Rotation and Revolution
... The rotation of the Earth • The side of the Earth that is facing the sun has daylight, the side of the Earth away from the sun has night. • It takes 24 hours for the Earth to complete one rotation. • The Earth is tilted on it’s axis at a 23.5 degree angle. • The Earth’s tilt is always in the directi ...
... The rotation of the Earth • The side of the Earth that is facing the sun has daylight, the side of the Earth away from the sun has night. • It takes 24 hours for the Earth to complete one rotation. • The Earth is tilted on it’s axis at a 23.5 degree angle. • The Earth’s tilt is always in the directi ...
Wednesday, October 29 - Otterbein University
... WUP: What is the Blackbody Curve and how does it depend on temperature? • jj: The blackbody curve describes the distribution of reemitted radiation from a blackbody (an object that absorbs and reemits all radiation falling upon it. The peak of the frequency on a blackbody curve is directly proporti ...
... WUP: What is the Blackbody Curve and how does it depend on temperature? • jj: The blackbody curve describes the distribution of reemitted radiation from a blackbody (an object that absorbs and reemits all radiation falling upon it. The peak of the frequency on a blackbody curve is directly proporti ...
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2
... be measured in the laboratory. This is key to radioactive age dating, which is used to determine the ages of rocks. The oldest rocks found anywhere in the solar system are meteorites, the bits of meteoroids that survive passing through the Earth’s atmosphere and land on our planet’s surface. Rad ...
... be measured in the laboratory. This is key to radioactive age dating, which is used to determine the ages of rocks. The oldest rocks found anywhere in the solar system are meteorites, the bits of meteoroids that survive passing through the Earth’s atmosphere and land on our planet’s surface. Rad ...
What is a star?
... • The sun is a star and is composed mostly of hydrogen and helium. It also contains oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. • At the center of the sun lies the core, where gases are compressed and heated and temperatures reach 15 million degrees Celsius. • The sun’s core is where matter is converted into ...
... • The sun is a star and is composed mostly of hydrogen and helium. It also contains oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. • At the center of the sun lies the core, where gases are compressed and heated and temperatures reach 15 million degrees Celsius. • The sun’s core is where matter is converted into ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... be measured in the laboratory. This is key to radioactive age dating, which is used to determine the ages of rocks. The oldest rocks found anywhere in the solar system are meteorites, the bits of meteoroids that survive passing through the Earth’s atmosphere and land on our planet’s surface. Rad ...
... be measured in the laboratory. This is key to radioactive age dating, which is used to determine the ages of rocks. The oldest rocks found anywhere in the solar system are meteorites, the bits of meteoroids that survive passing through the Earth’s atmosphere and land on our planet’s surface. Rad ...
The Scale of the Realms of the Universe
... • The Milky Way Galaxy is a giant disk of stars 160,000 light-years across and 1,000 light-years thick • The Sun is located at the edge of a spiral arm, 30,000 light-years from the center • It takes 250 Million years for the Sun to complete one orbit • There are over 100 Billion stars in the Milky W ...
... • The Milky Way Galaxy is a giant disk of stars 160,000 light-years across and 1,000 light-years thick • The Sun is located at the edge of a spiral arm, 30,000 light-years from the center • It takes 250 Million years for the Sun to complete one orbit • There are over 100 Billion stars in the Milky W ...
1705 Star Charts
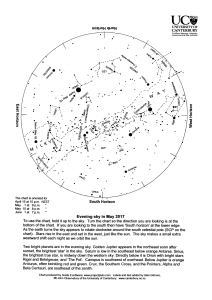
... The Evening Sky in May 2017 Two bright planets and the brightest stars share the evening sky this May. Soon after sunset golden Jupiter appears in the northeast. Beside Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Below Jupiter, near the horizon, is orange Arcturus, the brightest star in the nort ...
... The Evening Sky in May 2017 Two bright planets and the brightest stars share the evening sky this May. Soon after sunset golden Jupiter appears in the northeast. Beside Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Below Jupiter, near the horizon, is orange Arcturus, the brightest star in the nort ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
... The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a moderate sized research telescope. The telescope is controlled by a computer that allows you to move from star to star and make measurements. Different filters can be selected for each observation, and the ...
Simon P. Balm Astronomy 5, Test #1, Sample Questions
... combined mass is slightly greater than the original nucleus B) a heavy nucleus breaks apart into a number of smaller nuclei whose combined mass are less than the original nucleus C) two or more nuclei fuse or stick together to form a heavier nucleus whose combined mass is slightly less than the orig ...
... combined mass is slightly greater than the original nucleus B) a heavy nucleus breaks apart into a number of smaller nuclei whose combined mass are less than the original nucleus C) two or more nuclei fuse or stick together to form a heavier nucleus whose combined mass is slightly less than the orig ...
www.astro.utu.fi
... will the Earth spiral in to the Sun, or spiral outwards from it (and survive)? currently uncertain, as predictions depend on unclear physics of stellar “mass loss” In any case, it will boil the planet after about 2 billion years ...
... will the Earth spiral in to the Sun, or spiral outwards from it (and survive)? currently uncertain, as predictions depend on unclear physics of stellar “mass loss” In any case, it will boil the planet after about 2 billion years ...
Stellar Evolution
... • As hydrogen is being converted into helium in the core of a star, its structure changes slowly and stellar evolution begins. ...
... • As hydrogen is being converted into helium in the core of a star, its structure changes slowly and stellar evolution begins. ...
BROCK UNIVERSITY Return both the exam script
... gods and goddesses. (c) to honour important writers, artists, and politicians. (d) as aids in navigation and for keeping track of seasons. 19. The main reason that the Earth has a significant atmosphere and the Moon does not, is that (a) Earth has a lot more piano bars where laid-back jazz is played ...
... gods and goddesses. (c) to honour important writers, artists, and politicians. (d) as aids in navigation and for keeping track of seasons. 19. The main reason that the Earth has a significant atmosphere and the Moon does not, is that (a) Earth has a lot more piano bars where laid-back jazz is played ...
The Magnitude System
... It turns out that our eyes read out light signals logarithmically (this means that brightness and magnitudes have some type of logarithmic relation). The relationship was originally determined empirically and now it is used as a definition. It was found that a difference in 5 magnitudes corresponds ...
... It turns out that our eyes read out light signals logarithmically (this means that brightness and magnitudes have some type of logarithmic relation). The relationship was originally determined empirically and now it is used as a definition. It was found that a difference in 5 magnitudes corresponds ...
Final Review - PCHS SCIENCE
... Ancient astronomers assumed that the Sun, planets, and stars orbited a stationary Earth in what is now known as a geocentric model, meaning “Earth centered.” Some aspects of planetary motion were difficult to explain with a geocentric model. – The normal direction of motion for all planets, as obser ...
... Ancient astronomers assumed that the Sun, planets, and stars orbited a stationary Earth in what is now known as a geocentric model, meaning “Earth centered.” Some aspects of planetary motion were difficult to explain with a geocentric model. – The normal direction of motion for all planets, as obser ...
A Unique Environmental Studies Program
... The Pointers. Not very far from the Southern Cross you will see two quite bright stars. These are known as "The Pointers". They form part of the constellation of "The Centaur" and, being the two brightest stars in that constellation, are called Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri. If you look at Alpha ...
... The Pointers. Not very far from the Southern Cross you will see two quite bright stars. These are known as "The Pointers". They form part of the constellation of "The Centaur" and, being the two brightest stars in that constellation, are called Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri. If you look at Alpha ...
Astrophysics
... a) (5 points) There are four commonly used distances in extra-galactic astronomy, the co-moving line-of-sight distance, the co-moving transverse distance, the luminosity distance, and the angular diameter distance. Given a cosmological object at a redshift z (z > 1), describe how to calculate these ...
... a) (5 points) There are four commonly used distances in extra-galactic astronomy, the co-moving line-of-sight distance, the co-moving transverse distance, the luminosity distance, and the angular diameter distance. Given a cosmological object at a redshift z (z > 1), describe how to calculate these ...
The Copernican Cosmos
... Kepler’s Three Laws of Planetary Motion -Third Law. T 2 = R 3 the square of the time of one orbital period (T2) is equal to the cube of its average orbital radius (R3). Problem: What is Venus’s average distance from the sun? Well, we know Venus takes 224.7 earth days to orbit the sun. Venus’s orbit ...
... Kepler’s Three Laws of Planetary Motion -Third Law. T 2 = R 3 the square of the time of one orbital period (T2) is equal to the cube of its average orbital radius (R3). Problem: What is Venus’s average distance from the sun? Well, we know Venus takes 224.7 earth days to orbit the sun. Venus’s orbit ...
Hot-plate model of stars Test 2 & grades • Public viewing sessions
... Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram H-R plotted luminosity vs. surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram H-R plotted luminosity vs. surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. ...
Star - Danielle`s science9 weebly
... Objects in the sky have fascinated humans throughout time. The explanations of how these celestial objects came to be are even more fascinating. Ancients developed their ideas of what was happening in the sky and explained it with their frame of reference. The constellations were patterns that seeme ...
... Objects in the sky have fascinated humans throughout time. The explanations of how these celestial objects came to be are even more fascinating. Ancients developed their ideas of what was happening in the sky and explained it with their frame of reference. The constellations were patterns that seeme ...
CONSTELLATIONS
... Winter Solstice / December 21 Vernal Equinox / March 21 Summer Solstice / June 21 Autumnal Equinox / September 21 THE PLANETS As you have seen, the dashed line on the planisphere marks the ecliptic. As our Earth moves around in its orbit, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets also appear along this lin ...
... Winter Solstice / December 21 Vernal Equinox / March 21 Summer Solstice / June 21 Autumnal Equinox / September 21 THE PLANETS As you have seen, the dashed line on the planisphere marks the ecliptic. As our Earth moves around in its orbit, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets also appear along this lin ...
Document
... in launching 1922–1923, of proved conclusively Telescope honor of Hubble) in 1990 onpart the Space that these (named nebulaeinwere much too distant to be of Shuttle, in were, low-Earth orbit taking photos of the Milkyremains Way and in fact, entire galaxies outside astronomical observations. our own ...
... in launching 1922–1923, of proved conclusively Telescope honor of Hubble) in 1990 onpart the Space that these (named nebulaeinwere much too distant to be of Shuttle, in were, low-Earth orbit taking photos of the Milkyremains Way and in fact, entire galaxies outside astronomical observations. our own ...
File
... • Two types of supernovae: 1. Type I: hydrogen poor, formed from the detonation of a carbon white dwarf 2. Type II: hydrogen rich, formed by the implosion-explosion of the core of a massive star (core-collapse supernova) ...
... • Two types of supernovae: 1. Type I: hydrogen poor, formed from the detonation of a carbon white dwarf 2. Type II: hydrogen rich, formed by the implosion-explosion of the core of a massive star (core-collapse supernova) ...
Photographs of a Star Cluster Spectra of a Star Cluster
... Star Q would appear red and Star T would appear blue. Star Q would appear blue and Star T would appear red. Both stars would appear the same color. The color of the stars cannot be determined from this information. ...
... Star Q would appear red and Star T would appear blue. Star Q would appear blue and Star T would appear red. Both stars would appear the same color. The color of the stars cannot be determined from this information. ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17)
... Stefan’s law (see ch.3 if you have forgotten): The rate of emission of energy of all light, at all wavelengths, by an object, by a unit area of its surface, per unit time (e.g. per second), E, is proportional to the fourth power of the surface (photospheric) temperature T4. Writing L for the luminos ...
... Stefan’s law (see ch.3 if you have forgotten): The rate of emission of energy of all light, at all wavelengths, by an object, by a unit area of its surface, per unit time (e.g. per second), E, is proportional to the fourth power of the surface (photospheric) temperature T4. Writing L for the luminos ...
Stellar Evolution – Life of a Star
... continue after Fe, internal mass increases, thermal imbalance occurs and the star collapses. The pressure causes the protons and electrons to become neutrons. The additional neutrons are ...
... continue after Fe, internal mass increases, thermal imbalance occurs and the star collapses. The pressure causes the protons and electrons to become neutrons. The additional neutrons are ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.