Answer - Physics@Brock
... Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Examination date: 1 October 2016 Time of Examination: 12:00 – 12:50 ...
... Course: ASTR 1P01, Section 2 Examination date: 1 October 2016 Time of Examination: 12:00 – 12:50 ...
Variable Star Spectroscopy 2008
... rotational) of the objects or the material that they consist of, which can be measured by the red or blue Doppler shift. Here the tiny 50A part of the Vega spectrum containing the Hydrogen alpha line (which is equivalent the resolution achieved by the Star Analyser) is expanded to the full width of ...
... rotational) of the objects or the material that they consist of, which can be measured by the red or blue Doppler shift. Here the tiny 50A part of the Vega spectrum containing the Hydrogen alpha line (which is equivalent the resolution achieved by the Star Analyser) is expanded to the full width of ...
Unpublished draft available in format
... the citation order between, say, several different arrays of stars (by stage - novae, dwarfs, etc.; by spectral type - blue, white, etc.; by other radiation phenomena - variable, quasar, etc.). if any astronomer users of the schedule think that a more helpful citation order could be achieved than th ...
... the citation order between, say, several different arrays of stars (by stage - novae, dwarfs, etc.; by spectral type - blue, white, etc.; by other radiation phenomena - variable, quasar, etc.). if any astronomer users of the schedule think that a more helpful citation order could be achieved than th ...
Volume 1 (Issue 7), July 2012
... release of energy from fusion, as it has ceased), gravity compacts the matter inward until the electrons that compose a white dwarf's atoms, is smashed together. In normal circumstances, identical electrons (those with the same "spin") are not allowed to occupy the same energy level. Since there are ...
... release of energy from fusion, as it has ceased), gravity compacts the matter inward until the electrons that compose a white dwarf's atoms, is smashed together. In normal circumstances, identical electrons (those with the same "spin") are not allowed to occupy the same energy level. Since there are ...
Accretion Disk
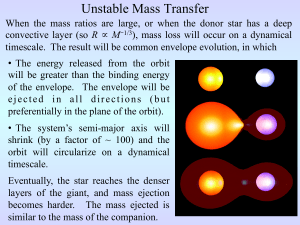
... • Super-Soft X-ray Sources: Probably the result of continuous accretion and fusion of matter onto a white dwarf. • LMXBs (Low-Mass X-ray Binaries): The donor object is a lowmass (convective envelope) star and the accreting object is a neutron star or black hole. Because of the greater potential, ~ ...
... • Super-Soft X-ray Sources: Probably the result of continuous accretion and fusion of matter onto a white dwarf. • LMXBs (Low-Mass X-ray Binaries): The donor object is a lowmass (convective envelope) star and the accreting object is a neutron star or black hole. Because of the greater potential, ~ ...
1_Introduction
... First star to have its parallax angle measured: 61 Cygni (in the year 1838). Parallax angle = 0.287 arcseconds Distance = 1 parsec / 0.287 = 3.48 parsecs ...
... First star to have its parallax angle measured: 61 Cygni (in the year 1838). Parallax angle = 0.287 arcseconds Distance = 1 parsec / 0.287 = 3.48 parsecs ...
ppt - Institute for Astronomy
... stars and brown dwarfs. Some of the remaining gas falls in around these protostars to form circumstellar disks, helping to build up the masses of the protostars. ...
... stars and brown dwarfs. Some of the remaining gas falls in around these protostars to form circumstellar disks, helping to build up the masses of the protostars. ...
Telling Time by the Sun - Cornell Astronomy
... 2. The Earth revolves around the Sun once every ~365 days (year). 3. The Moon revolves around the Earth once every ~28 days (month). 4. The orbital planes of objects in the Solar System lie (almost) in the equatorial planes of the major body (but not quite; there are a few exceptions) 5. The Earth’s ...
... 2. The Earth revolves around the Sun once every ~365 days (year). 3. The Moon revolves around the Earth once every ~28 days (month). 4. The orbital planes of objects in the Solar System lie (almost) in the equatorial planes of the major body (but not quite; there are a few exceptions) 5. The Earth’s ...
Lecture 39
... principal emissions (color), called, most stars fall along an array defining the “main sequence”. Since wavelength is inversely related to the fourth power of temperature, this correlation means that hot stars give off more energy than cooler stars. Mass is also related to temperature for main seque ...
... principal emissions (color), called, most stars fall along an array defining the “main sequence”. Since wavelength is inversely related to the fourth power of temperature, this correlation means that hot stars give off more energy than cooler stars. Mass is also related to temperature for main seque ...
Lecture 10
... Disks are ubiquitous to nature. (disks of Be stars form from stellar winds, not accretion disks) ...
... Disks are ubiquitous to nature. (disks of Be stars form from stellar winds, not accretion disks) ...
PowerPoint - Division for Planetary Sciences
... • If the planet rotates faster it would have two sunrises & sunsets each day Which Sun rose first could vary. The Suns would move at different and variable rates through the sky. They would sometimes eclipse each other. There would still be night. Discoveries in Planetary Science ...
... • If the planet rotates faster it would have two sunrises & sunsets each day Which Sun rose first could vary. The Suns would move at different and variable rates through the sky. They would sometimes eclipse each other. There would still be night. Discoveries in Planetary Science ...
Review Sheet and Study Hints - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... Draw and label it Include magnitude (M), luminosity (L/Lo), color or color index (B-V), spectral type OBAFGKM and temperature. Point towards increasing luminosity, temperature, radius, redder color. Point arrows towards increasing main-sequence-radius and m.-s.-mass. Evolutionary Tracks draw ...
... Draw and label it Include magnitude (M), luminosity (L/Lo), color or color index (B-V), spectral type OBAFGKM and temperature. Point towards increasing luminosity, temperature, radius, redder color. Point arrows towards increasing main-sequence-radius and m.-s.-mass. Evolutionary Tracks draw ...
Night Sky
... The only thing the stars in Orion have in common is that they lie in approximately the same direction from Earth. ...
... The only thing the stars in Orion have in common is that they lie in approximately the same direction from Earth. ...
File
... The gravitational force on Earth changes. The universe appears to be expanding. The Jovian planets are aligned with the Sun. Galaxies are becoming more numerous. ...
... The gravitational force on Earth changes. The universe appears to be expanding. The Jovian planets are aligned with the Sun. Galaxies are becoming more numerous. ...
PC3692: Physics of Stellar Structure (and Evolution)
... Fig. 7.— HR diagram for 41453 nearby stars with accurate distance measured by the Hipparcos satellite. The horizontal axis is the V − I colour index, while the vertical axis is the absolute magnitude in the Hipparcos passband. The I-band is a filter centred around 8000Å. One striking feature is the ...
... Fig. 7.— HR diagram for 41453 nearby stars with accurate distance measured by the Hipparcos satellite. The horizontal axis is the V − I colour index, while the vertical axis is the absolute magnitude in the Hipparcos passband. The I-band is a filter centred around 8000Å. One striking feature is the ...
Assignment 10
... b. long jets of radio emissions c. two lobes (regions of radio emission) that can be quite far from the galaxy's center d. all of the above e. none of the above ____ 24. A friend of yours who is a science fiction fan hears you talk about the fact that astronomers now believe that the mechanism for ...
... b. long jets of radio emissions c. two lobes (regions of radio emission) that can be quite far from the galaxy's center d. all of the above e. none of the above ____ 24. A friend of yours who is a science fiction fan hears you talk about the fact that astronomers now believe that the mechanism for ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.