Earth and Environmental Science Review
... 109. What is the composition of the sun? 110. What are the characteristics of sunspots? 111. What is the source of the sun’s energy? 112. Describe the relationship of color and temperature of stars. 113. What do light-years measure? 114. What characteristic of a star does magnitude describe? 115. De ...
... 109. What is the composition of the sun? 110. What are the characteristics of sunspots? 111. What is the source of the sun’s energy? 112. Describe the relationship of color and temperature of stars. 113. What do light-years measure? 114. What characteristic of a star does magnitude describe? 115. De ...
Study Guide for Earth Science Final
... 109. What is the composition of the sun? 110. What are the characteristics of sunspots? 111. What is the source of the sun’s energy? 112. Describe the relationship of color and temperature of stars. 113. What do light-years measure? 114. What characteristic of a star does magnitude describe? 115. De ...
... 109. What is the composition of the sun? 110. What are the characteristics of sunspots? 111. What is the source of the sun’s energy? 112. Describe the relationship of color and temperature of stars. 113. What do light-years measure? 114. What characteristic of a star does magnitude describe? 115. De ...
exo planets
... On April 17, 2014, NASA made an historic announcement – the first discovery of an Earth-sized planet orbiting in the Goldilocks Zone of another star. The planet may have the potential for life to exist. The world circles a red dwarf star in the constellation of Cygnus and is about 500 light years aw ...
... On April 17, 2014, NASA made an historic announcement – the first discovery of an Earth-sized planet orbiting in the Goldilocks Zone of another star. The planet may have the potential for life to exist. The world circles a red dwarf star in the constellation of Cygnus and is about 500 light years aw ...
X-rays - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... • There is a variety of line profile morphologies seen in Chandra observations of massive stars, indicating that a surprising variety of high-energy physical processes are occurring in this class of stars. •Normal massive stars with strong radiation-driven winds have x-ray emitting plasma distribute ...
... • There is a variety of line profile morphologies seen in Chandra observations of massive stars, indicating that a surprising variety of high-energy physical processes are occurring in this class of stars. •Normal massive stars with strong radiation-driven winds have x-ray emitting plasma distribute ...
Dark Matter - UW - Laramie, Wyoming | University of Wyoming
... bend the light from a more distant galaxy. Image of the galaxy is strongly distorted into arcs. ...
... bend the light from a more distant galaxy. Image of the galaxy is strongly distorted into arcs. ...
here - Atomki
... The Virial theorem can be obtain by multiplying the hydrostatic equil. Eqn. (2) by the volume (V=4/3 πr3) and integrate over the total mass, M: ∫V dP/dm = - 1/3 ∫(Gm/r) dm = 1/3 Egrav The left hand-side term is related to the internal energy, E int. After some algebra, one obtains for an ideal mono- ...
... The Virial theorem can be obtain by multiplying the hydrostatic equil. Eqn. (2) by the volume (V=4/3 πr3) and integrate over the total mass, M: ∫V dP/dm = - 1/3 ∫(Gm/r) dm = 1/3 Egrav The left hand-side term is related to the internal energy, E int. After some algebra, one obtains for an ideal mono- ...
Document
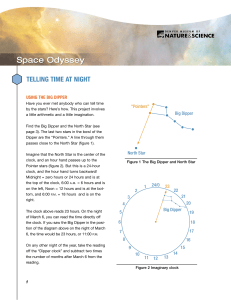
... Cassiopeia has five stars that form a shape like a "W" on its side. The North Star is straight out from Cassiopeia's center star. ...
... Cassiopeia has five stars that form a shape like a "W" on its side. The North Star is straight out from Cassiopeia's center star. ...
space - Net Start Class
... Key Concept 1: A star is a large ball of gas that generates its own energy by fusing hydrogen atoms to make helium. It is held together by its own gravity. This process emits a tremendous amount of energy, and some of the energy is in the form of light. Stars come in a variety of sizes and compositi ...
... Key Concept 1: A star is a large ball of gas that generates its own energy by fusing hydrogen atoms to make helium. It is held together by its own gravity. This process emits a tremendous amount of energy, and some of the energy is in the form of light. Stars come in a variety of sizes and compositi ...
81 KB - CSIRO Publishing
... We note that tidal dwarf galaxies, that form out of the collapse of disk material in a tidal tail after a merger, are not expected to contain much dark matter (Barnes & Hernquist 1992; Gentile et al. 2007). Thus if any of the dSph galaxies which surround the Milky Way in a disk of satellites (Metz e ...
... We note that tidal dwarf galaxies, that form out of the collapse of disk material in a tidal tail after a merger, are not expected to contain much dark matter (Barnes & Hernquist 1992; Gentile et al. 2007). Thus if any of the dSph galaxies which surround the Milky Way in a disk of satellites (Metz e ...
The Sun The Sun
... The Sun is a star located at the center of our Solar System. This huge, spinning ball of hot, glowing gases lights up Earth and provides us with heat. The Sun has a north and south pole, just like Earth, and rotates on its axis. A planet’s distance from the Sun, along with its atmosphere, determines ...
... The Sun is a star located at the center of our Solar System. This huge, spinning ball of hot, glowing gases lights up Earth and provides us with heat. The Sun has a north and south pole, just like Earth, and rotates on its axis. A planet’s distance from the Sun, along with its atmosphere, determines ...
Sky Maps Teacher`s Guide - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Clusters of stars are found all over the sky. There are two types of clusters. Open clusters tend to be young stars that formed from the same nebula cloud. Open clusters often contain between 250-600 stars. Globular clusters are much larger clusters of hundreds of thousands and sometimes millions of ...
... Clusters of stars are found all over the sky. There are two types of clusters. Open clusters tend to be young stars that formed from the same nebula cloud. Open clusters often contain between 250-600 stars. Globular clusters are much larger clusters of hundreds of thousands and sometimes millions of ...
MS PowerPoint - National Schools` Observatory
... If there were no external factors at play, the absorption spectrum of a star would show very thin spectral line features at the exact wavelengths corresponding to amount of energy transferred to the atom when one of its electrons has been excited to a higher energy level. ...
... If there were no external factors at play, the absorption spectrum of a star would show very thin spectral line features at the exact wavelengths corresponding to amount of energy transferred to the atom when one of its electrons has been excited to a higher energy level. ...
Part1
... Relation to Millimeter and IR astronomy: o The infrared continuum is a key tracer of the distribution of dust and the dust-to-gas ratio is intimately related to heavy element enrichment (e.g., you need dust to see IR!). o Along similar lines, millimeter line tracers of the ISM are key to robustly me ...
... Relation to Millimeter and IR astronomy: o The infrared continuum is a key tracer of the distribution of dust and the dust-to-gas ratio is intimately related to heavy element enrichment (e.g., you need dust to see IR!). o Along similar lines, millimeter line tracers of the ISM are key to robustly me ...
The James Webb Space Telescope: A Vision for the Future
... Longer wavelengths of light, such as infrared, result in lower-resolution images. To improve image sharpness, astronomers need a large mirror to collect a lot of light. The bigger the mirror, the more light it can collect. Webb will be able to see back to a few hundred million years after the Big Ba ...
... Longer wavelengths of light, such as infrared, result in lower-resolution images. To improve image sharpness, astronomers need a large mirror to collect a lot of light. The bigger the mirror, the more light it can collect. Webb will be able to see back to a few hundred million years after the Big Ba ...
24.1 Hubble`s Galaxy Classification
... for the spirals in Figure 24.2, except that now the spiral arms begin at either end of a bar through the galactic center. In frame (c), the bright star is a foreground object in our own Galaxy; the object at top center is another galaxy that is probably interacting with NGC 6872. ...
... for the spirals in Figure 24.2, except that now the spiral arms begin at either end of a bar through the galactic center. In frame (c), the bright star is a foreground object in our own Galaxy; the object at top center is another galaxy that is probably interacting with NGC 6872. ...
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
... What have we learned? • How big is the universe? – The observable universe is 14 billion light-years in radius (no it is considerably bigger and depends upon the expansion rate and the history of the expansion rate which has changed) and contains over 100 billion galaxies with a total number of sta ...
... What have we learned? • How big is the universe? – The observable universe is 14 billion light-years in radius (no it is considerably bigger and depends upon the expansion rate and the history of the expansion rate which has changed) and contains over 100 billion galaxies with a total number of sta ...
starwalk2 manual en - Vito Technology Inc.
... If your device has built-in compass tilt your device and the Star Spotter function will be activated. Star Walk™2 uses the digital compass to learn which way you are looking. A live representation of what you see in the sky will appear on your display and the sky will start following your movements ...
... If your device has built-in compass tilt your device and the Star Spotter function will be activated. Star Walk™2 uses the digital compass to learn which way you are looking. A live representation of what you see in the sky will appear on your display and the sky will start following your movements ...
Sky-High 2013 - Irish Astronomical Society
... couple of drawbacks. Each chart is correct for only one time on a given night, say 10 p.m. If you are observing two hours later you would need the following month's chart. These charts also show the planets visible for a particular month, so they can be confusing unless you tippex them out. When lea ...
... couple of drawbacks. Each chart is correct for only one time on a given night, say 10 p.m. If you are observing two hours later you would need the following month's chart. These charts also show the planets visible for a particular month, so they can be confusing unless you tippex them out. When lea ...
the astrolabe - IREM Aix
... Front of the astrolabe 1. Matrix or mother: a disc of brass or bronze 10 to 50 cm in diameter which accommodates the various parts of the instrument. 2. Tympanum: an engraved plate that is placed on the mother. Designed for a given latitude, certain astrolabes possess several of these. 3. Spider (or ...
... Front of the astrolabe 1. Matrix or mother: a disc of brass or bronze 10 to 50 cm in diameter which accommodates the various parts of the instrument. 2. Tympanum: an engraved plate that is placed on the mother. Designed for a given latitude, certain astrolabes possess several of these. 3. Spider (or ...
Document
... Venn & Lambert (2008) have argued that this may not be the case. Peculiar stars such as post AGB stars and l Boo stars have iron abundances as low as [Fe/H] ~ –5. These are thought to be due to the separation of gas and dust beyond the stellar surface followed by an accretion of the dust-depleted g ...
... Venn & Lambert (2008) have argued that this may not be the case. Peculiar stars such as post AGB stars and l Boo stars have iron abundances as low as [Fe/H] ~ –5. These are thought to be due to the separation of gas and dust beyond the stellar surface followed by an accretion of the dust-depleted g ...
Life Stages of High
... • After core helium fusion stops, He fuses into carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer. • This double-shell-burning stage never reaches equilibrium—the fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. • With each spike, con ...
... • After core helium fusion stops, He fuses into carbon in a shell around the carbon core, and H fuses to He in a shell around the helium layer. • This double-shell-burning stage never reaches equilibrium—the fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses. • With each spike, con ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.