Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016 - Edexcel
... Universe was originally very small Expanded outwards after Big Bang CMB = ‘left over’ radiation from the Big Bang Wavelength of CMB agreed with estimates of rate of cooling of Universe (or similar argument based on temperature) Quasars are (only) observed at very large distances/high red-shifts Indi ...
... Universe was originally very small Expanded outwards after Big Bang CMB = ‘left over’ radiation from the Big Bang Wavelength of CMB agreed with estimates of rate of cooling of Universe (or similar argument based on temperature) Quasars are (only) observed at very large distances/high red-shifts Indi ...
Introduction - Cambridge University Press
... burning; that is left for Chapter 3. We begin by considering the question of just what we mean by ‘a star’. The starting point for the formation of a star is a cloud of cold gas, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with traces of heavier elements (usually referred to as metals). The cloud col ...
... burning; that is left for Chapter 3. We begin by considering the question of just what we mean by ‘a star’. The starting point for the formation of a star is a cloud of cold gas, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with traces of heavier elements (usually referred to as metals). The cloud col ...
Presentation file
... Some thoughts on the evolutionary state of the RSGs Why not more VY CMa’s ? Evidence for increased mass loss, CS ejecta, with higher luminosity and cooler temperatures Do RSGs evolve through the red supergiant stage getting apparently cooler, more extended envelopes and high mass loss episodes? Lik ...
... Some thoughts on the evolutionary state of the RSGs Why not more VY CMa’s ? Evidence for increased mass loss, CS ejecta, with higher luminosity and cooler temperatures Do RSGs evolve through the red supergiant stage getting apparently cooler, more extended envelopes and high mass loss episodes? Lik ...
Science performance of Gaia, ESA`s space
... drifting through space in isolation and in orbit around other stars (Haywood and Jordi 2002). This data is vital for investigating the physics of star formation since brown dwarfs represent stars that “just did not make it” to core hydrogen fusion. • Gaia will contribute to solar-system science beca ...
... drifting through space in isolation and in orbit around other stars (Haywood and Jordi 2002). This data is vital for investigating the physics of star formation since brown dwarfs represent stars that “just did not make it” to core hydrogen fusion. • Gaia will contribute to solar-system science beca ...
argo and other tidal structures around the milky way
... sample was limited to −25◦ < b < +25◦ , in order to avoid the Magellanic Clouds. The solar position is X = −8 kpc, Y = 0 kpc. A number of known structures can be seen in these plots: The Monoceros stream, Sagittarius, the TriAnd and Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004). The large southern hemis ...
... sample was limited to −25◦ < b < +25◦ , in order to avoid the Magellanic Clouds. The solar position is X = −8 kpc, Y = 0 kpc. A number of known structures can be seen in these plots: The Monoceros stream, Sagittarius, the TriAnd and Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004). The large southern hemis ...
arXiv:astro-ph/0508448v1 22 Aug 2005
... their stellar type (Lynn et al. 2004) as opposed to the fast rotation which might be expected for the secondary from an interacting binary. Hoogerwerf, de Bruijne & de Zeeuw (2001) trace the paths of runaway stars back to their parent clusters, and find perhaps two thirds are the result of supernova ...
... their stellar type (Lynn et al. 2004) as opposed to the fast rotation which might be expected for the secondary from an interacting binary. Hoogerwerf, de Bruijne & de Zeeuw (2001) trace the paths of runaway stars back to their parent clusters, and find perhaps two thirds are the result of supernova ...
On the Cosmic Nuclear Cycle and the Similarity of Nuclei and Stars
... papers [3–9], compact nuclear matter or black holes had been considered as the likely energy sources for the violent, more energetic events, like gamma ray bursts and quasars, but not as an energy source that might sustain luminosity in ordinary stars for billions of years. However if the collapse o ...
... papers [3–9], compact nuclear matter or black holes had been considered as the likely energy sources for the violent, more energetic events, like gamma ray bursts and quasars, but not as an energy source that might sustain luminosity in ordinary stars for billions of years. However if the collapse o ...
MESSIER - EarthLink
... Simulation of the 30 Doradus System with 12,144 stars Globular Cluster in Large Magellanic Cloud ...
... Simulation of the 30 Doradus System with 12,144 stars Globular Cluster in Large Magellanic Cloud ...
Field Trip Hayden Planetarium
... _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Exhibit name where you found the answer: _____________________________________ Page ...
... _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Exhibit name where you found the answer: _____________________________________ Page ...
The Be/X-ray transient V0332153: evidence for a tilt between the
... infrared excess when compared to normal stars of the same spectral types are attributed to the presence of a circumstellar disc. Most Be/X-ray binaries have relatively eccentric orbits, and the neutron star companion is normally far away from the disc surrounding the Be star. Due to their different ...
... infrared excess when compared to normal stars of the same spectral types are attributed to the presence of a circumstellar disc. Most Be/X-ray binaries have relatively eccentric orbits, and the neutron star companion is normally far away from the disc surrounding the Be star. Due to their different ...
Celestial Navigation in 60 min
... Imagine the Earth in space surrounded by a celestial sphere on which all the heavenly bodies are moving. This is representation of the universe, but this is enough for our purposes. We are just poor seamen (correction, I am). Th centred on Earth with the celestial equator passing through the Earth e ...
... Imagine the Earth in space surrounded by a celestial sphere on which all the heavenly bodies are moving. This is representation of the universe, but this is enough for our purposes. We are just poor seamen (correction, I am). Th centred on Earth with the celestial equator passing through the Earth e ...
Stars and the Milky Way
... • the Milky Way is made up of over 200 billion stars Other facts about the Milky Way • The Sun is just one of the stars in the Milky Way. • It is called the Milky Way because when astronomers looked up at the sky, they saw a line of light that looked like some milk had been spilt. • Stars in our Mil ...
... • the Milky Way is made up of over 200 billion stars Other facts about the Milky Way • The Sun is just one of the stars in the Milky Way. • It is called the Milky Way because when astronomers looked up at the sky, they saw a line of light that looked like some milk had been spilt. • Stars in our Mil ...
Lecture 3 - University of Washington
... • The measurements show that rotation curves are “flat” – they are not ap√ proching the vc(R) ∝ 1/ R behavior expected in the outer parts of disks • Therefore, there must be an invisible galaxy component that is capable of producing gravitational force • Earlier (1930’s) suggested by Fritz Zwicky, b ...
... • The measurements show that rotation curves are “flat” – they are not ap√ proching the vc(R) ∝ 1/ R behavior expected in the outer parts of disks • Therefore, there must be an invisible galaxy component that is capable of producing gravitational force • Earlier (1930’s) suggested by Fritz Zwicky, b ...
Lecture
... The previous chapter took you on a cosmic zoom to explore the universe in space and time. That quick preview only sets the stage for the drama to come. Now it is time to return to Earth and look closely at the sky. To understand what you are in the universe, you must know where you are. As you look ...
... The previous chapter took you on a cosmic zoom to explore the universe in space and time. That quick preview only sets the stage for the drama to come. Now it is time to return to Earth and look closely at the sky. To understand what you are in the universe, you must know where you are. As you look ...
Spiral Arms - Harry Kroto
... The spiral arms are regions where stars' and gas clouds' orbits bunch up closer to one another and the region becomes overdense. Stars go in and move out of the pattern, but the pattern persists and moves at its own rate. Since the region is overdense when gas clouds enter it they are compressed and ...
... The spiral arms are regions where stars' and gas clouds' orbits bunch up closer to one another and the region becomes overdense. Stars go in and move out of the pattern, but the pattern persists and moves at its own rate. Since the region is overdense when gas clouds enter it they are compressed and ...
The Mazzaroth (Zodiac)
... for telling where in the sky different stars can be found. Many of the brightest stars have individual names that come from Greek, Latin, or Arabic, and the navigators of ships and aircraft call them by these names. Astronomers, however, find it more convenient to name them by their constellations, ...
... for telling where in the sky different stars can be found. Many of the brightest stars have individual names that come from Greek, Latin, or Arabic, and the navigators of ships and aircraft call them by these names. Astronomers, however, find it more convenient to name them by their constellations, ...
aaswinter06
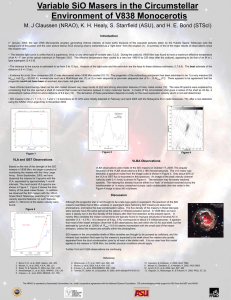
... • The distance to the source is estimated to be from 5 to 12 kpc. Analysis of the light echo and the extinction are the keys to these distance estimates (1,7,8,9). The best estimate of the distance is 9 +/- 2 kpc. • Evidence for a hot, blue companion (B3 V) was discovered when V838 Mon cooled (10,11 ...
... • The distance to the source is estimated to be from 5 to 12 kpc. Analysis of the light echo and the extinction are the keys to these distance estimates (1,7,8,9). The best estimate of the distance is 9 +/- 2 kpc. • Evidence for a hot, blue companion (B3 V) was discovered when V838 Mon cooled (10,11 ...
1. The catalogue structure
... not correspond to zodiacal constellations, which is why the stars that pertain to a single zodiacal constellation can wind up in different zodiacal signs. The canonical version of the Almagest catalogue contained in the work of Peters and Knobel ([1339]) is presented as a table that consists of six ...
... not correspond to zodiacal constellations, which is why the stars that pertain to a single zodiacal constellation can wind up in different zodiacal signs. The canonical version of the Almagest catalogue contained in the work of Peters and Knobel ([1339]) is presented as a table that consists of six ...
AST301.Ch18.InterstelMed - University of Texas Astronomy
... more-or-less random directions), and often found in “supershells” of expanding gas driven by luminous young stars. The illustration on p. 479 shows how our solar system is actually located within a cavity bounded by one of these supershells—it is believed that a number of supernovae must have explod ...
... more-or-less random directions), and often found in “supershells” of expanding gas driven by luminous young stars. The illustration on p. 479 shows how our solar system is actually located within a cavity bounded by one of these supershells—it is believed that a number of supernovae must have explod ...
- Cosmotography
... A candidate diffuse stellar substructure was previously reported in the halo of the nearby dwarf starburst galaxy NGC 4449 by Karachentsev et al. We map and analyze this feature using a unique combination of deep integrated-light images from the Black Bird 0.5-meter telescope, and high-resolution wi ...
... A candidate diffuse stellar substructure was previously reported in the halo of the nearby dwarf starburst galaxy NGC 4449 by Karachentsev et al. We map and analyze this feature using a unique combination of deep integrated-light images from the Black Bird 0.5-meter telescope, and high-resolution wi ...
Planetary Fact Sheet – Metric
... The star is best seen at night. That requires that the Sun be far away from the star on the celestial sphere, since the area around the Sun will be daylight. For simplicity, lets that the sky is light 6 hours either side of the Sun. So, the best time to observe the star will be when the Sun is as fa ...
... The star is best seen at night. That requires that the Sun be far away from the star on the celestial sphere, since the area around the Sun will be daylight. For simplicity, lets that the sky is light 6 hours either side of the Sun. So, the best time to observe the star will be when the Sun is as fa ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.