I. Layers of the Sun
... Flares: Violent eruptions shooting outward from the sun at high speeds. ...
... Flares: Violent eruptions shooting outward from the sun at high speeds. ...
The Death of Stars
... 1. The lowest-mass stars cannot become giants because a. they do not contain helium. b. they rotate too slowly. c. they cannot heat their centers hot enough. d. they contain strong magnetic fields. e. they never use up their hydrogen. 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medi ...
... 1. The lowest-mass stars cannot become giants because a. they do not contain helium. b. they rotate too slowly. c. they cannot heat their centers hot enough. d. they contain strong magnetic fields. e. they never use up their hydrogen. 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medi ...
First Light for May, 2001 - South Bay Astronomical Society
... Harbor City – On Saturday evening, August 27th, just before sunset, I got my binoculars out and walked down to the corner where I had a good view to the west. Without any good marks to use for sighting, it took me a while to find the small bright speck of Venus in the fading sunset. It took about an ...
... Harbor City – On Saturday evening, August 27th, just before sunset, I got my binoculars out and walked down to the corner where I had a good view to the west. Without any good marks to use for sighting, it took me a while to find the small bright speck of Venus in the fading sunset. It took about an ...
S E N S ` 2 0 0 6
... solar nebula is contracted to a flattened disk with rotation. The composition of planets themselves are dependent on their location. Near the protostar, ices will be vaporized by the high temperature and a rocky solid portion will remain. However, the ice covered dust grains are able to sustain furt ...
... solar nebula is contracted to a flattened disk with rotation. The composition of planets themselves are dependent on their location. Near the protostar, ices will be vaporized by the high temperature and a rocky solid portion will remain. However, the ice covered dust grains are able to sustain furt ...
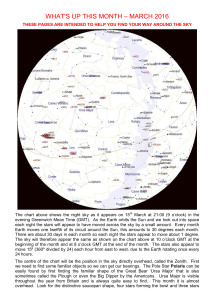
what`s up this month – march 2016
... The night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 on 15 thMarch The chart above shows the night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 (9 o’clock in the evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an ...
... The night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 on 15 thMarch The chart above shows the night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 (9 o’clock in the evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an ...
apparent magnitude
... An invisible phantom lurks in space, ready to swallow everything that comes near it. Once trapped in its grasp, matter is stretched, torn, and crushed into oblivion. Does this tale sound like a horror story? Guess again! Scientists call this phantom a black hole. As a star runs out of fuel, it cools ...
... An invisible phantom lurks in space, ready to swallow everything that comes near it. Once trapped in its grasp, matter is stretched, torn, and crushed into oblivion. Does this tale sound like a horror story? Guess again! Scientists call this phantom a black hole. As a star runs out of fuel, it cools ...
exam1guide - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Scientific Methods: the definition and purpose of science, scientific accuracy, the natural world, “the” scientific method, hypothesis, theory and accepted theory, definitions of meter, liter, kilogram. The Universe: molecules, atoms, protons, neutrons, electrons, quarks, elements, isotopes, weak nu ...
... Scientific Methods: the definition and purpose of science, scientific accuracy, the natural world, “the” scientific method, hypothesis, theory and accepted theory, definitions of meter, liter, kilogram. The Universe: molecules, atoms, protons, neutrons, electrons, quarks, elements, isotopes, weak nu ...
Seasonal Visibility of Stars, and Visibility of Planets in 2014
... star will appear about 11° east of that planet? (8) In which constellation will the Full Moon appear on the night of April 3-4, 2015? Which bright star will appear about 10° east of the Moon that night? As the Earth rotates on its axis, the star will appear to follow the Moon across the sky that nig ...
... star will appear about 11° east of that planet? (8) In which constellation will the Full Moon appear on the night of April 3-4, 2015? Which bright star will appear about 10° east of the Moon that night? As the Earth rotates on its axis, the star will appear to follow the Moon across the sky that nig ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1
... Polaris is almost exactly above the pole of Earth’s rotational axis, so Polaris moves only slightly around the pole during one rotation of Earth. ...
... Polaris is almost exactly above the pole of Earth’s rotational axis, so Polaris moves only slightly around the pole during one rotation of Earth. ...
Introduction To Astronomy
... • Because Illumination of moon tells us Earth-Sun orientation, we can use it as a clock!! * 1) Find the terminator 2) Match it to an hour between 6PM-6AM according to the diagram on the right 3) Is it lit from West or ...
... • Because Illumination of moon tells us Earth-Sun orientation, we can use it as a clock!! * 1) Find the terminator 2) Match it to an hour between 6PM-6AM according to the diagram on the right 3) Is it lit from West or ...
Why Star Positions?
... was used to make clear that what is being measured is the motion originating from the star itself, and not that due to other effects like the Earth’s rotation. It also reminds us that what has been measured is an angular shift over time, and not the actual speed of the star through space. The two ar ...
... was used to make clear that what is being measured is the motion originating from the star itself, and not that due to other effects like the Earth’s rotation. It also reminds us that what has been measured is an angular shift over time, and not the actual speed of the star through space. The two ar ...
Stars - cayugascience
... data forms a distinct band that stretches from the top left of the diagram to the bottom right. This is called the main sequence. The Sun is a main sequence star. These stars are thought to be in the stable main part of their life cycle. They have evolved to this stage since formation but will gradu ...
... data forms a distinct band that stretches from the top left of the diagram to the bottom right. This is called the main sequence. The Sun is a main sequence star. These stars are thought to be in the stable main part of their life cycle. They have evolved to this stage since formation but will gradu ...
21structure1i
... More than 2000 galaxies and covers 100 square degrees in the sky 15 Mpc or 50 million light years away Centered on giant ellipticals larger than the entire local group Local group is a poor cluster, Virgo is a rich one ...
... More than 2000 galaxies and covers 100 square degrees in the sky 15 Mpc or 50 million light years away Centered on giant ellipticals larger than the entire local group Local group is a poor cluster, Virgo is a rich one ...
AST1001.ch2
... The brightest stars in a constellation… • all belong to the same star cluster. • all lie at about the same distance from Earth. • may actually be quite far away from each other. ...
... The brightest stars in a constellation… • all belong to the same star cluster. • all lie at about the same distance from Earth. • may actually be quite far away from each other. ...
upperMS - CWRU Astronomy
... 60% of a star over 15% of its main sequence lifetime If 40% of the remaining mass can be removed in the final 85% of the lifetime, then it’s a nitrogen rich star It’s ok to lose this much mass and still be OB, but if it loses much more, then its luminosity will be too low Often present in young clus ...
... 60% of a star over 15% of its main sequence lifetime If 40% of the remaining mass can be removed in the final 85% of the lifetime, then it’s a nitrogen rich star It’s ok to lose this much mass and still be OB, but if it loses much more, then its luminosity will be too low Often present in young clus ...
Lecture 7 February 9
... x-ray photon at 100A than the infrared light photons emitted by every living human? (Assuming 10,000nm wavelength of infrared light). • A. Ten times as powerful. • B. A hundred times more powerful. • C. A thousand times more powerful. • D. 1x1012 (a trillion) times more powerful. • E. 1x1015 (a quad ...
... x-ray photon at 100A than the infrared light photons emitted by every living human? (Assuming 10,000nm wavelength of infrared light). • A. Ten times as powerful. • B. A hundred times more powerful. • C. A thousand times more powerful. • D. 1x1012 (a trillion) times more powerful. • E. 1x1015 (a quad ...
Exercises
... i-iii. Answer question (a) iii, iv and v for the dynamical timescale. iv. In stellar evolution models one often assumes that stars evolve quasi-statically, i.e. that the star remains in hydrostatic equilibrium throughout. Why can we make this assumption? v. Rapid changes that are sometimes observed ...
... i-iii. Answer question (a) iii, iv and v for the dynamical timescale. iv. In stellar evolution models one often assumes that stars evolve quasi-statically, i.e. that the star remains in hydrostatic equilibrium throughout. Why can we make this assumption? v. Rapid changes that are sometimes observed ...
Asymptotic Giant Branch
... • Most AGB stars (see later) and obviously also a large fraction of the RGB stars are variable • Variations in brightness, colour, velocity and extension observed • Possibility to „look“ into the stellar interior ...
... • Most AGB stars (see later) and obviously also a large fraction of the RGB stars are variable • Variations in brightness, colour, velocity and extension observed • Possibility to „look“ into the stellar interior ...
WFPC2
... •WFPC 2 was installed during Hubble’s 1st Servicing Mission, in December of 1993 •WFPC 2 replaced the original WFPC, and contained corrective optics to compensate for the spherical aberration caused by the flawed main mirror •WFPC 2 remained in orbit for 15 years, until replaced by WFPC 3 in May of ...
... •WFPC 2 was installed during Hubble’s 1st Servicing Mission, in December of 1993 •WFPC 2 replaced the original WFPC, and contained corrective optics to compensate for the spherical aberration caused by the flawed main mirror •WFPC 2 remained in orbit for 15 years, until replaced by WFPC 3 in May of ...
chap18_f04_probs
... = 1.7 10-24 kilogram / meter3 4/3 R3 = 1.7 10-24 kilogram / meter3 13.51 (6.4 106 meters)3 = 1.7 10-24 kilogram / meter3 1.1 1021 meters3 = 0.0019 kilograms or 1.9 grams (!) A very small mass. PROBLEM 18-10: To ionize interstellar hydrogen, a photon must have a wavelength ...
... = 1.7 10-24 kilogram / meter3 4/3 R3 = 1.7 10-24 kilogram / meter3 13.51 (6.4 106 meters)3 = 1.7 10-24 kilogram / meter3 1.1 1021 meters3 = 0.0019 kilograms or 1.9 grams (!) A very small mass. PROBLEM 18-10: To ionize interstellar hydrogen, a photon must have a wavelength ...
Lecture 10 Spectra of Stars and Binaries
... The Spectral Sequence is a Temperature Sequence • Gross differences among the spectral types are due to differences in Temperature. • ComposiZon differences are minor at best. – Demonstrated by Cecilia Payne‐Gaposhkin in 1920’s ...
... The Spectral Sequence is a Temperature Sequence • Gross differences among the spectral types are due to differences in Temperature. • ComposiZon differences are minor at best. – Demonstrated by Cecilia Payne‐Gaposhkin in 1920’s ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements: How are the lives of stars with
... • Our Goals for Learning • What is a neutron star? • How were neutron stars discovered? • What can happen to a neutron star in a close binary system? ...
... • Our Goals for Learning • What is a neutron star? • How were neutron stars discovered? • What can happen to a neutron star in a close binary system? ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.