Name
... 17) Which two bodies have the strongest attractive force between them? A) Two 1 kg balls that are 1 meter apart. B) Two bodies each with the mass of the Sun that are one light year apart. C) Two bodies each with the mass of the Earth that are 1 AU apart. D) Two bodies each with the mass of Jupiter t ...
... 17) Which two bodies have the strongest attractive force between them? A) Two 1 kg balls that are 1 meter apart. B) Two bodies each with the mass of the Sun that are one light year apart. C) Two bodies each with the mass of the Earth that are 1 AU apart. D) Two bodies each with the mass of Jupiter t ...
galctr
... 32 objects tracked within 1” of Sgr A* Especially interesting stars: SO-2 (orbital period 15 yrs); SO-6 (highly eccentric orbit); SO-16 (periapse 80 AU from Sgr A*) Based on independent orbit solutions, MBH =3.7 106 M (R0/8kpc)3 ...
... 32 objects tracked within 1” of Sgr A* Especially interesting stars: SO-2 (orbital period 15 yrs); SO-6 (highly eccentric orbit); SO-16 (periapse 80 AU from Sgr A*) Based on independent orbit solutions, MBH =3.7 106 M (R0/8kpc)3 ...
Our Galaxy, the Milky Way Galaxy
... The further away a star is, the greater the errors can be when calculating their temperature/color because of the ISM interference The further away a star is, the more reddening occurs o We cannot see past a few thousand light years in the PLANE of the Milky Way Galaxy because of ISM We don’t kn ...
... The further away a star is, the greater the errors can be when calculating their temperature/color because of the ISM interference The further away a star is, the more reddening occurs o We cannot see past a few thousand light years in the PLANE of the Milky Way Galaxy because of ISM We don’t kn ...
Astrophysics - Mr Priest`s Physics Notes
... Infrared astronomers study parts of the infrared spectrum, which consists of electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from just longer than visible light to 1,000 times longer than visible light. Earth’s atmosphere absorbs infrared radiation, so astronomers must collect infrared radiation from ...
... Infrared astronomers study parts of the infrared spectrum, which consists of electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from just longer than visible light to 1,000 times longer than visible light. Earth’s atmosphere absorbs infrared radiation, so astronomers must collect infrared radiation from ...
The star is born
... of the core’s temperature, which in turn leads to an increase in pressure. The star is not in balance. Instead, gravity always stays half a step ahead of the pressure force. This is because energy is leaking out of the star in form of radiation. 2) The accretion disks also contribute to the total lu ...
... of the core’s temperature, which in turn leads to an increase in pressure. The star is not in balance. Instead, gravity always stays half a step ahead of the pressure force. This is because energy is leaking out of the star in form of radiation. 2) The accretion disks also contribute to the total lu ...
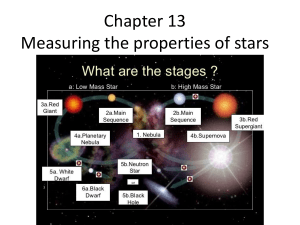
Chapter 13 Measuring the properties of stars
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
Exoplanets for Amateur Astronomers
... (July 7,2005) “…on June 30th, California amateur astronomer Ron Bissinger detected a partial transit of planet HD 149026b. He also detected partial transits during the next two opportunities, allowing him to produce a composite light curve of an entire event. This new find is now the third transitin ...
... (July 7,2005) “…on June 30th, California amateur astronomer Ron Bissinger detected a partial transit of planet HD 149026b. He also detected partial transits during the next two opportunities, allowing him to produce a composite light curve of an entire event. This new find is now the third transitin ...
Activity: Doppler Effect
... • The top panel shows two stars (Blue = “A”; red = “B”) orbiting one another. The green dot represents the Earth. This diagram is NOT TO SCALE. • The bottom panel shows the combined absorption-line spectrum of the stars (with the lines from each star labeled “A” and “B”). A thin "stationary" absorpt ...
... • The top panel shows two stars (Blue = “A”; red = “B”) orbiting one another. The green dot represents the Earth. This diagram is NOT TO SCALE. • The bottom panel shows the combined absorption-line spectrum of the stars (with the lines from each star labeled “A” and “B”). A thin "stationary" absorpt ...
WORD - UWL faculty websites
... The top panel shows two stars (Blue = “A”; red = “B”) orbiting one another. The green dot represents the Earth. This diagram is NOT TO SCALE. The bottom panel shows the combined absorption-line spectrum of the stars (with the lines from each star labeled “A” and “B”). A thin "stationary" absorpt ...
... The top panel shows two stars (Blue = “A”; red = “B”) orbiting one another. The green dot represents the Earth. This diagram is NOT TO SCALE. The bottom panel shows the combined absorption-line spectrum of the stars (with the lines from each star labeled “A” and “B”). A thin "stationary" absorpt ...
No Slide Title
... star formation and there are many bright stars.In the bulge there are many globular clusters. 5.M74-a photogenic spiral galaxy in Pisces.It is about 30 Mly away and has about 1011 stars. This is more or less how the Milky Way must look from outside.Picture taken with the Gemini North telescope on Ma ...
... star formation and there are many bright stars.In the bulge there are many globular clusters. 5.M74-a photogenic spiral galaxy in Pisces.It is about 30 Mly away and has about 1011 stars. This is more or less how the Milky Way must look from outside.Picture taken with the Gemini North telescope on Ma ...
EF Eri: Its White Dwarf Primary and L Dwarf Secondary
... --> Polar or AM Herculis type. These contain no accretion disk. ...
... --> Polar or AM Herculis type. These contain no accretion disk. ...
Document
... The Sun is a star at the center of our Solar System. The Sun will consume the Earth one day. When all the hydrogen has been burned, the Sun will continue for about 130 million more years burning helium. It will expand and engulf Mercury, Venus, and Earth. At that point it will become a Red Gi ...
... The Sun is a star at the center of our Solar System. The Sun will consume the Earth one day. When all the hydrogen has been burned, the Sun will continue for about 130 million more years burning helium. It will expand and engulf Mercury, Venus, and Earth. At that point it will become a Red Gi ...
NCCVT Integrated Fin..
... This portion of the test will be videotaped. For this portion of the test, the examiner will read each question to you. After the question is asked, you will be given the opportunity to either answer it orally or skip it. At the end of the oral portion of the exam, you will be allowed to return to a ...
... This portion of the test will be videotaped. For this portion of the test, the examiner will read each question to you. After the question is asked, you will be given the opportunity to either answer it orally or skip it. At the end of the oral portion of the exam, you will be allowed to return to a ...
Read the information on Hertzsprung
... radiates in one second, but you can think of it as how bright or how dim the star appears. The luminosity scale is a "ratio scale" in which stars are compared to each other based upon a reference (our sun). The horizontal axis represents the star’s surface temperature (not the star’s core temperatur ...
... radiates in one second, but you can think of it as how bright or how dim the star appears. The luminosity scale is a "ratio scale" in which stars are compared to each other based upon a reference (our sun). The horizontal axis represents the star’s surface temperature (not the star’s core temperatur ...
transparencies
... • The frequency of the bursts activity will decrease from a few emissions per 10 years to a few emissions per 100 years • The amplitude should decrease, because the angular velocity is reduced • Both feautures reflect the progressive draining of the energy source wich, in this model, is the Rotation ...
... • The frequency of the bursts activity will decrease from a few emissions per 10 years to a few emissions per 100 years • The amplitude should decrease, because the angular velocity is reduced • Both feautures reflect the progressive draining of the energy source wich, in this model, is the Rotation ...
Section 4 Formation of the Universe Chapter 19
... star late in its life cycle. • In this third stage, a star can become a red giant. As the center of the star shrinks, the atmosphere of the star grows very large and cools to form a red giant or a red supergiant. ...
... star late in its life cycle. • In this third stage, a star can become a red giant. As the center of the star shrinks, the atmosphere of the star grows very large and cools to form a red giant or a red supergiant. ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... differs enormously. We can divide the HRD into four sections, defined by mass ranges within which the evolution is similar (or related). ...
... differs enormously. We can divide the HRD into four sections, defined by mass ranges within which the evolution is similar (or related). ...
Deducing Temperatures and Luminosities of Stars
... – L measures star’s “intrinsic” brightness, rather than “apparent” brightness seen from Earth ...
... – L measures star’s “intrinsic” brightness, rather than “apparent” brightness seen from Earth ...
SC.4.E.5.4,5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Earth & Space
... 2. Why do stars appear to move across the night sky? Answer: The stars appear to move because of Earth’s rotation. Constellations or patterns of stars also change with the seasons because Earth is orbiting around the sun. 3. Why do constellations change with the seasons? Answer: The constellations h ...
... 2. Why do stars appear to move across the night sky? Answer: The stars appear to move because of Earth’s rotation. Constellations or patterns of stars also change with the seasons because Earth is orbiting around the sun. 3. Why do constellations change with the seasons? Answer: The constellations h ...
DSLR Photometry
... Des says in theory it is advisable to also construct master flat field frames in order to remove the effects of the edge distortions of lens. Des has found, however, that the field of view of a DSLR is so wide that a flat field is not required, if you are using high quality lenses, provided the targ ...
... Des says in theory it is advisable to also construct master flat field frames in order to remove the effects of the edge distortions of lens. Des has found, however, that the field of view of a DSLR is so wide that a flat field is not required, if you are using high quality lenses, provided the targ ...
norfolk skies - Norfolk Astronomical Society
... method described above. The nebula forms the apex of a triangle with two stars of equal brightness. Good luck on this difficult object. NGC 2327 - An interesting nebula extending north from a faint double star. It reminds me of the more famous NGC 2261 in Monocerous (Hubble’s Variable Nebula) becaus ...
... method described above. The nebula forms the apex of a triangle with two stars of equal brightness. Good luck on this difficult object. NGC 2327 - An interesting nebula extending north from a faint double star. It reminds me of the more famous NGC 2261 in Monocerous (Hubble’s Variable Nebula) becaus ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.