SELF-REFLECTIVE MACHINE LEARNING
... One can measure the ability of self-reflection by comparing the output of the selfreflective model the learner has acquired with the actual output of the learner for a given set of inputs. While this criterion may seem self-centred, and not measuring the learner’s ability to learn about its environm ...
... One can measure the ability of self-reflection by comparing the output of the selfreflective model the learner has acquired with the actual output of the learner for a given set of inputs. While this criterion may seem self-centred, and not measuring the learner’s ability to learn about its environm ...
How Much AI Does a Cognitive Science Major Need to Know?
... So where does that leave us? How much AI does a cognitive science major need to know? One point to makeimmediately is that cognitive scientists need to have a good understanding of computation in general. If one of the fundamental claims of cognitive science is that the mind is somehowcomputational, ...
... So where does that leave us? How much AI does a cognitive science major need to know? One point to makeimmediately is that cognitive scientists need to have a good understanding of computation in general. If one of the fundamental claims of cognitive science is that the mind is somehowcomputational, ...
The challenge of complexity for cognitive systems
... this issue), Polyscheme (see Kurup et al., this issue). Cognitive architectures offer the advantage that all models share the same general assumptions and constraints which makes it easier to compare concurring models in the same domain. On the other hand, a cognitive architecture restricts the algo ...
... this issue), Polyscheme (see Kurup et al., this issue). Cognitive architectures offer the advantage that all models share the same general assumptions and constraints which makes it easier to compare concurring models in the same domain. On the other hand, a cognitive architecture restricts the algo ...
Lecture Notes CS405 Introduction to AI What is Artificial Intelligence
... 6. Modeling Human Performance. As described earlier, machine intelligence need not pattern itself after human intelligence. Indeed, many AI programs are engineered to solve useful problems without regard for their similarities to human mental architecture. These systems give us another benchmark to ...
... 6. Modeling Human Performance. As described earlier, machine intelligence need not pattern itself after human intelligence. Indeed, many AI programs are engineered to solve useful problems without regard for their similarities to human mental architecture. These systems give us another benchmark to ...
Apprenticeship Scheduling for Human
... much to be desired. As such, we need to develop a technique that scales beyond the one-expert, one-apprentice model. In my thesis, I propose a technique, which I call “apprenticeship scheduling”, to capture this domain knowledge in the form of a scheduling policy and scale the power of the expert be ...
... much to be desired. As such, we need to develop a technique that scales beyond the one-expert, one-apprentice model. In my thesis, I propose a technique, which I call “apprenticeship scheduling”, to capture this domain knowledge in the form of a scheduling policy and scale the power of the expert be ...
agents - psu-is101
... you begin your analysis, you tell the DSS, using the user interface management component, which model (in the model management component) to use on what information (in the data management component). The model requests the information from the data management component, analyzes it and sends the re ...
... you begin your analysis, you tell the DSS, using the user interface management component, which model (in the model management component) to use on what information (in the data management component). The model requests the information from the data management component, analyzes it and sends the re ...
Cognitive Neuropsychology and Computational Cognitive Science
... “IF...THEN...” production rule, though no rules exist and a single network can embody many rules • Trained to associate particular outputs with particular inputs by ...
... “IF...THEN...” production rule, though no rules exist and a single network can embody many rules • Trained to associate particular outputs with particular inputs by ...
Intelligent Behavior in Humans and Machines
... the complex forms of cognition observed in humans. Some researchers took human intelligence as an inspiration and source of ideas without attempting to model its details. Other researchers, including Herbert Simon and Allen Newell, generally viewed as two of the field’s co-founders, viewed themselve ...
... the complex forms of cognition observed in humans. Some researchers took human intelligence as an inspiration and source of ideas without attempting to model its details. Other researchers, including Herbert Simon and Allen Newell, generally viewed as two of the field’s co-founders, viewed themselve ...
Ethical and Legal issues
... • Artificial intelligence: science of enabling computers to behave intelligently • Knowledge-based system (or expert system): a program which exhibits, within a specific domain, a degree of expertise in problem solving that is comparable with a human expert • expert: person with superior knowledge i ...
... • Artificial intelligence: science of enabling computers to behave intelligently • Knowledge-based system (or expert system): a program which exhibits, within a specific domain, a degree of expertise in problem solving that is comparable with a human expert • expert: person with superior knowledge i ...
Course Wrap-up
... Software is a key and strategic factor in present-day and future technology and it must be dependable as more or less all of our vital functions depend on it. How is dependability assured? Source of errors: hardware, wired/wireless networks, environment, malicious faults. Fault tolerance and redunda ...
... Software is a key and strategic factor in present-day and future technology and it must be dependable as more or less all of our vital functions depend on it. How is dependability assured? Source of errors: hardware, wired/wireless networks, environment, malicious faults. Fault tolerance and redunda ...
Philosophy and History of AI
... • Karel Capek coined the term “robot” (1921) • Isaac Asimov wrote many sf books and essays (I, Robot (1950) introduced the Laws of Robotics – if you haven’t read it, you should!) ...
... • Karel Capek coined the term “robot” (1921) • Isaac Asimov wrote many sf books and essays (I, Robot (1950) introduced the Laws of Robotics – if you haven’t read it, you should!) ...
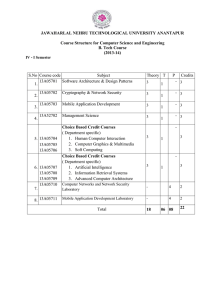
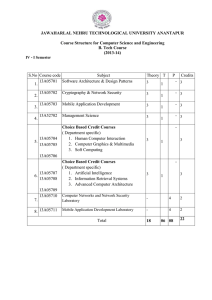
IV-I Sem R15 Syllabus for for the Academic Year 2016
... (13A52702) MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to equip the student the fundamental knowledge of Management Science and its application to effective management of human resources, materials and operations of an organization. It also aims to expose the students abou ...
... (13A52702) MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to equip the student the fundamental knowledge of Management Science and its application to effective management of human resources, materials and operations of an organization. It also aims to expose the students abou ...
Click Here For
... (13A52702) MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to equip the student the fundamental knowledge of Management Science and its application to effective management of human resources, materials and operations of an organization. It also aims to expose the students abou ...
... (13A52702) MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Course Objective: The objectives of this course are to equip the student the fundamental knowledge of Management Science and its application to effective management of human resources, materials and operations of an organization. It also aims to expose the students abou ...
FA08 cs188 lecture 1..
... Predicted by 2000, a 30% chance of fooling a lay person for 5 minutes Anticipated all major arguments against AI in following 50 years Suggested major components of AI: knowledge, reasoning, language understanding, learning ...
... Predicted by 2000, a 30% chance of fooling a lay person for 5 minutes Anticipated all major arguments against AI in following 50 years Suggested major components of AI: knowledge, reasoning, language understanding, learning ...
Artificial Intelligence
... Psychological Perspective • AI is about understanding and modeling human intelligence • Cognitive Science movement (ca. 1950s) – replace stimulus/response model ...
... Psychological Perspective • AI is about understanding and modeling human intelligence • Cognitive Science movement (ca. 1950s) – replace stimulus/response model ...
Artificial Intelligence in Accounting and Auditing:
... "How expert systems can be used to create value?" is the focus of the first section and the only paper in that section. O'Leary finds that expert systems create value for a number of reasons, including reducing the risk of doing business, coordinating multiple actors and through generating economies ...
... "How expert systems can be used to create value?" is the focus of the first section and the only paper in that section. O'Leary finds that expert systems create value for a number of reasons, including reducing the risk of doing business, coordinating multiple actors and through generating economies ...
project
... more natural (close to the sequence when done by human) ? – Declare different salience for rules ...
... more natural (close to the sequence when done by human) ? – Declare different salience for rules ...