Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
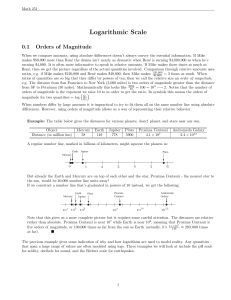
... More on the Magnitude Scale Converting from magnitude to luminosity in solar units: This graph allows us to perform this conversion simply by reading horizontally. A reduction of 5 in magnitude corresponds to an increase in a factor of 100 in luminosity, as it should. ...
... More on the Magnitude Scale Converting from magnitude to luminosity in solar units: This graph allows us to perform this conversion simply by reading horizontally. A reduction of 5 in magnitude corresponds to an increase in a factor of 100 in luminosity, as it should. ...
Universal Gravitation Chapter 13
... astronomer Claudius Ptolemy (c. 100–c. 170) in the second century A.D. and was accepted for the next 1 400 years. In 1543 the Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543) suggested that the Earth and the other planets revolved in circular orbits around the Sun (the heliocentric model ). The Dan ...
... astronomer Claudius Ptolemy (c. 100–c. 170) in the second century A.D. and was accepted for the next 1 400 years. In 1543 the Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543) suggested that the Earth and the other planets revolved in circular orbits around the Sun (the heliocentric model ). The Dan ...
PDF - BYU Studies
... The unchanging nature of heavenly bodies has probably remained the belief of most people from the dawn of human existence. Philosophermathematician René Descartes (1596–1650) presented this idea in its extreme form: the immutable nature of God requires that objects he created must also be immutable. ...
... The unchanging nature of heavenly bodies has probably remained the belief of most people from the dawn of human existence. Philosophermathematician René Descartes (1596–1650) presented this idea in its extreme form: the immutable nature of God requires that objects he created must also be immutable. ...
2nd Planet from the Sun
... Like Mercury, Venus was also originally thought to be 2 different planets They were called Eosphorus (morning star) and Hesperus (evening star) ◗ Venus is the 3rd brightest object in the sky (besides sun & moon) ◗ Because Venus is an inferior planet (between us and moon), it has phases as Galileo o ...
... Like Mercury, Venus was also originally thought to be 2 different planets They were called Eosphorus (morning star) and Hesperus (evening star) ◗ Venus is the 3rd brightest object in the sky (besides sun & moon) ◗ Because Venus is an inferior planet (between us and moon), it has phases as Galileo o ...
Last Final Review - Steady Server Pages
... What is the estimated age earth and how do we postulate it? A. 13.7 billion yrs, Uranium-Lead dating B. 4.5 billion yrs, Various radiometric dating methods C. 4.5 million yrs, Carbon dating D. 6,000 yrs, Archbishop James Usher ...
... What is the estimated age earth and how do we postulate it? A. 13.7 billion yrs, Uranium-Lead dating B. 4.5 billion yrs, Various radiometric dating methods C. 4.5 million yrs, Carbon dating D. 6,000 yrs, Archbishop James Usher ...
Kohoutek Is Coming - Institute of Current World Affairs
... God in his Providence doth so order, as that sometimes Blazing Stars are seen in heaven. Such Stars are called Comets for the stream like long Hair, which useth to at tend them. Such a Star is Prodigious and a Fearful Sight These Fearful Sights are many times Presages of those things which make way ...
... God in his Providence doth so order, as that sometimes Blazing Stars are seen in heaven. Such Stars are called Comets for the stream like long Hair, which useth to at tend them. Such a Star is Prodigious and a Fearful Sight These Fearful Sights are many times Presages of those things which make way ...
Small images
... Due to the interaction of an earth that is not perfectly spherical with the gravitational pull of the sun and moon ...
... Due to the interaction of an earth that is not perfectly spherical with the gravitational pull of the sun and moon ...
The definition of a planet - the Solar System Support Pages
... planet?” Does this definition allow us to answer that question, does it solve the problem? No, it doesn’t solve the problem, it merely changes the value of X. There are already twelve more candidates, and to decide if they qualify will require knowledge that is going to be very difficult to get. Co ...
... planet?” Does this definition allow us to answer that question, does it solve the problem? No, it doesn’t solve the problem, it merely changes the value of X. There are already twelve more candidates, and to decide if they qualify will require knowledge that is going to be very difficult to get. Co ...
a MS Word version.
... (...actually whole universe), how long did it remain the unquestioned authority on Astronomy? ...
... (...actually whole universe), how long did it remain the unquestioned authority on Astronomy? ...
5 Habitable zones and Planetary atmospheres
... Huygens' camera captured many images, and its other five instruments sampled Titan's atmosphere to determine its composition. This is the first probe that has ever been landed in the outer solar system. Once Huygens landed, it measured the wind, weather, energy flux and surface features, relaying th ...
... Huygens' camera captured many images, and its other five instruments sampled Titan's atmosphere to determine its composition. This is the first probe that has ever been landed in the outer solar system. Once Huygens landed, it measured the wind, weather, energy flux and surface features, relaying th ...
see figure 2 - California Academy of Sciences
... 8. After one day of shadow measurements you are ready to draw the North-South line. On your completed shadow plot draw a smooth curve through all of the marks that you have made, without moving the paper. The more often you have taken your measurements, the easier it will be to draw this curve accur ...
... 8. After one day of shadow measurements you are ready to draw the North-South line. On your completed shadow plot draw a smooth curve through all of the marks that you have made, without moving the paper. The more often you have taken your measurements, the easier it will be to draw this curve accur ...
Basic properties of stars
... The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as ...
... The Sun-centered model of the solar system laid out by Copernicus in De Revolutionibus (1543) made a very specific prediction: that the nearby stars should exhibit parallax shifts with respect to the distant background of stars. Tycho Brahe improved positional measures from +/- 10 arc minutes to as ...
The earliest datable observation of the aurora borealis
... Gelb et al. 1964, Hunger 1992), which indicate that the term akukutu could apply to either a daytime or night-time phenomenon. The following examples may be cited: (i) “If in Sivan (month III) an akukutu blazes, there will be hostility in the land.” (ii) “If the day becomes overcast and there is an ...
... Gelb et al. 1964, Hunger 1992), which indicate that the term akukutu could apply to either a daytime or night-time phenomenon. The following examples may be cited: (i) “If in Sivan (month III) an akukutu blazes, there will be hostility in the land.” (ii) “If the day becomes overcast and there is an ...
1. Chapter 10
... These patterns of stars remained the same night after night. People observing the sky also noticed five bright “stars” that wandered among these fixed patterns. They called these moving stars planets (the Greek word for wanderer). The planets were given the names Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and S ...
... These patterns of stars remained the same night after night. People observing the sky also noticed five bright “stars” that wandered among these fixed patterns. They called these moving stars planets (the Greek word for wanderer). The planets were given the names Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and S ...
Word document - Moray`s Astronomy Club, SIGMA
... them if they’re under 16 years of age. You can ‘try before you buy’ as the first meeting is free. So do come along and join us. SIGMA holds its meetings on the first Friday of every month (with the exception of January and July) at Birnie Village Hall, Thomshill, just south of Elgin as depicted on t ...
... them if they’re under 16 years of age. You can ‘try before you buy’ as the first meeting is free. So do come along and join us. SIGMA holds its meetings on the first Friday of every month (with the exception of January and July) at Birnie Village Hall, Thomshill, just south of Elgin as depicted on t ...
THE EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE
... Click on play. What happens to the observer on the surface of the earth? Why? At what time is it midday? When is it the middle of the night? At what time does the sun set and when does it rise? You might want to use the point of view control to answer some of these questions. A2: Observe the dir ...
... Click on play. What happens to the observer on the surface of the earth? Why? At what time is it midday? When is it the middle of the night? At what time does the sun set and when does it rise? You might want to use the point of view control to answer some of these questions. A2: Observe the dir ...
K-12 Science
... 1. Describe how objects in the solar system are in regular and predictable motions that explain such phenomena as days, years, seasons, eclipses, tides and moon cycles. 2. Explain that gravitational force is the dominant force determining motions in the solar system and in particular keeps the plane ...
... 1. Describe how objects in the solar system are in regular and predictable motions that explain such phenomena as days, years, seasons, eclipses, tides and moon cycles. 2. Explain that gravitational force is the dominant force determining motions in the solar system and in particular keeps the plane ...