Main Types of Galaxies
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
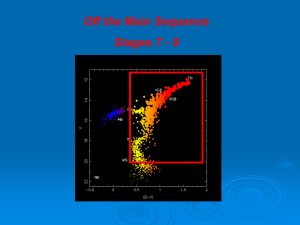
Common Stages 7 to 9
... While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
... While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
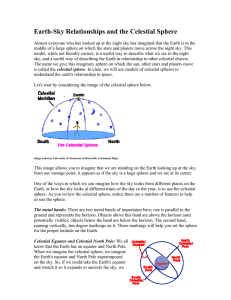
Earth-Sky Relationships and the Celestial Sphere
... NCP. (By the way, Polaris is not the brightest star in the night sky, contrary to much popular belief. It is approximately the 20th brightest star in the night sky, but is the brightest star near the NCP.) Lines of Celestial Latitude and Longitude: If you look carefully at the celestial spheres, you ...
... NCP. (By the way, Polaris is not the brightest star in the night sky, contrary to much popular belief. It is approximately the 20th brightest star in the night sky, but is the brightest star near the NCP.) Lines of Celestial Latitude and Longitude: If you look carefully at the celestial spheres, you ...
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) Consists of the sun (a typical star
... a planet or other body was probably swept out of the forming planetary system by the intense stellar winds that are observed around all young stars. (See Fig. 15.4) The whole process probably took 10 to100 million years, although this is wildly uncertain. The main thing that is certain is that the f ...
... a planet or other body was probably swept out of the forming planetary system by the intense stellar winds that are observed around all young stars. (See Fig. 15.4) The whole process probably took 10 to100 million years, although this is wildly uncertain. The main thing that is certain is that the f ...
Talk - The Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics
... • Temperature vs. luminosity is “H-R Diagram” – After discoverers, Hertzsprung and Russell – Temp on x-axis, luminosity on y – For us, color on x-axis, magnitude on y ...
... • Temperature vs. luminosity is “H-R Diagram” – After discoverers, Hertzsprung and Russell – Temp on x-axis, luminosity on y – For us, color on x-axis, magnitude on y ...
INTERSTELLAR MedLab
... Reflection – dust clouds that reflect (scatter) a star’s light to us Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. These are also where molecules are likely to be found. During the course of this laboratory exercise, you will study th ...
... Reflection – dust clouds that reflect (scatter) a star’s light to us Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. These are also where molecules are likely to be found. During the course of this laboratory exercise, you will study th ...
Small star patterns for telescopes and binoculars Demelza Ramakers
... (that forms the golf ball) within 1/3e distance from this line (count from Almach). Circle is 4 degrees ...
... (that forms the golf ball) within 1/3e distance from this line (count from Almach). Circle is 4 degrees ...
View the presentation slides
... Fortunately, optical techniques are capable of exquisite accuracy. Let’s look at some data. This is a “Jupiter” (M ~ 0.96 MJ) orbiting a “Sol” (M = 0.88 MS). The orbital period is 9 years (Jupiter’s is 12), because the orbit is a bit smaller (4.2 AU instead of 5.2). This is how astronomers 60 light- ...
... Fortunately, optical techniques are capable of exquisite accuracy. Let’s look at some data. This is a “Jupiter” (M ~ 0.96 MJ) orbiting a “Sol” (M = 0.88 MS). The orbital period is 9 years (Jupiter’s is 12), because the orbit is a bit smaller (4.2 AU instead of 5.2). This is how astronomers 60 light- ...
15 May 2011 Gas Giants, (Rigel, Betelgeuse, Aldebaran etc
... which the mass MESCM which is represented by the glue holding together the neutronic mass (neutron and protons inside the star) undergoes transformation-degradation into MHeat (and eventual dissipation when MHeat reaches the surface of the Star). Nevertheless gravity is at the base of every transfor ...
... which the mass MESCM which is represented by the glue holding together the neutronic mass (neutron and protons inside the star) undergoes transformation-degradation into MHeat (and eventual dissipation when MHeat reaches the surface of the Star). Nevertheless gravity is at the base of every transfor ...
Solar System Formation
... IRAS (1983): The Turning Point IRAS excesses at 12, 25, and 60 microns over stellar photosphere Aumann (1985) gives nice statistics of IRAS catalog: 756 sources corresponding to stars 504 dwarfs or subgiants 267 have 12 and 25 micron fluxes 36 have 12, 25, and 60 micron fluxes 12 are “Vega-like” wi ...
... IRAS (1983): The Turning Point IRAS excesses at 12, 25, and 60 microns over stellar photosphere Aumann (1985) gives nice statistics of IRAS catalog: 756 sources corresponding to stars 504 dwarfs or subgiants 267 have 12 and 25 micron fluxes 36 have 12, 25, and 60 micron fluxes 12 are “Vega-like” wi ...
InternetArchive_ManagingBornDigitalData
... Q2: Find all galaxies with blue surface brightness between and 23 and 25 mag per square arcseconds, and -100.75.
Q4: Find galaxies with an isophotal su ...
... Q2: Find all galaxies with blue surface brightness between and 23 and 25 mag per square arcseconds, and -10
ADAS Simple Guide to Telescope Instrumentation and Operation
... upside-down, of the object observed. The eyepiece — which, consisting of a converging lens with short focal length, is actually a magnifying lens — enlarges the image formed by the objective. The image observed is however upside-down, so that the Keplerian telescope, at least for terrestrial use, mu ...
... upside-down, of the object observed. The eyepiece — which, consisting of a converging lens with short focal length, is actually a magnifying lens — enlarges the image formed by the objective. The image observed is however upside-down, so that the Keplerian telescope, at least for terrestrial use, mu ...
Inside the Rainbow
... Later, a scientist named Joseph Van Fraunhofer discovered that if you pass the light from a glowing object through a special lens (a spectrometer), you will get a rainbow or spectrum that has tiny amounts of some of the colors missing. Instead of a complete rainbow, you’ll see places with tiny black ...
... Later, a scientist named Joseph Van Fraunhofer discovered that if you pass the light from a glowing object through a special lens (a spectrometer), you will get a rainbow or spectrum that has tiny amounts of some of the colors missing. Instead of a complete rainbow, you’ll see places with tiny black ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... Search data set for interesting individual objects that represent rare classes of objects. ...
... Search data set for interesting individual objects that represent rare classes of objects. ...
Pressure Calculation of a Constant Density Star in the Dynamic
... Apart from the solar type constant density star two more stars were used so that the dynamic gravity effects could be calculated on the central pressure. These were neutron stars [9] and we must say these stars can not be really thought as constant density stars to really fit a simple constant densi ...
... Apart from the solar type constant density star two more stars were used so that the dynamic gravity effects could be calculated on the central pressure. These were neutron stars [9] and we must say these stars can not be really thought as constant density stars to really fit a simple constant densi ...
Celestial Sphere
... Jupiter: no restrictions on distance from Sun in sky Saturn: no restrictions on distance from Sun in sky ...
... Jupiter: no restrictions on distance from Sun in sky Saturn: no restrictions on distance from Sun in sky ...
Computer Modeling the Line of Sight Column Densities of Polars
... strong magnetic field around 100 million times earths magnetic field. The plasma is not allowed to form an accretion disc because it follows the magnetic field lines. The stream takes a more direct path toward the white dwarf. The high speeds of the impacting particles creates a hot spot ...
... strong magnetic field around 100 million times earths magnetic field. The plasma is not allowed to form an accretion disc because it follows the magnetic field lines. The stream takes a more direct path toward the white dwarf. The high speeds of the impacting particles creates a hot spot ...
Cepheid Calibration
... Henrietta Leavitt: Timeless Contributions Sometimes a great advance in science is achieved through selfless work performed by a modest person not striving for recognition on the stage of history. Such was the contribution of Henrietta Leavitt, one of many female “computers” working at the Harvard C ...
... Henrietta Leavitt: Timeless Contributions Sometimes a great advance in science is achieved through selfless work performed by a modest person not striving for recognition on the stage of history. Such was the contribution of Henrietta Leavitt, one of many female “computers” working at the Harvard C ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 37-
... So in the 1800s astronomers wanted to name stars all the way down to about 9 th magnitude. Now, that’s about 300,000 stars. That’s a lot of stars. And so you can’t really give them nice names like Rigel. You can’t use Greek letters. And even if you start using numbers, it’s just gonna be a big numbe ...
... So in the 1800s astronomers wanted to name stars all the way down to about 9 th magnitude. Now, that’s about 300,000 stars. That’s a lot of stars. And so you can’t really give them nice names like Rigel. You can’t use Greek letters. And even if you start using numbers, it’s just gonna be a big numbe ...
April 2016 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... Although the North Celestial Pole seems, to us, permanently located close to Polaris it does actually move over long periods of time. Earth has a wobble on its axis rather like a spinning top. The axis moving axis traces out a circle in the northern sky every 26,000 years. This wobble on the axis is ...
... Although the North Celestial Pole seems, to us, permanently located close to Polaris it does actually move over long periods of time. Earth has a wobble on its axis rather like a spinning top. The axis moving axis traces out a circle in the northern sky every 26,000 years. This wobble on the axis is ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.