on the mass distribution of stars in the solar neighbourhood
... After accepting the final results one meets the question how reliable they are. Here we have three main items to consider. The first concerns the fraction of low-mass stars because if it is not so high, as found in this paper, then the present results become doubtful. A comparison can be done with I ...
... After accepting the final results one meets the question how reliable they are. Here we have three main items to consider. The first concerns the fraction of low-mass stars because if it is not so high, as found in this paper, then the present results become doubtful. A comparison can be done with I ...
Highways in the Sky - Wyalusing State Park
... the handle), continue 15x this distance (through Polaris again) and then curving through the 2 stars forming the SE side of the ‘house’-like asterism (in Cepheus), that is 60 degrees of arc or two pink-to-thumb distances plus a little. There is Deneb or alpha CYG, the tail of the Swan (or the top of ...
... the handle), continue 15x this distance (through Polaris again) and then curving through the 2 stars forming the SE side of the ‘house’-like asterism (in Cepheus), that is 60 degrees of arc or two pink-to-thumb distances plus a little. There is Deneb or alpha CYG, the tail of the Swan (or the top of ...
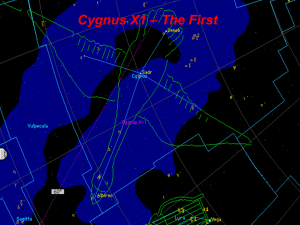
Cygnus X-1
... a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flicker in hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven that Cygnus X-1 is smaller than the Earth. Strangely enough, Cygnus X-1 has a companion star called HDE 226868. HDE 226868 is a supergiant with a tem ...
... a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flicker in hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven that Cygnus X-1 is smaller than the Earth. Strangely enough, Cygnus X-1 has a companion star called HDE 226868. HDE 226868 is a supergiant with a tem ...
The 2008 RBSE Journal - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... DRAGNs are found in starburst galaxies, which produce radio emission lines and are mainly formed in galaxies that are larger than their host galaxies, such as elliptical galaxies.(4) They are comprised of lobes, jets, and a core just as other radio galaxies are, and they also have hot spots in the l ...
... DRAGNs are found in starburst galaxies, which produce radio emission lines and are mainly formed in galaxies that are larger than their host galaxies, such as elliptical galaxies.(4) They are comprised of lobes, jets, and a core just as other radio galaxies are, and they also have hot spots in the l ...
Star Formation
... Protostars form by collapse of molecular clouds • Clouds must form dense and cold clumps or cores to ...
... Protostars form by collapse of molecular clouds • Clouds must form dense and cold clumps or cores to ...
Application Exercise: Distances to Stars Using Measured Parallax
... of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still just points of light. Although we may be able to tell a lot about a star through its light, these observations do n ...
... of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still just points of light. Although we may be able to tell a lot about a star through its light, these observations do n ...
Galaxy Powerpoint Notes
... II. Spiral Galaxy The appearance of spiral galaxies are very easy to distinguish. They feature a shape that looks like a disk that usually has a bulge in the center and with arms that spiral outwards as the galaxy rotates. The most common spiral galaxies in our universe are the Milky Way Galaxy (the ...
... II. Spiral Galaxy The appearance of spiral galaxies are very easy to distinguish. They feature a shape that looks like a disk that usually has a bulge in the center and with arms that spiral outwards as the galaxy rotates. The most common spiral galaxies in our universe are the Milky Way Galaxy (the ...
HET603-M05A01: Colours and Spectral Types: Learning about stars
... In this Activity, we have learnt about three different types of spectra - continous, absorption and emission. We also learnt how a star’s properties can affect its spectrum and in particular that • hot stars will have a high spectrum peaked towards the blue end; • cool stars will have a low, flat sp ...
... In this Activity, we have learnt about three different types of spectra - continous, absorption and emission. We also learnt how a star’s properties can affect its spectrum and in particular that • hot stars will have a high spectrum peaked towards the blue end; • cool stars will have a low, flat sp ...
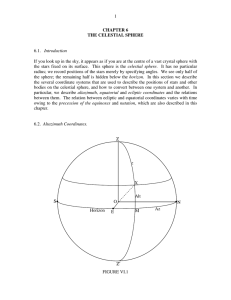
CHAPTER 6 THE CELESTIAL SPHERE
... (The reader may have noticed that I have just used the term “sidereal hours”. For the moment, just read this as “hours” – but a little later on we shall say what we mean by “sidereal” hours, and you may then want to come back and re-read this.) While it is useful to know the hour angle of a star at ...
... (The reader may have noticed that I have just used the term “sidereal hours”. For the moment, just read this as “hours” – but a little later on we shall say what we mean by “sidereal” hours, and you may then want to come back and re-read this.) While it is useful to know the hour angle of a star at ...
ppt
... takes approximately 100 times longer to move a given distance Have to halt the process: removal of disk; tidal/magnetic interactions between planet/star/disk Multiple-giant cases can explain high-eccentricity orbits by resonances or close encounters between giants Not clear how difficult it is for E ...
... takes approximately 100 times longer to move a given distance Have to halt the process: removal of disk; tidal/magnetic interactions between planet/star/disk Multiple-giant cases can explain high-eccentricity orbits by resonances or close encounters between giants Not clear how difficult it is for E ...
Latitude and Longitude - Northside Middle School
... Polaris is located directly over the tropic of cancer b) Polaris is the brightest and most easily located star c) The altitude of Polaris is equal to the observers latitude d) The position of Polaris changes with the seasons a) ...
... Polaris is located directly over the tropic of cancer b) Polaris is the brightest and most easily located star c) The altitude of Polaris is equal to the observers latitude d) The position of Polaris changes with the seasons a) ...
THE CONSTELLATIONS OF THE ZODIAC
... the vernal equinox has moved away from the Aries constellation due to the precession of the Earth’s axis of rotation. It is important to distinguish between the zodiacal signs and the constellations ...
... the vernal equinox has moved away from the Aries constellation due to the precession of the Earth’s axis of rotation. It is important to distinguish between the zodiacal signs and the constellations ...
THE CONSTELLATIONS OF THE ZODIAC G. Iafrate, M. Ramella
... the vernal equinox has moved away from the Aries constellation due to the precession of the Earth’s axis of rotation. It is important to distinguish between the zodiacal signs and the constellations ...
... the vernal equinox has moved away from the Aries constellation due to the precession of the Earth’s axis of rotation. It is important to distinguish between the zodiacal signs and the constellations ...
Manual - TUM
... The quickest part of this project is likely to be taking the images of the stellar clusters. Planning the observations including target selection and scheduling, planning the calibration frames and analysing the data are each likely to take longer. Therefore it is vital to plan your observations, as ...
... The quickest part of this project is likely to be taking the images of the stellar clusters. Planning the observations including target selection and scheduling, planning the calibration frames and analysing the data are each likely to take longer. Therefore it is vital to plan your observations, as ...
134-Notes-a
... Even more common than the light year is the parsec. A parsec is defined as the distance from the sun you would have to be in order for the angular distance between the earth and the sun to be arsecond. This somewhat strange choice of measurement was made so that an object at a distance of 1 parsec h ...
... Even more common than the light year is the parsec. A parsec is defined as the distance from the sun you would have to be in order for the angular distance between the earth and the sun to be arsecond. This somewhat strange choice of measurement was made so that an object at a distance of 1 parsec h ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 14 Notes: The Main
... value of 3.7 for the coefficient. This is shallower than the value of 5.6 we found for radiative stars with constant κ. As you will show on your homework, the value for radiative stars where κ is the free-free opacity differs slightly from these. II. Numerical Results on the ZAMS We have now pushed ...
... value of 3.7 for the coefficient. This is shallower than the value of 5.6 we found for radiative stars with constant κ. As you will show on your homework, the value for radiative stars where κ is the free-free opacity differs slightly from these. II. Numerical Results on the ZAMS We have now pushed ...
Chapter 26.2 notes
... The absolute brightnesses of stars vary even more than temperature, ranging from about one ten-thousandth to a million times that of the sun. ...
... The absolute brightnesses of stars vary even more than temperature, ranging from about one ten-thousandth to a million times that of the sun. ...
talk
... ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rotation curve data with theoretical models require baryons in dwarfs to occupy ...
... ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rotation curve data with theoretical models require baryons in dwarfs to occupy ...
The Hipparcos Star Globe Booklet - Cosmos
... gathered data for four years. The satellite span slowly, controlled in such a way as to gradually shift the axis of rotation so that over time the telescope could repeatedly scan the entire celestial sphere. A simultaneous onboard experiment named Tycho was also to provide astrometric and two-colour ...
... gathered data for four years. The satellite span slowly, controlled in such a way as to gradually shift the axis of rotation so that over time the telescope could repeatedly scan the entire celestial sphere. A simultaneous onboard experiment named Tycho was also to provide astrometric and two-colour ...
haajar slaughter
... 1848. That's still not it there are only 30 stars on the flag b now we still need 20 stars to go. The flag takes California as a star in 1851 and Minnesota in 1858, about seven years apart. Oregon looks as good as any star on the flag in 1859 when it was declared a state. ...
... 1848. That's still not it there are only 30 stars on the flag b now we still need 20 stars to go. The flag takes California as a star in 1851 and Minnesota in 1858, about seven years apart. Oregon looks as good as any star on the flag in 1859 when it was declared a state. ...
Document
... • Stars in the disk all orbit the galactic center in about the same plane and in the same direction. Halo stars also orbit the center of the galaxy, but with orbits randomly inclined to the disk of the galaxy. • How long does it take the Sun to orbit the galactic center? • Each orbit takes about 230 ...
... • Stars in the disk all orbit the galactic center in about the same plane and in the same direction. Halo stars also orbit the center of the galaxy, but with orbits randomly inclined to the disk of the galaxy. • How long does it take the Sun to orbit the galactic center? • Each orbit takes about 230 ...
New Double Stars from Asteroidal Occultations, 1971 - 2008
... The occultation is recorded as the sudden disappearance of the star, followed some seconds (or tens of seconds) later with a sudden reappearance of the star. For a small number of events, the occultation may involve: A partial drop in light, followed by a complete drop in light. The order of the lig ...
... The occultation is recorded as the sudden disappearance of the star, followed some seconds (or tens of seconds) later with a sudden reappearance of the star. For a small number of events, the occultation may involve: A partial drop in light, followed by a complete drop in light. The order of the lig ...
Resources: - Real Science
... as Earth is. But HD 189733b is more than 30 times closer to its star than Earth is to the Sun. This is why HD 189733b is so much hotter than Jupiter. The "holy grail" for planet-hunters is to find a planet like Earth that has water in its atmosphere, said Dr Tinetti. "When it happens, that discovery ...
... as Earth is. But HD 189733b is more than 30 times closer to its star than Earth is to the Sun. This is why HD 189733b is so much hotter than Jupiter. The "holy grail" for planet-hunters is to find a planet like Earth that has water in its atmosphere, said Dr Tinetti. "When it happens, that discovery ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.