Hot Horizontal Branch Stars in the Galactic Bulge. I
... The presence of BHB stars in high-metallicity populations and the reversal in their color distribution raise major questions as to their origin. Both observation and theory suggest that BHB stars in metal-rich systems may be produced by channels in addition to those operating in metal-poor systems. ...
... The presence of BHB stars in high-metallicity populations and the reversal in their color distribution raise major questions as to their origin. Both observation and theory suggest that BHB stars in metal-rich systems may be produced by channels in addition to those operating in metal-poor systems. ...
A Zoo of Galaxies
... The variety of different galaxies observed in the sky naturally caused people to wonder what they were. The scientific arguments surrounding this question at the start of the 20th century, are best represented perhaps, by the public debate held in 1920 between Heber Curtis and Harlow Shapley. Many o ...
... The variety of different galaxies observed in the sky naturally caused people to wonder what they were. The scientific arguments surrounding this question at the start of the 20th century, are best represented perhaps, by the public debate held in 1920 between Heber Curtis and Harlow Shapley. Many o ...
The chemical enrichment of the ICM from hydrodynamical simulations
... A number of authors have presented hydrodynamical simulations for the formation of cosmic structures, which include treatments of the chemical evolution at different levels of complexity. Raiteri et al. (1996) presented SPH simulations of the Galaxy, forming in an isolated halo, by following iron an ...
... A number of authors have presented hydrodynamical simulations for the formation of cosmic structures, which include treatments of the chemical evolution at different levels of complexity. Raiteri et al. (1996) presented SPH simulations of the Galaxy, forming in an isolated halo, by following iron an ...
The ATLAS3D project-XXII. Low-efficiency star formation in early
... using a universal local law to form stars in the simulations, we find that the earlytype galaxies are offset from the spirals on the large-scale Kennicutt relation, and form stars two to five times less efficiently. This offset is in agreement with previous results on morphological quenching: gas di ...
... using a universal local law to form stars in the simulations, we find that the earlytype galaxies are offset from the spirals on the large-scale Kennicutt relation, and form stars two to five times less efficiently. This offset is in agreement with previous results on morphological quenching: gas di ...
Brightest Stars : Discovering the Universe Through the Sky`s Most
... profile also offers the lore and legends connected with the star, for these are a measure of what the human race as a whole has found interesting and individual about the star. A key part of each profile, of course, is also what the science of astronomy has taught us about the physical nature of the ...
... profile also offers the lore and legends connected with the star, for these are a measure of what the human race as a whole has found interesting and individual about the star. A key part of each profile, of course, is also what the science of astronomy has taught us about the physical nature of the ...
Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and lithium abundances of six
... A resolution of R = λ/∆λ ≈ 20 000 and 28 000 for CASPEC and EMMI respectively were obtained. The reductions were carried out using the code by Spite (1990). Further details on the data and a log-book of the observations are given in Paper I. As in Paper I, the well studied galactic supergiant Arctur ...
... A resolution of R = λ/∆λ ≈ 20 000 and 28 000 for CASPEC and EMMI respectively were obtained. The reductions were carried out using the code by Spite (1990). Further details on the data and a log-book of the observations are given in Paper I. As in Paper I, the well studied galactic supergiant Arctur ...
No. 6
... may see a celestial body passing in front of another celestial body and preventing its light to reach to the Earth. This is called occultation. In occultation observations you see one body in the sky is getting dark, disappear or blinks when another body moves in front of it. Based on the bodies cre ...
... may see a celestial body passing in front of another celestial body and preventing its light to reach to the Earth. This is called occultation. In occultation observations you see one body in the sky is getting dark, disappear or blinks when another body moves in front of it. Based on the bodies cre ...
Black Holes in Binary Systems and Galaxy Nuclei
... the mass distribution of BHs has been considered by Postnov and Cherepashchuk (2003). Deficit of low-mass BH and the gap in the range (2 – 4) MSun may be due to enhanced quantum evaporation of BH which have been suggested in some multidimensional models of gravity (e.g. Randall and Sundrom, 1999). I ...
... the mass distribution of BHs has been considered by Postnov and Cherepashchuk (2003). Deficit of low-mass BH and the gap in the range (2 – 4) MSun may be due to enhanced quantum evaporation of BH which have been suggested in some multidimensional models of gravity (e.g. Randall and Sundrom, 1999). I ...
Cygnus X-2, super-Eddington mass transfer, and pulsar binaries
... Spectroscopic data give a low mass (M2 ≃ 0.5 − 0.7M⊙ ) and yet a large radius (R2 ≃ 7R⊙ ) and high luminosity (L2 ≃ 150L⊙ ). We show that this star closely resembles a remnant of early massive Case B evolution, during which the neutron star ejected most of the ∼ 3M⊙ transferred from the donor (initi ...
... Spectroscopic data give a low mass (M2 ≃ 0.5 − 0.7M⊙ ) and yet a large radius (R2 ≃ 7R⊙ ) and high luminosity (L2 ≃ 150L⊙ ). We show that this star closely resembles a remnant of early massive Case B evolution, during which the neutron star ejected most of the ∼ 3M⊙ transferred from the donor (initi ...
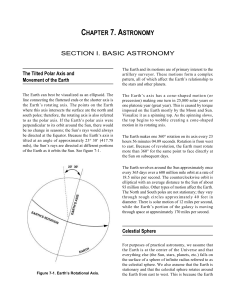
MCWP 3-16.7 Chapter 7: Astronomy
... The Earth and its motions are of primary interest to the artillery surveyor. These motions form a complex pattern, all of which affect the Earth’s relationship to the stars and other planets. The Earth’s axis has a cone-shaped motion (or precession) making one turn in 25,800 solar years or one plato ...
... The Earth and its motions are of primary interest to the artillery surveyor. These motions form a complex pattern, all of which affect the Earth’s relationship to the stars and other planets. The Earth’s axis has a cone-shaped motion (or precession) making one turn in 25,800 solar years or one plato ...
Gas fraction and star formation efficiency at z \< 1.0⋆⋆⋆⋆⋆⋆
... Article published by EDP Sciences ...
... Article published by EDP Sciences ...
starry night companion
... Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus, to show us how wrong we had been: Instead of the center of the universe, Copernicus said, our world is one of many planets and moons circling the Sun in a celestial clockwork. Some 250 years later the Apollo 8 astronauts became the first humans to see the truth ...
... Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus, to show us how wrong we had been: Instead of the center of the universe, Copernicus said, our world is one of many planets and moons circling the Sun in a celestial clockwork. Some 250 years later the Apollo 8 astronauts became the first humans to see the truth ...
Astrophysics Lab “A”
... Since the majority of the photons originate from the stellar “surface” (photosphere), i.e., from “inside”, the ions are, on average, accelerated into the outward direction. – After a relatively short time, the so called mean lifetime (of the order of 10−8 s), the electron “falls” back to its ground ...
... Since the majority of the photons originate from the stellar “surface” (photosphere), i.e., from “inside”, the ions are, on average, accelerated into the outward direction. – After a relatively short time, the so called mean lifetime (of the order of 10−8 s), the electron “falls” back to its ground ...
– 1 – 1. Galaxy Observations 1.1.
... Many studies for many types of galaxies at various redshifts have demonstrated that there is a correlation between the galaxy luminosity and the mean metallicity of a galaxy. By galaxy luminosity we mean emitted flux across a wavelength bandpass sufficiently red that current star formation has littl ...
... Many studies for many types of galaxies at various redshifts have demonstrated that there is a correlation between the galaxy luminosity and the mean metallicity of a galaxy. By galaxy luminosity we mean emitted flux across a wavelength bandpass sufficiently red that current star formation has littl ...
to - NexStar Resource Site
... 9) Jupiter The king of our Solar System of planets. It is believed that with a little more mass, Jupiter could have become a small star. What a different place our Earth would be with 2 Suns. Jupiter orbits 778,330,000 km (5.20 AU) from the Sun. Its mass is about 318 times that of the Earth and cont ...
... 9) Jupiter The king of our Solar System of planets. It is believed that with a little more mass, Jupiter could have become a small star. What a different place our Earth would be with 2 Suns. Jupiter orbits 778,330,000 km (5.20 AU) from the Sun. Its mass is about 318 times that of the Earth and cont ...
The Young Stars
... In 1945, Alfred Joy classified a group of 11 stars as ‘T Tauri variables’, named after the prototype discovered in the constellation of Taurus. They displayed erratic optical variability, strong chromospheric lines and could be identified through their strong Hα emission lines. They were found to co ...
... In 1945, Alfred Joy classified a group of 11 stars as ‘T Tauri variables’, named after the prototype discovered in the constellation of Taurus. They displayed erratic optical variability, strong chromospheric lines and could be identified through their strong Hα emission lines. They were found to co ...
Electronic version
... Within the twenty odd years since the discovery of the seismological relevance of the "five-minute oscillation" stupendous progress has been made in experiment and theory, both qualitatively and quantitatively. This symposium is a comprehensive presentation of the most recent achievements of "Helios ...
... Within the twenty odd years since the discovery of the seismological relevance of the "five-minute oscillation" stupendous progress has been made in experiment and theory, both qualitatively and quantitatively. This symposium is a comprehensive presentation of the most recent achievements of "Helios ...
Test 4 Review Clicker Questions
... b) the globular clusters formed first. c) the disk component started out thin and grew. d) spiral density waves formed first. e) the bar in the bulge formed first. ...
... b) the globular clusters formed first. c) the disk component started out thin and grew. d) spiral density waves formed first. e) the bar in the bulge formed first. ...
WILLIAM HERSCHEL AND THE `GARNET` STARS: μ CEPHEI AND
... in the zone observations made by Friedrich Wilhelm August Argelander (1799 –1875; Figure 7) at the Bonn Observatory from 1841 to 1844. The measurement was made on 11 September 1842. Argelander listed the position for 1842 and noted it as ―… very red.‖ (see Oelzen, 1852). The magnitude was estimated ...
... in the zone observations made by Friedrich Wilhelm August Argelander (1799 –1875; Figure 7) at the Bonn Observatory from 1841 to 1844. The measurement was made on 11 September 1842. Argelander listed the position for 1842 and noted it as ―… very red.‖ (see Oelzen, 1852). The magnitude was estimated ...
The Chemical Composition of Carbon-Rich, Very Metal
... put forward to account for the moderately metal-poor classical CH stars ([Fe/H]∼ −1.5). These are usually explained by a model involving mass transfer from a carbon-enhanced asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star (one that has since evolved to the white dwarf stage and cannot now be seen) to its lower-m ...
... put forward to account for the moderately metal-poor classical CH stars ([Fe/H]∼ −1.5). These are usually explained by a model involving mass transfer from a carbon-enhanced asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star (one that has since evolved to the white dwarf stage and cannot now be seen) to its lower-m ...
GRB EXPERIMENT
... after its formation • Coupled with rapid rotation (~1 ms period), this makes the neutron star a likely site for dynamo action • If the rotation period is less than the convective overturn time, magnetic field amplification is possible • In principle, B ~ 3 x 1017 G can be generated (magnetic field e ...
... after its formation • Coupled with rapid rotation (~1 ms period), this makes the neutron star a likely site for dynamo action • If the rotation period is less than the convective overturn time, magnetic field amplification is possible • In principle, B ~ 3 x 1017 G can be generated (magnetic field e ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.