8th Grade - Astronomy
... not time. Example: Our next nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri which is 4.2 light-years from Earth. (p. 602) The apparent change in position of an object when seen from different places Astronomers use parallax to measure distances to nearby stars by measuring the Parallax apparent movement o ...
... not time. Example: Our next nearest star neighbor is Proxima Centauri which is 4.2 light-years from Earth. (p. 602) The apparent change in position of an object when seen from different places Astronomers use parallax to measure distances to nearby stars by measuring the Parallax apparent movement o ...
7.1 Space Flight to the Stars
... fathom the distance in units like metres and kilometres. -For this reason, we use units such as the astronomical unit (AU) -One astronomical unit is equal to the average distance between the Sun and Earth, which is about 150 million kilometres. -Once we get past our solar system, the distance to oth ...
... fathom the distance in units like metres and kilometres. -For this reason, we use units such as the astronomical unit (AU) -One astronomical unit is equal to the average distance between the Sun and Earth, which is about 150 million kilometres. -Once we get past our solar system, the distance to oth ...
Module 7 Developmental task - Number
... Eight planets rotate the Sun in our solar system – our Earth being the third planet from the Sun. The planets vary in size – the smallest, Mercury, has a radius of only 2 439 km, whereas the largest planet, Jupiter, has a radius more than 70 000 km at its equator. ...
... Eight planets rotate the Sun in our solar system – our Earth being the third planet from the Sun. The planets vary in size – the smallest, Mercury, has a radius of only 2 439 km, whereas the largest planet, Jupiter, has a radius more than 70 000 km at its equator. ...
2 Kepler`s Laws
... Two same stars are orbitting about the center of mass half way between them. The orbital speed of each star is 220km/s and the orbital period of each is 14.4 days. Find the mass M of each star. ...
... Two same stars are orbitting about the center of mass half way between them. The orbital speed of each star is 220km/s and the orbital period of each is 14.4 days. Find the mass M of each star. ...
parallax and triangulation
... discuss what observations you might be able to use to determine which objects are closest to Earth. • Do size and brightness always lead to accurate conclusions about the distances between Earth and objects out in space? ...
... discuss what observations you might be able to use to determine which objects are closest to Earth. • Do size and brightness always lead to accurate conclusions about the distances between Earth and objects out in space? ...
measure
... nearest star (after the Sun) is about 40 million million km from the Earth. It takes light more than 4 years to travel this distance. If the distance from the Earth to the Sun were the width of this screen, the next nearest star would be in Rome. ...
... nearest star (after the Sun) is about 40 million million km from the Earth. It takes light more than 4 years to travel this distance. If the distance from the Earth to the Sun were the width of this screen, the next nearest star would be in Rome. ...
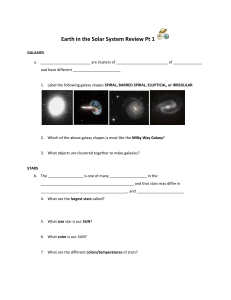
Earth in the Solar System - San Diego Unified School District
... between the _______________, ________________ and ____________________ 8. What is a light year (LY)? 9. What is an Astronomical Unit (AU)? 10. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from the Earth to the Asteroid Belt? 11. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from ...
... between the _______________, ________________ and ____________________ 8. What is a light year (LY)? 9. What is an Astronomical Unit (AU)? 10. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from the Earth to the Asteroid Belt? 11. Which measurement would you use to measure the distance from ...
The Hubble Deep Field (HDF)
... It’s very hard for us to understand just how large the Universe is. Scientists tell us that the largest number our minds can really comprehend, or grasp, is about a hundred thousand (100,000). Because astronomers study objects over such extremely large distances, they commonly use units of length t ...
... It’s very hard for us to understand just how large the Universe is. Scientists tell us that the largest number our minds can really comprehend, or grasp, is about a hundred thousand (100,000). Because astronomers study objects over such extremely large distances, they commonly use units of length t ...
The Hubble Deep Field (HDF)
... It’s very hard for us to understand just how large the Universe is. Scientists tell us that the largest number our minds can really comprehend, or grasp, is about a hundred thousand (100,000). Because astronomers study objects over such extremely large distances, they commonly use units of length t ...
... It’s very hard for us to understand just how large the Universe is. Scientists tell us that the largest number our minds can really comprehend, or grasp, is about a hundred thousand (100,000). Because astronomers study objects over such extremely large distances, they commonly use units of length t ...
Solar System Bead Distance Primary Audience
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
... Our Solar System is immense in size by normal standards. We think of the planets as revolving around the Sun, but rarely consider how far each planet is from the Sun. Furthermore, we fail to appreciate the even greater distances to the other stars. Astronomers use the distance from the Sun to the Ea ...
word - IMCCE
... The unit of length of the international system (SI) is the meter, defined as follows: - the meter is the length of the way traversed in the vacuum by the light throughout one 1/299 792 458 second. The basic unit used in astronomy to measure the distances is the "astronomical unit", defined as follow ...
... The unit of length of the international system (SI) is the meter, defined as follows: - the meter is the length of the way traversed in the vacuum by the light throughout one 1/299 792 458 second. The basic unit used in astronomy to measure the distances is the "astronomical unit", defined as follow ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... 23,330 miles (modern value: 25,000 miles – only 7% off ...
... 23,330 miles (modern value: 25,000 miles – only 7% off ...
Astronomy Miscellaneous Items Test
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
AST 101 Lecture 8 Astronomy in the 17th and 18th Centuries
... beginning with Newton's work, which was strongly influenced by astronomical observations. •1684: Ole Rømer publishes an analysis of the orbits and eclipses of the moons of Jupiter. – Eclipses occurred about 16 minutes late when Jupiter was in conjunction with the Sun. – From Kepler's third law, the ...
... beginning with Newton's work, which was strongly influenced by astronomical observations. •1684: Ole Rømer publishes an analysis of the orbits and eclipses of the moons of Jupiter. – Eclipses occurred about 16 minutes late when Jupiter was in conjunction with the Sun. – From Kepler's third law, the ...
17 th and 18 th Century Astronomy
... beginning with Newton's work, which was strongly influenced by astronomical observations. •1684: Ole Rømer publishes an analysis of the orbits and eclipses of the moons of Jupiter. – Eclipses occurred about 16 minutes late when Jupiter was in conjunction with the Sun. – From Kepler's third law, the ...
... beginning with Newton's work, which was strongly influenced by astronomical observations. •1684: Ole Rømer publishes an analysis of the orbits and eclipses of the moons of Jupiter. – Eclipses occurred about 16 minutes late when Jupiter was in conjunction with the Sun. – From Kepler's third law, the ...
14.1 History of the Solar System
... the planets still rotated around earth, but in small circles around a ...
... the planets still rotated around earth, but in small circles around a ...
Ancient Mathematics 450 B.C. 400 B.C. 350 B.C. 300 B.C. 250 B.C.
... Student of Plato who built philosophy based on observation, induction of general principles. Theory of causes determined motion and material of celestial objects. Aristarchus of Samos 310 B.C. – 230 B.C. Determined the distance from the earth to the moon and sun (correct method, incorrect results), ...
... Student of Plato who built philosophy based on observation, induction of general principles. Theory of causes determined motion and material of celestial objects. Aristarchus of Samos 310 B.C. – 230 B.C. Determined the distance from the earth to the moon and sun (correct method, incorrect results), ...
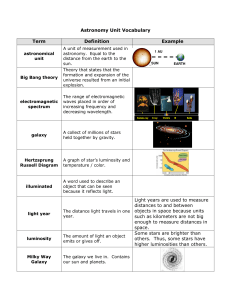
Astronomy Unit Vocabulary Term Definition Example Light years are
... Some stars are brighter than The amount of light an object others. Thus, some stars have emits or gives off. higher luminosities than others. The galaxy we live in. Contains our sun and planets. ...
... Some stars are brighter than The amount of light an object others. Thus, some stars have emits or gives off. higher luminosities than others. The galaxy we live in. Contains our sun and planets. ...
tire
... 8. A telescopes optical system that is continuously and automatically adjusted to compensate for the distortion caused by the Earth’s atmosphere. 9. A configuration of stars often named after an object, a person or an animal. 10. The blocking of all or part of the sunlight on the Moon by the Earth. ...
... 8. A telescopes optical system that is continuously and automatically adjusted to compensate for the distortion caused by the Earth’s atmosphere. 9. A configuration of stars often named after an object, a person or an animal. 10. The blocking of all or part of the sunlight on the Moon by the Earth. ...