2 Galaxy morphology and classification
... or more. The spheroid is thought to be among the first stellar components to form. The stellar halo is a di↵use, roughly spherical, system of stars and globular clusters that surrounds most large galaxies. It is comprised mostly of old, metal-poor, stars. The halo has little or no net angular moment ...
... or more. The spheroid is thought to be among the first stellar components to form. The stellar halo is a di↵use, roughly spherical, system of stars and globular clusters that surrounds most large galaxies. It is comprised mostly of old, metal-poor, stars. The halo has little or no net angular moment ...
EARTH REVOVLES ROUND THE SUN IN A SPIRAL PATH
... and shifts towards the red end of the visible spectrum, which is called the red shift. The Scientist E. Hubble, who studied the light emitted by different galaxies and observed the red shift in the spectrum of light coming far from galaxies. This proves that galaxies are moving away from one another ...
... and shifts towards the red end of the visible spectrum, which is called the red shift. The Scientist E. Hubble, who studied the light emitted by different galaxies and observed the red shift in the spectrum of light coming far from galaxies. This proves that galaxies are moving away from one another ...
Unit 11: Stellar Evolution
... The core temperature becomes so high that the nuclei themselves are broken down into individual protons and neutrons absorbing still more energy. At still-higher temperatures, electrons and protons combine to produce neutrons and neutrinos; again, an energy-absorbing reaction. Because the number of ...
... The core temperature becomes so high that the nuclei themselves are broken down into individual protons and neutrons absorbing still more energy. At still-higher temperatures, electrons and protons combine to produce neutrons and neutrinos; again, an energy-absorbing reaction. Because the number of ...
The Sun has been stable for 4 billion years.
... The radius, temperature, luminosity, and lifetime of a main sequence star are determined by its mass. Pressure balance A star is an immense ball of gas. The pressure at any point is equal to the total weight of the gas above it. Because a star is so massive, the gas inside it is very compressed and ...
... The radius, temperature, luminosity, and lifetime of a main sequence star are determined by its mass. Pressure balance A star is an immense ball of gas. The pressure at any point is equal to the total weight of the gas above it. Because a star is so massive, the gas inside it is very compressed and ...
Review questions with attached answer key
... 1. A camera was placed in an open field and pointed toward the northern sky. The lens of the camera was left open for a certain amount of time. The result is shown in the photograph below. The angle of the arc through which two of the stars appeared to move during this time exposure is shown. ...
... 1. A camera was placed in an open field and pointed toward the northern sky. The lens of the camera was left open for a certain amount of time. The result is shown in the photograph below. The angle of the arc through which two of the stars appeared to move during this time exposure is shown. ...
Stellar Evolution
... quickly on the main sequence and die explosively as supernovae. The shock sent out by such a supernova can excite further star formation. I. The Free-Fall Stage of Stellar Birth. 1. As a portion of a GMC begins to contract, cloud complexes with masses greater than ∼ 50 M become unstable and fragmen ...
... quickly on the main sequence and die explosively as supernovae. The shock sent out by such a supernova can excite further star formation. I. The Free-Fall Stage of Stellar Birth. 1. As a portion of a GMC begins to contract, cloud complexes with masses greater than ∼ 50 M become unstable and fragmen ...
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
... They found a relation between the MV and (V-I), that was then used to derive MV for those stars which did not have a distance estimate. Most stars are MS dwarfs and hence such a relation is not very surprising. Contamination due to giant stars starts to become important at (V-I) ~ 2.3, which for dwa ...
... They found a relation between the MV and (V-I), that was then used to derive MV for those stars which did not have a distance estimate. Most stars are MS dwarfs and hence such a relation is not very surprising. Contamination due to giant stars starts to become important at (V-I) ~ 2.3, which for dwa ...
Astronomical Filters on Skynet Telescopes
... energy into a number of "lines" that can be sampled with narrow-band filters, namely filters that transmit only a small range of wavelengths. These filters are named after the line that is sampled, e.g. Halpha, OIII, SII. A gas cloud can be ionized by the ultraviolet radiation given off by a neighbo ...
... energy into a number of "lines" that can be sampled with narrow-band filters, namely filters that transmit only a small range of wavelengths. These filters are named after the line that is sampled, e.g. Halpha, OIII, SII. A gas cloud can be ionized by the ultraviolet radiation given off by a neighbo ...
DO IT YOURSELF SIMPLE TEMPLATE FORMAT
... orbits by gravity. Name all of the objects you can think of that orbit the Sun. Write down what you know about each one. This activity will look specifically at planets, which are relatively large objects circling the Sun. You will run a model and be able to change a planet's mass, velocity and posi ...
... orbits by gravity. Name all of the objects you can think of that orbit the Sun. Write down what you know about each one. This activity will look specifically at planets, which are relatively large objects circling the Sun. You will run a model and be able to change a planet's mass, velocity and posi ...
H Exhaustion - University of Arizona
... • Sun will spend ~4 Gyr moving from core H exhaustion to RGB - 40% of total H consumption and lifetime ...
... • Sun will spend ~4 Gyr moving from core H exhaustion to RGB - 40% of total H consumption and lifetime ...
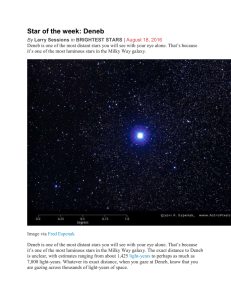
in BRIGHTEST STARS
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
Gone in a flash: supernovae in the survey era
... and a very slowly evolving light curve. The lack normal SNe, the SLSNe-I have hydrogen-free (Cooke et al. 2012). It should also be possible to of an apparent host galaxy meant that even the optical spectra, and may possibly be related study them in large numbers using projects such redshift was unkn ...
... and a very slowly evolving light curve. The lack normal SNe, the SLSNe-I have hydrogen-free (Cooke et al. 2012). It should also be possible to of an apparent host galaxy meant that even the optical spectra, and may possibly be related study them in large numbers using projects such redshift was unkn ...
Testing
... A. Blown out of galaxy B. Still recycling just like now C. Locked into white dwarfs and low-mass stars ...
... A. Blown out of galaxy B. Still recycling just like now C. Locked into white dwarfs and low-mass stars ...
Nonlinear Tides in Exoplanet Host Stars - CIERA
... If decay times really short, you should be able to measure the frequency dependence of the tidal Q from the observed distribution. ...
... If decay times really short, you should be able to measure the frequency dependence of the tidal Q from the observed distribution. ...
celestial clock - the sun, the moon, and the stars
... adding the extra month, there are still 4.24 days lost. So, every twenty one years, another month is added. By this method the difference every twenty one years is only 0.08 day. It would take 7,434 years before such a lunar calendar would be one whole day off true. That is a very accurate clock! TH ...
... adding the extra month, there are still 4.24 days lost. So, every twenty one years, another month is added. By this method the difference every twenty one years is only 0.08 day. It would take 7,434 years before such a lunar calendar would be one whole day off true. That is a very accurate clock! TH ...
The Far Future Sun and the Ultimate Fates of
... The maximum temperature a planet achieves depends on its distance from the Sun and the maximum luminosity of the Sun - both of these, in turn, depend on the mass loss that ends the AGB. ...
... The maximum temperature a planet achieves depends on its distance from the Sun and the maximum luminosity of the Sun - both of these, in turn, depend on the mass loss that ends the AGB. ...
ASTRONOMY 113 Laboratory Lab 5: Spectral Classification of the
... Subaru to the Japanese; you might recognize the pattern of the brightest stars as the logo on Subaru automobiles.) The cluster also contains several hundred much fainter stars. Since the Pleiades are close to the Sun (≈120 pc distant), even these fainter stars are accessible to Earth-based telescope ...
... Subaru to the Japanese; you might recognize the pattern of the brightest stars as the logo on Subaru automobiles.) The cluster also contains several hundred much fainter stars. Since the Pleiades are close to the Sun (≈120 pc distant), even these fainter stars are accessible to Earth-based telescope ...
Extragalactic Distances from Planetary Nebulae
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
Theme 7.2 -- The Complete Solar System
... Not only is the earth's atmosphere secondary, but it has also undergone considerable evolution over the billions of years since the planet itself formed. One of the main reasons for this, of course, is the emergence of life, several billion years ago, which led to the absorption of carbon dioxide fr ...
... Not only is the earth's atmosphere secondary, but it has also undergone considerable evolution over the billions of years since the planet itself formed. One of the main reasons for this, of course, is the emergence of life, several billion years ago, which led to the absorption of carbon dioxide fr ...
Chapter 16 Lives of the Stars (Low Mass)
... from the solar wind, so Earth might lose momentum and its orbit shrink from drag. In this graph, the orbit of Earth is the dotted line and drag is taken into account. When the Sun reaches a certain size, Earth is pulled into the Sun. ...
... from the solar wind, so Earth might lose momentum and its orbit shrink from drag. In this graph, the orbit of Earth is the dotted line and drag is taken into account. When the Sun reaches a certain size, Earth is pulled into the Sun. ...
Description
... There is no pre-requisite on the science background. Some multimedia online materials will be incorporated into our study. A non-graded pre-test will be required from each student at the beginning of the course. Course Objectives ...
... There is no pre-requisite on the science background. Some multimedia online materials will be incorporated into our study. A non-graded pre-test will be required from each student at the beginning of the course. Course Objectives ...
A new Cosmos – a novel Physics
... 16th century: If the earth rotates around the sun, which is located in the center of the universe, then one should observe a small variation of the stars’ positions during the year. Such an effect, called parallax, could not be observed by 16th century astronomers. From this it was correctly conclud ...
... 16th century: If the earth rotates around the sun, which is located in the center of the universe, then one should observe a small variation of the stars’ positions during the year. Such an effect, called parallax, could not be observed by 16th century astronomers. From this it was correctly conclud ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.