and the radius 20 times as large. _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Q4 Find the acceleration due to gravity at a height of 300 km from the surface of ear ...
... strength) on a planet 10 times as massive as the earth and the radius 20 times as large. _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Q4 Find the acceleration due to gravity at a height of 300 km from the surface of ear ...
... The Venus Transit on 8 June 2012, is the 8th transit of Venus since the invention of the telescope. Historically, the Venus transits have played an important role in the advancement of our knowledge, so far as our solar system is concerned. If you have seen the last transit of Venus which occurred o ...
Document
... 2. The radial line – the line from the sun to the planet – sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The square of the period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis. ...
... 2. The radial line – the line from the sun to the planet – sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The square of the period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis. ...
Powerpoint
... How bright are they? How hot? How old, and how long do they live? What is their chemical composition? How are they moving? Are they isolated or in clusters? By answering these questions, we not only learn about stars, but about the structure and evolution of galaxies they live in, and the ...
... How bright are they? How hot? How old, and how long do they live? What is their chemical composition? How are they moving? Are they isolated or in clusters? By answering these questions, we not only learn about stars, but about the structure and evolution of galaxies they live in, and the ...
Scientific astrology
... Saturn, will not prove to be wholly unfounded. The prepondering planet Jupiter will in such case mainly determine the length and height of the wave of the spot-period; Saturn will cause small variations in the length and height; and finally, the earth and Venus will change the smooth wave-line into ...
... Saturn, will not prove to be wholly unfounded. The prepondering planet Jupiter will in such case mainly determine the length and height of the wave of the spot-period; Saturn will cause small variations in the length and height; and finally, the earth and Venus will change the smooth wave-line into ...
IAU 29th General Assembly
... - Grazing occultations observed since 1962 - Total occultations, both current and from published obs. - Spectroscopic binaries (including 1-line) were included to encourage observation of their occultations. • Too many dubious events were included; especially visual observers often reported “gradual ...
... - Grazing occultations observed since 1962 - Total occultations, both current and from published obs. - Spectroscopic binaries (including 1-line) were included to encourage observation of their occultations. • Too many dubious events were included; especially visual observers often reported “gradual ...
Earth - Space Science - Volusia County Schools
... • describe scientific knowledge as durable and robust and open to change. Scientific knowledge can change because it is often examined and reexamined by new investigations and scientific argumentation. Students will: • design a controlled experiment on an earth or space topic • use tools (this inclu ...
... • describe scientific knowledge as durable and robust and open to change. Scientific knowledge can change because it is often examined and reexamined by new investigations and scientific argumentation. Students will: • design a controlled experiment on an earth or space topic • use tools (this inclu ...
earth science - charlesburrows.com
... 5 Which motion causes the constellation Orion to be visible at midnight from New York State in ? winter but not in summer? (1) rotation of Earth (2) rotation of Orion (3) revolution of Earth (4) revolution of Orion 6 The model below shows the Sun’s apparent path across the sky for an observer in New ...
... 5 Which motion causes the constellation Orion to be visible at midnight from New York State in ? winter but not in summer? (1) rotation of Earth (2) rotation of Orion (3) revolution of Earth (4) revolution of Orion 6 The model below shows the Sun’s apparent path across the sky for an observer in New ...
949 - Scope, Sequence, and Coordination
... Observe the light produced by gases in discharge tubes as you did in Activity 1. This time, however, view it through a spectroscope. Record both the color and the location of the lines. Then repeat the flame tests that you did in Activity 2, but view the flames through a spectroscope. Record both th ...
... Observe the light produced by gases in discharge tubes as you did in Activity 1. This time, however, view it through a spectroscope. Record both the color and the location of the lines. Then repeat the flame tests that you did in Activity 2, but view the flames through a spectroscope. Record both th ...
PPT
... Some collide with the gas giants Some perform a gravitational slingshot and are thrown out to great distances Some are thrown out of the solar system completely ...
... Some collide with the gas giants Some perform a gravitational slingshot and are thrown out to great distances Some are thrown out of the solar system completely ...
The surface of Venus is rather smooth in many places, though not
... Full view of Venus Venus is the second planet from the Sun. With a nearly circular orbit, it an orbits the sun every 225 days. Venus is peculiar in that its axis rotation is retrograde (in the opposite sense of the Earth and all other planets except Uranus) and because it is very slow: a Solar day o ...
... Full view of Venus Venus is the second planet from the Sun. With a nearly circular orbit, it an orbits the sun every 225 days. Venus is peculiar in that its axis rotation is retrograde (in the opposite sense of the Earth and all other planets except Uranus) and because it is very slow: a Solar day o ...
The surface of Venus is rather smooth in many places, though not
... Full view of Venus Venus is the second planet from the Sun. With a nearly circular orbit, it an orbits the sun every 225 days. Venus is peculiar in that its axis rotation is retrograde (in the opposite sense of the Earth and all other planets except Uranus) and because it is very slow: a Solar day o ...
... Full view of Venus Venus is the second planet from the Sun. With a nearly circular orbit, it an orbits the sun every 225 days. Venus is peculiar in that its axis rotation is retrograde (in the opposite sense of the Earth and all other planets except Uranus) and because it is very slow: a Solar day o ...
Presentation - University of Idaho
... Distribution of galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey ...
... Distribution of galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey ...
The trisection of the angle. The trisection of the
... cube and the quadrature of the circle). Around 300 B.C., Euclid showed in Elements I:10 how to divide a given angle into two equal parts by means of ruler and compass. The trisection of the angle is the problem to divide a given angle into three equal parts. The European mathematician Pierre L. Want ...
... cube and the quadrature of the circle). Around 300 B.C., Euclid showed in Elements I:10 how to divide a given angle into two equal parts by means of ruler and compass. The trisection of the angle is the problem to divide a given angle into three equal parts. The European mathematician Pierre L. Want ...
Astronomy and the Quran
... explanations are given in the Mufradat, and perhaps all three apply here: (1) that the moon once appeared cleft asunder in the valley of Makkah within sight of the Prophet, his Companions, and some Unbelievers; (2) that the prophetic past tense indicates the future, the cleaving asunder of the moon ...
... explanations are given in the Mufradat, and perhaps all three apply here: (1) that the moon once appeared cleft asunder in the valley of Makkah within sight of the Prophet, his Companions, and some Unbelievers; (2) that the prophetic past tense indicates the future, the cleaving asunder of the moon ...
NATS1311_082108_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... new moon to new moon on an all-sky diagram as shown below. In an all-sky diagram, zenith is at the center and the edge of the circle is the horizon with the compass points indicated as in the figure. Estimate the compass direction of the moon (use a compass or the north star) and the angle of the mo ...
... new moon to new moon on an all-sky diagram as shown below. In an all-sky diagram, zenith is at the center and the edge of the circle is the horizon with the compass points indicated as in the figure. Estimate the compass direction of the moon (use a compass or the north star) and the angle of the mo ...
Volume 4 (Issue 3), March 2015
... and was expected to produce another meteor storm. The predicted date was 17 November, 258 days after the comet had passed through perihelion, but in fact the richest display was seen on 16 November – not a ‘storm’, but certainly striking. It was calculated that the dust stream left behind by the com ...
... and was expected to produce another meteor storm. The predicted date was 17 November, 258 days after the comet had passed through perihelion, but in fact the richest display was seen on 16 November – not a ‘storm’, but certainly striking. It was calculated that the dust stream left behind by the com ...
btg_2016_astromony
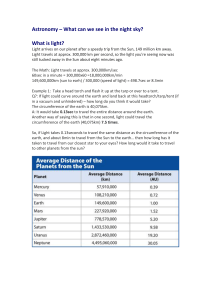
... Astronomy – What can we see in the night sky? What is light? Light arrives on our planet after a speedy trip from the Sun, 149 million km away. Light travels at approx. 300,000 km per second, so the light you're seeing now was still tucked away in the Sun about eight minutes ago. The Math: Light tra ...
... Astronomy – What can we see in the night sky? What is light? Light arrives on our planet after a speedy trip from the Sun, 149 million km away. Light travels at approx. 300,000 km per second, so the light you're seeing now was still tucked away in the Sun about eight minutes ago. The Math: Light tra ...
Astronomy I – Vocabulary you need to know:
... passing through an object. Meridian - An imaginary north-south line in the sky that passes through the observer's zenith. Precession – The small wobbling motion around the Earth's axis that the Earth makes as it spins (just like the wobbling motion of a spinning top). This causes the Earth's axis to ...
... passing through an object. Meridian - An imaginary north-south line in the sky that passes through the observer's zenith. Precession – The small wobbling motion around the Earth's axis that the Earth makes as it spins (just like the wobbling motion of a spinning top). This causes the Earth's axis to ...