Chapter 15
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
class 1,F10
... We are on a planet, orbiting a star, in a galaxy (which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster) • How did we come to be? • How can we know what the universe was like in the past? • Can we see the entire universe? ...
... We are on a planet, orbiting a star, in a galaxy (which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster) • How did we come to be? • How can we know what the universe was like in the past? • Can we see the entire universe? ...
Measuring Starlight Deflection during the 2017 Eclipse: Repeating
... All previous eclipse experiments required imaging the same star field six months before or after the eclipse, in order to determine the un-deflected star positions to sub-arcsecond accuracy. Parallax was not important, since the geometry of the sun and the earth was the same. This was one of the mos ...
... All previous eclipse experiments required imaging the same star field six months before or after the eclipse, in order to determine the un-deflected star positions to sub-arcsecond accuracy. Parallax was not important, since the geometry of the sun and the earth was the same. This was one of the mos ...
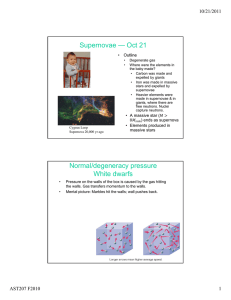
Supernovae — Oct 21 10/21/2011 • Outline
... Pressure on the walls of the box is caused by the gas hitting the walls. Gas transfers momentum to the walls. Mental picture: Marbles hit the walls; wall pushes back. ...
... Pressure on the walls of the box is caused by the gas hitting the walls. Gas transfers momentum to the walls. Mental picture: Marbles hit the walls; wall pushes back. ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... AST1100 Lecture Notes 22: The end state of stars We will continue the discussion on stellar evolution from lecture 20. The star has reached the asymptotic giant branch having a radius of up to 1000 times the original radius. The core consists of carbon and oxygen but the temperature is not high enou ...
... AST1100 Lecture Notes 22: The end state of stars We will continue the discussion on stellar evolution from lecture 20. The star has reached the asymptotic giant branch having a radius of up to 1000 times the original radius. The core consists of carbon and oxygen but the temperature is not high enou ...
ppt document
... position. The North Star is directly above the North Pole. So we give the North Star a declination of +90o (just like the North pole has a latitude of 90o North). The positions of the sky directly over the equator have a declination of 0o just like the equator has a latitude of 0o. Anything that is ...
... position. The North Star is directly above the North Pole. So we give the North Star a declination of +90o (just like the North pole has a latitude of 90o North). The positions of the sky directly over the equator have a declination of 0o just like the equator has a latitude of 0o. Anything that is ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... AST1100 Lecture Notes 22: The end state of stars We will continue the discussion on stellar evolution from lecture 20. The star has reached the asymptotic giant branch having a radius of up to 1000 times the original radius. The core consists of carbon and oxygen but the temperature is not high enou ...
... AST1100 Lecture Notes 22: The end state of stars We will continue the discussion on stellar evolution from lecture 20. The star has reached the asymptotic giant branch having a radius of up to 1000 times the original radius. The core consists of carbon and oxygen but the temperature is not high enou ...
1-structure-of-the-universe-and-the-big-bang
... the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red shift of light from galaxies moving away from Earth led to the theory of an expanding universe. This expansion implies that the universe was ...
... the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red shift of light from galaxies moving away from Earth led to the theory of an expanding universe. This expansion implies that the universe was ...
Solutions for Midterm
... gibbous, be sure to indicate whether it is wanning or waxing. New or Wanning Crescent. A hint from class: our originally scheduled night lab on Friday 10/18 was a lunar eclipse, and hence a fu ...
... gibbous, be sure to indicate whether it is wanning or waxing. New or Wanning Crescent. A hint from class: our originally scheduled night lab on Friday 10/18 was a lunar eclipse, and hence a fu ...
NAME: SECTION: Mon Tue Wed Thu ASTRONOMY LAB Stellarium
... millennium by millennium, in what year (3010, 4010,…) does Vega get closest to the NCP? Next millennium when Vega is closest to the NCP: ____________________________ …and the subsequent millennium when Vega is again closest to the NCP: _______________ Difference, in years, between those two closest ...
... millennium by millennium, in what year (3010, 4010,…) does Vega get closest to the NCP? Next millennium when Vega is closest to the NCP: ____________________________ …and the subsequent millennium when Vega is again closest to the NCP: _______________ Difference, in years, between those two closest ...
Explores Angular Size - Chandra X
... how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need to know is how far away the object is from us. The moon is 324,000 kilometers away, and Venus is about 40 million kilometers away from Earth at its closest distance. The f ...
... how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need to know is how far away the object is from us. The moon is 324,000 kilometers away, and Venus is about 40 million kilometers away from Earth at its closest distance. The f ...
ASTR 1120-001 Final Examination Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
... Ultraviolet, X-rays, visible, infrared, radio X-rays, visible, ultraviolet, infrared, radio Ultraviolet, X-rays, visible, radio, infrared X-rays, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, radio Radio, infrared, visible, X-rays, ultraviolet ...
... Ultraviolet, X-rays, visible, infrared, radio X-rays, visible, ultraviolet, infrared, radio Ultraviolet, X-rays, visible, radio, infrared X-rays, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, radio Radio, infrared, visible, X-rays, ultraviolet ...
starwalk2 manual en - Vito Technology Inc.
... Search allows you to find any star, constellation, Solar system body (the planets, the Sun, the Moon), Deep Space object or satellite, meteor showers, dwarf planets, asteroids and comets. Information icon appears in middle of the bottom part of the screen when you select any celestial body on the sc ...
... Search allows you to find any star, constellation, Solar system body (the planets, the Sun, the Moon), Deep Space object or satellite, meteor showers, dwarf planets, asteroids and comets. Information icon appears in middle of the bottom part of the screen when you select any celestial body on the sc ...
No Slide Title
... very stable pulsation modes. The presence of a planet will be revealed in anomalous timings, just as with pulsar planets ...
... very stable pulsation modes. The presence of a planet will be revealed in anomalous timings, just as with pulsar planets ...
Starspots (AIP – Klaus G
... Magnetic fields likely play an important role in almost any astrophysical target, from the early Universe to the Sun, Earth, and its environment. While numerical 3-D MHD simulations became more and more sophisticated in the previous years, magnetic-field observations are still extremely rare (except ...
... Magnetic fields likely play an important role in almost any astrophysical target, from the early Universe to the Sun, Earth, and its environment. While numerical 3-D MHD simulations became more and more sophisticated in the previous years, magnetic-field observations are still extremely rare (except ...
Black-Body SNR Formulation of Astronomical Camera
... where m is the brightness magnitude assigned to a star observed from Earth, f (·) is the mean spectral flux density at top of Earth’s atmosphere averaged over a defined band and Q(·) is the normalizing constant for that band [8]. We will not go into more details about astronomical magnitude systems ...
... where m is the brightness magnitude assigned to a star observed from Earth, f (·) is the mean spectral flux density at top of Earth’s atmosphere averaged over a defined band and Q(·) is the normalizing constant for that band [8]. We will not go into more details about astronomical magnitude systems ...
CONSTELLATION POWER POINT PROJECT
... In the Greek legend, the Taurus is a disguise that Zeus uses to get what he wants. On this occasion, Zeus had fallen in love with Europa, the daughter of King Agenor. He transformed himself into a white bull that was so gentle, they felt no fear. As Europa and her maidens began to strongly trust the ...
... In the Greek legend, the Taurus is a disguise that Zeus uses to get what he wants. On this occasion, Zeus had fallen in love with Europa, the daughter of King Agenor. He transformed himself into a white bull that was so gentle, they felt no fear. As Europa and her maidens began to strongly trust the ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.