Section 15
... R 3κ We’ve assumed constant κ in the atmosphere of a given protostar, but the opacity will vary with time for any one object, and between different objects, according to their individual photospheric pressures and temperatures. We adopt the usual power-law dependence of opacity, κ = κ0 P a T b , ...
... R 3κ We’ve assumed constant κ in the atmosphere of a given protostar, but the opacity will vary with time for any one object, and between different objects, according to their individual photospheric pressures and temperatures. We adopt the usual power-law dependence of opacity, κ = κ0 P a T b , ...
Lecture 6: Multiple stars
... exactly where we see an excess. This is at least some evidence that our understanding of core collapse is correct. (A similar argument can be applied from disc fragmentation which should occur only at >100au.) ...
... exactly where we see an excess. This is at least some evidence that our understanding of core collapse is correct. (A similar argument can be applied from disc fragmentation which should occur only at >100au.) ...
Part II: Ideas in Conflict.
... • The bright region in the center of galaxy M87 has stars and gas held in tight orbits by a black hole. • Doppler shift measurements allow us to calculate the central mass of the galaxy. • M87’s bright nucleus (inset) is only about the size of the solar system and pulls on the nearby stars with so m ...
... • The bright region in the center of galaxy M87 has stars and gas held in tight orbits by a black hole. • Doppler shift measurements allow us to calculate the central mass of the galaxy. • M87’s bright nucleus (inset) is only about the size of the solar system and pulls on the nearby stars with so m ...
Complete the following review packet!
... 60. Compare the temperature of a red giant to the temperature of a white dwarf. 61. Position #2 on the diagram represents what stage of a star’s life? ...
... 60. Compare the temperature of a red giant to the temperature of a white dwarf. 61. Position #2 on the diagram represents what stage of a star’s life? ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
PHYS3380_102815_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... XZ Tauri - young system with two stars orbiting each other - separated by about 6 billion kilometers (about the distance from the Sun to Pluto) - shows bubble of hot, glowing gas extending nearly 96 billion kilometers from this young star system. - appears much broader than the narrow jets seen in o ...
... XZ Tauri - young system with two stars orbiting each other - separated by about 6 billion kilometers (about the distance from the Sun to Pluto) - shows bubble of hot, glowing gas extending nearly 96 billion kilometers from this young star system. - appears much broader than the narrow jets seen in o ...
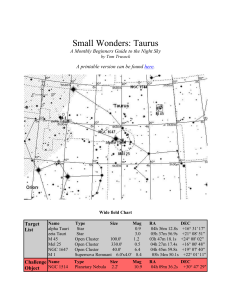
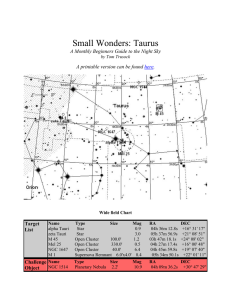
Small Wonders: Taurus
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
The Distances to the Stars
... Note that measuring such motions requires the existence of a fixed reference frame, provided by celestial objects whose motions are not detectable. Usually very distant stars will do, but for the most accurate astrometry astronomers use distant galaxies or quasars as reference points. Two thousand y ...
... Note that measuring such motions requires the existence of a fixed reference frame, provided by celestial objects whose motions are not detectable. Usually very distant stars will do, but for the most accurate astrometry astronomers use distant galaxies or quasars as reference points. Two thousand y ...
Planet-finding Activity Guide How do we find planets around other
... Definition: Parallax is the apparent change in the star’s position caused by the Earth’s annual motion around the Sun. Definition: The star’s proper motion is the actual path it takes in space as it moves through the galaxy. ...
... Definition: Parallax is the apparent change in the star’s position caused by the Earth’s annual motion around the Sun. Definition: The star’s proper motion is the actual path it takes in space as it moves through the galaxy. ...
Summer 2004 ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Professor: ER Capriotti Sample Questions
... A. believed Mars would look faintest when at opposition. B. used uniform circular motion to explain planetary motion. C. believed the Earth went around the Sun. D. made very accurate predictions of planetary motion. E. believed the Sun went around the Earth. 22. The Copernican universe has in order ...
... A. believed Mars would look faintest when at opposition. B. used uniform circular motion to explain planetary motion. C. believed the Earth went around the Sun. D. made very accurate predictions of planetary motion. E. believed the Sun went around the Earth. 22. The Copernican universe has in order ...
27A Stars and Spectroscopy
... So far, the light sources you observed contain only a few elements. However, stars’ atmospheres contain many elements and are much more complex. 1. Use the spectrometer to analyze the light of our closest star—the Sun. Do not point the spectrometer directly at the Sun. Instead, point it at reflected ...
... So far, the light sources you observed contain only a few elements. However, stars’ atmospheres contain many elements and are much more complex. 1. Use the spectrometer to analyze the light of our closest star—the Sun. Do not point the spectrometer directly at the Sun. Instead, point it at reflected ...
The Milky Way
... Flocculent (woolly) galaxies also have spiral patterns, but no dominant pair of spiral arms ...
... Flocculent (woolly) galaxies also have spiral patterns, but no dominant pair of spiral arms ...
with answers
... ● the Sun increases in luminosity as it ages and “moves up” the H-R diagram. This is an increase of approximately 1% every 110 million years (Schroder & Connon Smith 2008), which would lead to a higher rate of hydrogen loss. ○ “The helium "ashes" left behind are denser than hydrogen, so the hydrogen ...
... ● the Sun increases in luminosity as it ages and “moves up” the H-R diagram. This is an increase of approximately 1% every 110 million years (Schroder & Connon Smith 2008), which would lead to a higher rate of hydrogen loss. ○ “The helium "ashes" left behind are denser than hydrogen, so the hydrogen ...
Chapter 26: Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Stars
... brightness to the expected brightness. This is like asking, ―How far away would the Sun have to be to appear this dim?‖ ...
... brightness to the expected brightness. This is like asking, ―How far away would the Sun have to be to appear this dim?‖ ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... stars well away from the Milky Way, evidence arose that all was not well with this model. Spectroscopy [1] had given astronomers of the late nineteenth and early twentieth century a powerful tool – the Doppler effect. This is a basic property of light waves (see also the article on Doppler effect in ...
... stars well away from the Milky Way, evidence arose that all was not well with this model. Spectroscopy [1] had given astronomers of the late nineteenth and early twentieth century a powerful tool – the Doppler effect. This is a basic property of light waves (see also the article on Doppler effect in ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
... Table 6: Fill in the empty fields above. 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of al ...
... Table 6: Fill in the empty fields above. 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of al ...
The University of Sydney Page
... so the star becomes enormously large and red: a red giant. Stars like the Sun can increase in radius by a factor of 10–100, while more massive stars can increase by a factor of 1000. ...
... so the star becomes enormously large and red: a red giant. Stars like the Sun can increase in radius by a factor of 10–100, while more massive stars can increase by a factor of 1000. ...
M101: The Pinwheel Galaxy
... M101: The Pinwheel Galaxy A Star-studded Galaxy Giant spiral galaxies were not built in a day. Construction on these mammoth objects, like Messier 101 (M101) shown in this Hubble Space Telescope image, lasted billions of years. This photograph of M101, nicknamed the Pinwheel Galaxy, showcases a spir ...
... M101: The Pinwheel Galaxy A Star-studded Galaxy Giant spiral galaxies were not built in a day. Construction on these mammoth objects, like Messier 101 (M101) shown in this Hubble Space Telescope image, lasted billions of years. This photograph of M101, nicknamed the Pinwheel Galaxy, showcases a spir ...
Apr 2017 - Bays Mountain Park
... Her presentation was entitled, “A Trip Through Poland’s Scientific History.” A conference in Warsaw gave Robin and Adam the opportunity to explore Poland and visit many sites ...
... Her presentation was entitled, “A Trip Through Poland’s Scientific History.” A conference in Warsaw gave Robin and Adam the opportunity to explore Poland and visit many sites ...
bildsten
... Highlights so Far • Acoustic waves seen in nearly all evolved stars with amplitudes of 3-200 parts per million. • Measured frequency spacing and maximum observed frequency give R, M and D for >10,000 stars across the galaxy. Great test for GAIA and new galactic science enabled. • Useful diagnostics ...
... Highlights so Far • Acoustic waves seen in nearly all evolved stars with amplitudes of 3-200 parts per million. • Measured frequency spacing and maximum observed frequency give R, M and D for >10,000 stars across the galaxy. Great test for GAIA and new galactic science enabled. • Useful diagnostics ...
X-ray binaries
... Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classifiction is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a source is unidentified in optics, but exhibits T ...
... Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classifiction is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a source is unidentified in optics, but exhibits T ...
Stellar Structure and Evolution II
... more rapid fusion, making those stars both more luminous and shorter-lived • Stars of lower mass have cooler cores and slower fusion rates, giving them smaller luminosities and longer lifetimes ...
... more rapid fusion, making those stars both more luminous and shorter-lived • Stars of lower mass have cooler cores and slower fusion rates, giving them smaller luminosities and longer lifetimes ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.