Lunar eclipses
... Umbra is part of shadow where the sun is totally obscured, the dark part. Penumbra is the part of the shadow where the sun is partially obscured, the light part. Progress of a Lunar eclipse. The red glow is refracted red light from the Earth’s atmosphere, much like the red glow we see before s ...
... Umbra is part of shadow where the sun is totally obscured, the dark part. Penumbra is the part of the shadow where the sun is partially obscured, the light part. Progress of a Lunar eclipse. The red glow is refracted red light from the Earth’s atmosphere, much like the red glow we see before s ...
Sample Teacher PPT Brick Vocabulary
... for the key vocabulary of the week Step 2: Give 1 word to a team at a random, ask them to perform their charade for the other teams to solve in 30 seconds. The team that provides the correct solution first ...
... for the key vocabulary of the week Step 2: Give 1 word to a team at a random, ask them to perform their charade for the other teams to solve in 30 seconds. The team that provides the correct solution first ...
Terestialplanets
... • The sky seems to revolve around us because of Earth’s rotation • Additionally, planets move with respect to the fixed stars, that’s why they are called planets (greek: wanderers) • Due to the planet’s movement in their orbit, and Earth’s orbital motion, this additional motion – the apparent motion ...
... • The sky seems to revolve around us because of Earth’s rotation • Additionally, planets move with respect to the fixed stars, that’s why they are called planets (greek: wanderers) • Due to the planet’s movement in their orbit, and Earth’s orbital motion, this additional motion – the apparent motion ...
ch 2 the sky
... Angular distance – a measure of the separation between two objects in the sky Angular diameter – a measure of the size of an object in the sky Scientific model – an intellectual concept designed to help us think about a natural process without necessarily being a conjecture of truth South cir ...
... Angular distance – a measure of the separation between two objects in the sky Angular diameter – a measure of the size of an object in the sky Scientific model – an intellectual concept designed to help us think about a natural process without necessarily being a conjecture of truth South cir ...
Powerpoint for today
... Perhaps a planet was going to form there. But Jupiter's strong gravity disrupted the planetesimals' orbits, ejecting them out of Solar System. The Belt is the few left behind. ...
... Perhaps a planet was going to form there. But Jupiter's strong gravity disrupted the planetesimals' orbits, ejecting them out of Solar System. The Belt is the few left behind. ...
Size Color and Temperature
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
Atmosphere of Venus, Mars and Earth (PDF: 1.7MB)
... “light pollution”, excessive obtrusive artificial lights. Especially in and around the large city, artificial lights brighten the night sky and artificial lights brighten the night sky and prevent star observation. Under the sky glow of artificial lights which affect long exposure of artifici ...
... “light pollution”, excessive obtrusive artificial lights. Especially in and around the large city, artificial lights brighten the night sky and artificial lights brighten the night sky and prevent star observation. Under the sky glow of artificial lights which affect long exposure of artifici ...
Lecture 3 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... --gives angular position of objects in the sky, has arbitrary size, and earth turns underneath it. Zenith--point directly overhead on sphere. Local Coordinates—altitude and azimuth. Celestial poles--points just above N. and S. pole. Meridian--circle passing through poles and zenith. A great circle-- ...
... --gives angular position of objects in the sky, has arbitrary size, and earth turns underneath it. Zenith--point directly overhead on sphere. Local Coordinates—altitude and azimuth. Celestial poles--points just above N. and S. pole. Meridian--circle passing through poles and zenith. A great circle-- ...
grade vii and viii - Sacred Heart CMI Public School
... exist in solid form in the warm inner Solar System close to the Sun, and these would eventually form the rocky planets of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Because metallic elements only comprised a very small fraction of the solar nebula, the terrestrial planets could not grow very large. The giant ...
... exist in solid form in the warm inner Solar System close to the Sun, and these would eventually form the rocky planets of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Because metallic elements only comprised a very small fraction of the solar nebula, the terrestrial planets could not grow very large. The giant ...
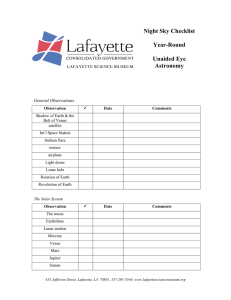
Night Sky Checklist Year-Round Unaided Eye Astronomy
... The daily rotation of Earth can be seen over the course of a half hour to an hour by noticing how the moon, stars, and planets appear to rise or set. The annual revolution of Earth around the sun can be seen by observing the sky once a week at the same time of night, and noticing the apparent shift ...
... The daily rotation of Earth can be seen over the course of a half hour to an hour by noticing how the moon, stars, and planets appear to rise or set. The annual revolution of Earth around the sun can be seen by observing the sky once a week at the same time of night, and noticing the apparent shift ...
Complete the following review packet!
... 65. What was the relative motion of this star compared to the observer? 66. What was inferred when the same results were noticed by analyzing spectrum from galaxies? 67. What is the name of our galaxy? What is its shape? ...
... 65. What was the relative motion of this star compared to the observer? 66. What was inferred when the same results were noticed by analyzing spectrum from galaxies? 67. What is the name of our galaxy? What is its shape? ...
The Dead Guys a.k.a: The development of astronomy
... Archeoastronomy The study of the astronomical practices, celestial lore, mythologies, religions and world-views of all ancient cultures. ...
... Archeoastronomy The study of the astronomical practices, celestial lore, mythologies, religions and world-views of all ancient cultures. ...
AGU Fall 2011 SH34B-08
... solar activity by planetary influences had really never yielded any satisfactory result. Nevertheless, the hypothesis rears it head from time to time, even today. I review several recent attempts, both proposed correlations and mechanisms. The recent discovery of exoplanets and the possibility of de ...
... solar activity by planetary influences had really never yielded any satisfactory result. Nevertheless, the hypothesis rears it head from time to time, even today. I review several recent attempts, both proposed correlations and mechanisms. The recent discovery of exoplanets and the possibility of de ...
Unit 6: Astronomy
... Copernicus lived during the height of the Renaissance period when men from a higher social class were expected to receive well-rounded educations. In 1491, Copernicus attended the University of Krakow where he studied mathematics and astronomy. After four years of study, his uncle appointed Copernic ...
... Copernicus lived during the height of the Renaissance period when men from a higher social class were expected to receive well-rounded educations. In 1491, Copernicus attended the University of Krakow where he studied mathematics and astronomy. After four years of study, his uncle appointed Copernic ...
A105 Stars and Galaxies
... Determining the Mass of the Sun How do we determine the mass of the Sun? Put the Sun on a scale and determine its weight??? Since gravity depends on the masses of both objects, we can look at how strongly the Sun attracts the Earth The Sun’s gravitational attraction keeps the Earth going ar ...
... Determining the Mass of the Sun How do we determine the mass of the Sun? Put the Sun on a scale and determine its weight??? Since gravity depends on the masses of both objects, we can look at how strongly the Sun attracts the Earth The Sun’s gravitational attraction keeps the Earth going ar ...
COMETS, ASTEROIDS, AND METEORS
... • As a comet approaches the sun and heats up, some of the gas and dust stream outward, forming a tail. The name “comet” means “long haired star” in Greek. Most comets have two tails, a gas tail and a dust tail. Both tails usually point away from the sun due to the force of solar wind from the sun. A ...
... • As a comet approaches the sun and heats up, some of the gas and dust stream outward, forming a tail. The name “comet” means “long haired star” in Greek. Most comets have two tails, a gas tail and a dust tail. Both tails usually point away from the sun due to the force of solar wind from the sun. A ...
Astronomy 350 Fall 2011 Homework #1
... The most massive solar system object beyond Neptune is not Pluto, but a body discovered three years ago, known as Eris (And now, officially, neither are planets). Eris has a semimajor axis a = 68 AU. How many times will the Earth go around the Sun when Eris does so once? Moon, 3rd Q ...
... The most massive solar system object beyond Neptune is not Pluto, but a body discovered three years ago, known as Eris (And now, officially, neither are planets). Eris has a semimajor axis a = 68 AU. How many times will the Earth go around the Sun when Eris does so once? Moon, 3rd Q ...
Coordinate Systems for Astronomy or: How to get
... alignments of its axis of rotation with the Sun, or 365.242 days. The Earth's orbital (sidereal) period around the Sun is 365.256 days. The 0.014 day (= 20 minutes) difference is caused by precession, which has a period of 25770 years (see above), as 365.25/25770 = 0.014 day/yr. The Earth turns once ...
... alignments of its axis of rotation with the Sun, or 365.242 days. The Earth's orbital (sidereal) period around the Sun is 365.256 days. The 0.014 day (= 20 minutes) difference is caused by precession, which has a period of 25770 years (see above), as 365.25/25770 = 0.014 day/yr. The Earth turns once ...