The first carbon-enhanced metal-poor star found in the Sculptor
... first stellar generation is still highly debated. In contrast to the Galactic halo, not many CEMP stars have been found in the dwarf spheroidal galaxies around the Milky Way. Here we present detailed abundances from ESO VLT/UVES high-resolution spectroscopy for ET0097, the first CEMP star found in t ...
... first stellar generation is still highly debated. In contrast to the Galactic halo, not many CEMP stars have been found in the dwarf spheroidal galaxies around the Milky Way. Here we present detailed abundances from ESO VLT/UVES high-resolution spectroscopy for ET0097, the first CEMP star found in t ...
The surface composition of Beta Pictoris
... Why does the signature of accretion not show up in the surface composition of β Pic? Accretion of gas depleted in refractory elements is thought to be responsible for the deficiency pattern of λ Boo stars, and direct evidence for the presence of CS matter is accumulating (e.g. Stürenburg 1993; HRH9 ...
... Why does the signature of accretion not show up in the surface composition of β Pic? Accretion of gas depleted in refractory elements is thought to be responsible for the deficiency pattern of λ Boo stars, and direct evidence for the presence of CS matter is accumulating (e.g. Stürenburg 1993; HRH9 ...
The Moon, Planets and Polaris
... Polaris is slightly different because it leads directly to a latitude. It is also one of the few bodies that we can use as a steering aid at night. Compass checking is an interesting and easy exercise. The problem is that, when out of sight of land, we have few ways to check the accuracy of the stee ...
... Polaris is slightly different because it leads directly to a latitude. It is also one of the few bodies that we can use as a steering aid at night. Compass checking is an interesting and easy exercise. The problem is that, when out of sight of land, we have few ways to check the accuracy of the stee ...
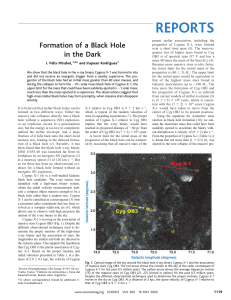
Star formation in a galactic outflow
... predict that such massive galactic outflows may ignite star formation within the outflow itself711 . This star-formation mode, in which stars form with high radial velocities, could contribute to the morphological evolution of galaxies12, to the evolution in size and velocity dispersion of the spher ...
... predict that such massive galactic outflows may ignite star formation within the outflow itself711 . This star-formation mode, in which stars form with high radial velocities, could contribute to the morphological evolution of galaxies12, to the evolution in size and velocity dispersion of the spher ...
Parallax
... 3. The smallest parallax angle that can be accurately measured from the ground is 0.01 arc seconds. If the angle is smaller than 0.01 arcseconds we do not have a protractor good enough to measure the angle. You measure a star to have a parallax angle of 0.01 arc seconds. How far away is that star i ...
... 3. The smallest parallax angle that can be accurately measured from the ground is 0.01 arc seconds. If the angle is smaller than 0.01 arcseconds we do not have a protractor good enough to measure the angle. You measure a star to have a parallax angle of 0.01 arc seconds. How far away is that star i ...
Planets Orbiting the Sun and Other Stars - Beck-Shop
... terrestrial planets and the region of the major planets. There are three main groupings, the Atens, the Amors and the Apollos. They are distinguished by their orbits. The Atens have a semi-major axis a < 1 AU and an aphelion greater than 0.988. This means they cross the orbit of Venus but lie within ...
... terrestrial planets and the region of the major planets. There are three main groupings, the Atens, the Amors and the Apollos. They are distinguished by their orbits. The Atens have a semi-major axis a < 1 AU and an aphelion greater than 0.988. This means they cross the orbit of Venus but lie within ...
Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 13 Neutron Stars
... Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
A spectroscopic investigation of the O
... 2. Observations and binary criteria Deriving the binary fraction of a given population requires an intense survey of the stars but also a good time sampling to constrain the short- as well as the long-period systems. This monitoring has to be as homogeneous as possible because combining data from th ...
... 2. Observations and binary criteria Deriving the binary fraction of a given population requires an intense survey of the stars but also a good time sampling to constrain the short- as well as the long-period systems. This monitoring has to be as homogeneous as possible because combining data from th ...
Nebula
... Originally nebula was a general name for any extended astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way (some examples of the older usage survive; for example, the Andromeda Galaxy was referred to as the Andromeda Nebula before galaxies were discovered by Edwin Hubble). ...
... Originally nebula was a general name for any extended astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way (some examples of the older usage survive; for example, the Andromeda Galaxy was referred to as the Andromeda Nebula before galaxies were discovered by Edwin Hubble). ...
Galaxies
... universes possible? Would they look like ours (have the same physics)? • Cosmological Principle - the Universe appears the same from any location - Isotropic - no center -no edge • Indication that the Universe is finite in time, is expanding, and it has been ever since it was created in the Big Ba ...
... universes possible? Would they look like ours (have the same physics)? • Cosmological Principle - the Universe appears the same from any location - Isotropic - no center -no edge • Indication that the Universe is finite in time, is expanding, and it has been ever since it was created in the Big Ba ...
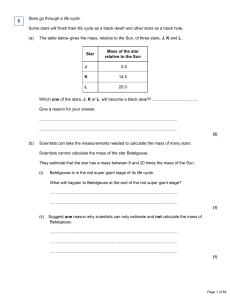
Stars go through a life cycle. Some stars will finish their life cycle as
... Why does lowering the control rods reduce the amount of energy released each second from the nuclear fuel? ...
... Why does lowering the control rods reduce the amount of energy released each second from the nuclear fuel? ...
Stellar evolution - Statistical Physics Group
... I n practice there are only a very limited number of really reliable mass determinations and almost all of these are for main-sequence stars. For only a few nearby giant stars has (viii) stellar radius been observed either by interferometric techniques or by occultation observations in an eclipsing ...
... I n practice there are only a very limited number of really reliable mass determinations and almost all of these are for main-sequence stars. For only a few nearby giant stars has (viii) stellar radius been observed either by interferometric techniques or by occultation observations in an eclipsing ...
Star formation rates and efficiencies in the Galactic Centre
... light measurements (e.g. infrared and free-free emission; refer to section 3.2.2 and 3.2.3). Our proximity to the centre of the Galaxy means that it is the only extreme environment in which comparison between YSO counting and integrated light measurement methods can be made. However, compared to the ...
... light measurements (e.g. infrared and free-free emission; refer to section 3.2.2 and 3.2.3). Our proximity to the centre of the Galaxy means that it is the only extreme environment in which comparison between YSO counting and integrated light measurement methods can be made. However, compared to the ...
The physics of white dwarfs
... place in the strong gravitational fields of the degenerate dwarfs, with heavier elements sinking below the atmospheric layers and the hydrogen floating up to the stellar surface. The estimated timescale for this process appears short enough to give rapid element separation in the high gravity fields ...
... place in the strong gravitational fields of the degenerate dwarfs, with heavier elements sinking below the atmospheric layers and the hydrogen floating up to the stellar surface. The estimated timescale for this process appears short enough to give rapid element separation in the high gravity fields ...
A Search for Exozodiacal Dust and Faint Companions near Sirius
... detected photometrically by spatially resolving the critical regions less than 10 AU from nearby stars. Coronagraphic images can also reveal faint companions to nearby stars. Such companions can go undetected by radial velocity surveys because of their small masses or long orbital periods. Both Siri ...
... detected photometrically by spatially resolving the critical regions less than 10 AU from nearby stars. Coronagraphic images can also reveal faint companions to nearby stars. Such companions can go undetected by radial velocity surveys because of their small masses or long orbital periods. Both Siri ...
NSDL_WS_1_Astonomy
... Astronomy is a dynamic science. New discoveries add to our knowledge of the universe and our own solar system. • New images brought to use by the Hubble Space Telescope show that star formation is more complex and violent than anyone had believed. • Supersonic jets of particles and dense clots of d ...
... Astronomy is a dynamic science. New discoveries add to our knowledge of the universe and our own solar system. • New images brought to use by the Hubble Space Telescope show that star formation is more complex and violent than anyone had believed. • Supersonic jets of particles and dense clots of d ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.