Lesson 55 – The Structure of the Universe - science
... comparison spectrum of an element on Earth, at rest compared with the observer, is shown above and below each galactic spectrum. For very high speeds the simple formula cannot be used and the effects of special relativity have to be allowed for. It is important to realise that the Doppler shift will ...
... comparison spectrum of an element on Earth, at rest compared with the observer, is shown above and below each galactic spectrum. For very high speeds the simple formula cannot be used and the effects of special relativity have to be allowed for. It is important to realise that the Doppler shift will ...
THE PERIOD OF ROTATION OF THE SUN
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
HR DIAGRAMS OF STAR CLUSTERS
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
... your cluster HR diagram. Once you have matched the zero-age main-sequence, you can then call up the isochrone-fitting tool. On the menu bar of the ColorMagnitude diagram window, call up Tools > Isochrones, and you will see an isochrone plotted on your HR diagram near the plot of your cluster stars. ...
File - Mr. Catt`s Class
... 1. Hubble’s tuning fork diagram relates the various types of galaxies. In his plan, S0 galaxies form the connecting link, because they have characteristics of both elliptical and spiral galaxies. 2. Astronomers once also thought the diagram represented an evolutionary sequence, but this interpretati ...
... 1. Hubble’s tuning fork diagram relates the various types of galaxies. In his plan, S0 galaxies form the connecting link, because they have characteristics of both elliptical and spiral galaxies. 2. Astronomers once also thought the diagram represented an evolutionary sequence, but this interpretati ...
When Stars Attack! In Search of Killer Supernovae
... noticed that a new and unusual star, surpassing the other stars in brilliancy, was shining ... and since I had, from boyhood, known all the stars of the heavens perfectly, it was quite evident to me that there had never been any star in that place of the sky ... I was so astonished of this sight ... ...
... noticed that a new and unusual star, surpassing the other stars in brilliancy, was shining ... and since I had, from boyhood, known all the stars of the heavens perfectly, it was quite evident to me that there had never been any star in that place of the sky ... I was so astonished of this sight ... ...
The Final Version of the White Paper is available.
... from an era of discovery to one of physical and chemical characterization. This will eventually lead to the remote analysis of planet atmospheres with the ultimate goal of life detection. The bulk of the exoplanets detected by Doppler surveys are gas giants orbiting solar-type stars. In stark contra ...
... from an era of discovery to one of physical and chemical characterization. This will eventually lead to the remote analysis of planet atmospheres with the ultimate goal of life detection. The bulk of the exoplanets detected by Doppler surveys are gas giants orbiting solar-type stars. In stark contra ...
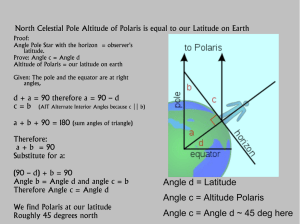
Angle d = Latitude Angle c = Altitude Polaris Angle c
... Our Observing Latitude determines what celestial objects are seen above our local horizon ...
... Our Observing Latitude determines what celestial objects are seen above our local horizon ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... paths, set in the west, and then again appear in the east at the same point as before. An observer at the equator sees all (sufficiently bright) stars rise and set. Now, if a star rises on the eastern horizon at a particular time today, it will rise again tomorrow, from the same point, but about 4 m ...
... paths, set in the west, and then again appear in the east at the same point as before. An observer at the equator sees all (sufficiently bright) stars rise and set. Now, if a star rises on the eastern horizon at a particular time today, it will rise again tomorrow, from the same point, but about 4 m ...
Stars & Galaxies - newmanlib.ibri.org
... that they differ in brightness. • As one looks at the stars more carefully, it becomes apparent that they are not all the same color. • Look at the constellation of Orion shown in the next panel. ...
... that they differ in brightness. • As one looks at the stars more carefully, it becomes apparent that they are not all the same color. • Look at the constellation of Orion shown in the next panel. ...
MPhil Thesis - Final - Suzanne Knight
... low mass planets as it ascends the red giant and asymptotic giant branch evolutionary tracks, but larger mass objects and those further out will survive.! A substellar companion detected around a white dwarf would prove that it could survive the final stages of stellar evolution and place constraint ...
... low mass planets as it ascends the red giant and asymptotic giant branch evolutionary tracks, but larger mass objects and those further out will survive.! A substellar companion detected around a white dwarf would prove that it could survive the final stages of stellar evolution and place constraint ...
Emergency Land Navigation
... other and thus are called fixed stars. Out of the many stars found on the sphere, there are only 57 of them, which we consider are bright enough to help us in our navigation. Planets as a class move among the fixed stars; the navigational planets are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, the Moon a ...
... other and thus are called fixed stars. Out of the many stars found on the sphere, there are only 57 of them, which we consider are bright enough to help us in our navigation. Planets as a class move among the fixed stars; the navigational planets are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, the Moon a ...
1: Properties of Pulsars
... from the central "strange" star, identifying it as a pulsar. It turned out later, that these "giant pulses" which they observed, occur every two minutes or so, and that the true pulse period was in fact as short as 33 milliseconds. The short period of 33 milliseconds ruled out white dwarfs for being ...
... from the central "strange" star, identifying it as a pulsar. It turned out later, that these "giant pulses" which they observed, occur every two minutes or so, and that the true pulse period was in fact as short as 33 milliseconds. The short period of 33 milliseconds ruled out white dwarfs for being ...
Intel® Shooting StarTM Drones Featured in First
... Feb. 5, 2017 – During the Pepsi* Zero Sugar Super Bowl LI Halftime Show, three hundred Intel® Shooting Star™ drones lit up the sky in a choreographed aerial show to kick-off the performance. Below are interesting facts about the show: ...
... Feb. 5, 2017 – During the Pepsi* Zero Sugar Super Bowl LI Halftime Show, three hundred Intel® Shooting Star™ drones lit up the sky in a choreographed aerial show to kick-off the performance. Below are interesting facts about the show: ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
instructor notes stellar evolution, star clusters
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
... of stars of different spectral types and luminosity classes. The general method of using a calibrated zero-age mainsequence (ZAMS) to derive cluster distances is outlined by Blaauw in Basic Astronomical Data. However, the necessary zero-point calibration involves the independent determination of the ...
Active Galaxies
... object at the very center of the Galaxy a million times more luminous than the Sun (IR, radio, X-ray, and gamma ray source) ...
... object at the very center of the Galaxy a million times more luminous than the Sun (IR, radio, X-ray, and gamma ray source) ...
Geometry of orbits - Harpursville Middle School
... Chunks of rock and metal that circle the sun Range in size from hundreds of km to mm Most are in a belt between Mars and Jupiter Rarely cross Earth’s orbit May have caused the extinction of dinosaurs ...
... Chunks of rock and metal that circle the sun Range in size from hundreds of km to mm Most are in a belt between Mars and Jupiter Rarely cross Earth’s orbit May have caused the extinction of dinosaurs ...
The population of young stars in Orion A: X-rays and... Ignazio Pillitteri , S. J. Wolk , L. Allen
... Through Spitzer and XMM-Newton we identify ∼ 702 PMS stars that emit in X-rays out of 1060 X-ray sources. By assuming the same fraction of X-ray detection of WTT stars and CTT stars we estimate a population of ∼ 1850 PMS stars, for an overall detection efficiency of ∼ 38% among PMS stars and a mean ...
... Through Spitzer and XMM-Newton we identify ∼ 702 PMS stars that emit in X-rays out of 1060 X-ray sources. By assuming the same fraction of X-ray detection of WTT stars and CTT stars we estimate a population of ∼ 1850 PMS stars, for an overall detection efficiency of ∼ 38% among PMS stars and a mean ...
Lecture8_v2 - Lick Observatory
... • The ~ 500 planets we have detected to date are only a sub-set of potential planets out there • These new solar systems have raised big questions about how our own Solar System formed • Future search methods have high probability of finding more (and more varied) planets ...
... • The ~ 500 planets we have detected to date are only a sub-set of potential planets out there • These new solar systems have raised big questions about how our own Solar System formed • Future search methods have high probability of finding more (and more varied) planets ...
Abstracts - Physics of Evolved Stars 2015
... and dusty stellar wind. This wind eventually grows to such high mass-loss rates that the central star becomes entirely enshrouded by a dense, dusty superwind. Before reaching such high massloss rates, these stars go through a phase of a lower mass-loss rate of at most a few times 10^-6 solar masses ...
... and dusty stellar wind. This wind eventually grows to such high mass-loss rates that the central star becomes entirely enshrouded by a dense, dusty superwind. Before reaching such high massloss rates, these stars go through a phase of a lower mass-loss rate of at most a few times 10^-6 solar masses ...
T Einstein’s Mirage Paul L. Schechter
... being imaged—it is a mirror image, but distorted. At least one of the other images must have the correct handedness, but it will also be distorted. The French call such distorted images gravitational mirages. In the half century following the confirmation of general relativity, the idea that cosmic ...
... being imaged—it is a mirror image, but distorted. At least one of the other images must have the correct handedness, but it will also be distorted. The French call such distorted images gravitational mirages. In the half century following the confirmation of general relativity, the idea that cosmic ...
Comparing stars - The Open University
... than the Sun, and appears bluish-white. It has the greatest apparent visual brightness (most negative apparent visual magnitude!) of any star in the night sky. This is, as we have seen, not because it is very luminous, but because it is both fairly luminous and rather close - at 2.63 pc it's the sev ...
... than the Sun, and appears bluish-white. It has the greatest apparent visual brightness (most negative apparent visual magnitude!) of any star in the night sky. This is, as we have seen, not because it is very luminous, but because it is both fairly luminous and rather close - at 2.63 pc it's the sev ...
What are Messier Objects? - Bowling Green State University
... NGC 4736 in Canes Venatici. Discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781. Has an extremely bright inner region surrounded by a ring of ...
... NGC 4736 in Canes Venatici. Discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781. Has an extremely bright inner region surrounded by a ring of ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.