File - Adriana Romo
... Interviewer: Describe the physical properties of white dwarf stars- what would one look like up close? Scientist: White dwarfs are about the size of earth or 10,000 km. In diameter, very hot and very dim. Interviewer: What is the surface temperature of a white dwarf? Scientist: Its about 20,000 deg ...
... Interviewer: Describe the physical properties of white dwarf stars- what would one look like up close? Scientist: White dwarfs are about the size of earth or 10,000 km. In diameter, very hot and very dim. Interviewer: What is the surface temperature of a white dwarf? Scientist: Its about 20,000 deg ...
KS1 Education Guide - Immersive Theatres
... The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in a system that includes the Moon, the Sun, seven other planets and their moons, and smaller objects, such as asteroids and comets. The Sun, an average star, is the central and largest body in the Solar System. (5 – 8 Standard) ...
... The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in a system that includes the Moon, the Sun, seven other planets and their moons, and smaller objects, such as asteroids and comets. The Sun, an average star, is the central and largest body in the Solar System. (5 – 8 Standard) ...
Specification Topic 1 – Earth, Moon and Sun 1.1 Planet Earth
... interpret data (eg a Butterfly Diagram) in order to describe the long-term latitude drift of sunspots, determine the length of the solar cycle and predict the year of the next solar maximum ...
... interpret data (eg a Butterfly Diagram) in order to describe the long-term latitude drift of sunspots, determine the length of the solar cycle and predict the year of the next solar maximum ...
High precision astrometry as a tool for Fundamental
... orbital positions over a few years Requirement: few µas final precision Small field (~10-20 arcmin) to have several reference stars (e.g. from Gaia) ...
... orbital positions over a few years Requirement: few µas final precision Small field (~10-20 arcmin) to have several reference stars (e.g. from Gaia) ...
PHYSICAL SETTING EARTH SCIENCE
... takes approximately one (1) day (3) month (2) week (4) year 2 The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth. ...
... takes approximately one (1) day (3) month (2) week (4) year 2 The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth. ...
MCWP 3-16.7 Chapter 7: Astronomy
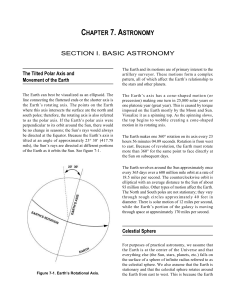
... one platonic year (great year). This is caused by torque imposed on the Earth mostly by the Moon and Sun. Visualize it as a spinning top. As the spinning slows, the top begins to wobble creating a cone-shaped motion in its rotating axis. The Earth makes one 360° rotation on its axis every 23 hours 5 ...
... one platonic year (great year). This is caused by torque imposed on the Earth mostly by the Moon and Sun. Visualize it as a spinning top. As the spinning slows, the top begins to wobble creating a cone-shaped motion in its rotating axis. The Earth makes one 360° rotation on its axis every 23 hours 5 ...
Article “What Astronomers Do” (appendix C) one per student
... because of the significant differences he noticed among the various stellar spectra. It would not be until half a century later that an appropriate explanation was given for the mysterious lines seen in the stars' spectra. In 1859, the German physicist Gustav Kirchoff (in collaboration with the Germ ...
... because of the significant differences he noticed among the various stellar spectra. It would not be until half a century later that an appropriate explanation was given for the mysterious lines seen in the stars' spectra. In 1859, the German physicist Gustav Kirchoff (in collaboration with the Germ ...
Principal Features of the Sky - Beck-Shop
... with sets of (modern) stellar coordinates was that of Paolo Galluci (from 1588). In this case, the coordinates were with respect to the path of the Sun, the ecliptic (see §2.3.3 for a discussion of this system of coordinates). Chinese atlases and charts used measurements somewhat akin to hour angles ...
... with sets of (modern) stellar coordinates was that of Paolo Galluci (from 1588). In this case, the coordinates were with respect to the path of the Sun, the ecliptic (see §2.3.3 for a discussion of this system of coordinates). Chinese atlases and charts used measurements somewhat akin to hour angles ...
First Light for May, 2001 - South Bay Astronomical Society
... motion towards or away from Earth. Thus, the Wobble method provides for a wider range of planetary systems. If both methods can be used on a exo-system, the size and mass of the planets can be determined. Given these two methods, it’s not entirely surprising that many of the earliest exo-planets dis ...
... motion towards or away from Earth. Thus, the Wobble method provides for a wider range of planetary systems. If both methods can be used on a exo-system, the size and mass of the planets can be determined. Given these two methods, it’s not entirely surprising that many of the earliest exo-planets dis ...
Principal Features of the Sky
... with sets of (modern) stellar coordinates was that of Paolo Galluci (from 1588). In this case, the coordinates were with respect to the path of the Sun, the ecliptic (see §2.3.3 for a discussion of this system of coordinates). Chinese atlases and charts used measurements somewhat akin to hour angles ...
... with sets of (modern) stellar coordinates was that of Paolo Galluci (from 1588). In this case, the coordinates were with respect to the path of the Sun, the ecliptic (see §2.3.3 for a discussion of this system of coordinates). Chinese atlases and charts used measurements somewhat akin to hour angles ...
Earth in Space Conceptest
... of several distant objects that were similar size or larger than Pluto • International Astronomical Union (IAU) could either 1. Consider the new objects as new planets OR 2. Classify the new objects – and Pluto – as a new group of objects ...
... of several distant objects that were similar size or larger than Pluto • International Astronomical Union (IAU) could either 1. Consider the new objects as new planets OR 2. Classify the new objects – and Pluto – as a new group of objects ...
Gilmore - Astrometry and Astrophysics in the Gaia sky
... – clean Hertzsprung-Russell sequences throughout the Galaxy – solar neighbourhood mass function and luminosity function e.g. white dwarfs (~200,000) and brown dwarfs (~50,000) – initial mass and luminosity functions in star forming regions – luminosity function for pre main-sequence stars – detectio ...
... – clean Hertzsprung-Russell sequences throughout the Galaxy – solar neighbourhood mass function and luminosity function e.g. white dwarfs (~200,000) and brown dwarfs (~50,000) – initial mass and luminosity functions in star forming regions – luminosity function for pre main-sequence stars – detectio ...
lecture3
... • What is the cause of the seasons on Earth? • As the Earth orbits the sun, the tilt of the axis causes different portions of the Earth to receive more or less direct sunlight at different times of year. The two hemispheres have opposite seasons. The summer solstice is the time when the northern hem ...
... • What is the cause of the seasons on Earth? • As the Earth orbits the sun, the tilt of the axis causes different portions of the Earth to receive more or less direct sunlight at different times of year. The two hemispheres have opposite seasons. The summer solstice is the time when the northern hem ...
Magnitude of Stars - What`s Out Tonight?
... stars, they classified them by their brightness. We still use this same system of magnitudes today, however, we now have instruments to accurately measure a star’s brightness. The range of magnitudes varies from –27 (spoken as “minus twenty-seven” or “negative twenty-seven”) for the Sun to over +30 ...
... stars, they classified them by their brightness. We still use this same system of magnitudes today, however, we now have instruments to accurately measure a star’s brightness. The range of magnitudes varies from –27 (spoken as “minus twenty-seven” or “negative twenty-seven”) for the Sun to over +30 ...
tut35 Magnitudes
... EXAMPLE 8. A magnitude +2 meteor is sighted with a zenith angle of 600. Assume we already know its height h, is 120 km. Find the absolute magnitude of the meteor. Using Equation 13, with z = 600 and h = 120 km yields distance d = 234 km. It’s obvious that if the meteor were at the zenith and a heigh ...
... EXAMPLE 8. A magnitude +2 meteor is sighted with a zenith angle of 600. Assume we already know its height h, is 120 km. Find the absolute magnitude of the meteor. Using Equation 13, with z = 600 and h = 120 km yields distance d = 234 km. It’s obvious that if the meteor were at the zenith and a heigh ...
Stargazer - Everett Astronomical Society
... ([email protected]) but I don't check my email daily. They can email me for directions if they never have been out here.” Listed below are proposed dates for planned EAS star parties at my *Ron Tam’s+ place, depending upon the weather, of course. Call Ron about spur-ofthe-moment observing. Please ...
... ([email protected]) but I don't check my email daily. They can email me for directions if they never have been out here.” Listed below are proposed dates for planned EAS star parties at my *Ron Tam’s+ place, depending upon the weather, of course. Call Ron about spur-ofthe-moment observing. Please ...
The Marine Sextant
... • A marine sextant is nothing more than a device designed to measure the angle between two objects with a great deal of precision. • In celestial navigation, these two objects are – a celestial body (star, sun, moon, or planet) – the visible horizon ...
... • A marine sextant is nothing more than a device designed to measure the angle between two objects with a great deal of precision. • In celestial navigation, these two objects are – a celestial body (star, sun, moon, or planet) – the visible horizon ...
Hubble Diagram Instruction Sheet
... A. Discussion question: You may have noticed that all your redshift figures are positive. What would it mean if your redshift were negative? Calculating Distances Measuring distances in space is a daunting task. One method of measuring distances is to use an object with a known absolute magnitude (M ...
... A. Discussion question: You may have noticed that all your redshift figures are positive. What would it mean if your redshift were negative? Calculating Distances Measuring distances in space is a daunting task. One method of measuring distances is to use an object with a known absolute magnitude (M ...