The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
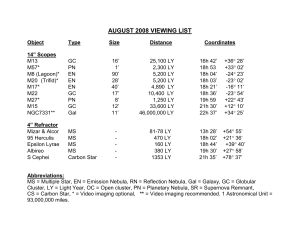
August
... Mizar & Alcor This pair in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh, MAY-jer) is a visual double. However, Mizar takes its place in the celestial hall of fame as the first known Binary Star, one that consists of a pair of gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. Found to be double in 1650, t ...
... Mizar & Alcor This pair in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh, MAY-jer) is a visual double. However, Mizar takes its place in the celestial hall of fame as the first known Binary Star, one that consists of a pair of gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. Found to be double in 1650, t ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • Matter started to “_______” back together • This was due to __________ • The ________, _______ and __________ formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are __________ of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of __________ of stars ...
... • Matter started to “_______” back together • This was due to __________ • The ________, _______ and __________ formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are __________ of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of __________ of stars ...
ภาพนิ่ง 1 - ILM.COM.PK
... peppered with vast volcanoes such as Olympus Mons and rift valleys such as Valles Marineris, shows geological activity that may have persisted until as recently as 2 million years ago. Its red colour comes from iron oxide (rust) in its soil. Mars has two tiny natural satellites (Deimos and Phobos) t ...
... peppered with vast volcanoes such as Olympus Mons and rift valleys such as Valles Marineris, shows geological activity that may have persisted until as recently as 2 million years ago. Its red colour comes from iron oxide (rust) in its soil. Mars has two tiny natural satellites (Deimos and Phobos) t ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... star’s surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of stars in our galaxy are main sequence stars. ...
... star’s surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of stars in our galaxy are main sequence stars. ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... How is energy produced in the Sun’s core? How does the Sun’s magnetic field influence each type of solar activity discussed in class (sunspots, plages, prominences, solar flares, coronal mass ejections)? Why is it important for us to be able to predict such events? What causes the Sun to leave the M ...
... How is energy produced in the Sun’s core? How does the Sun’s magnetic field influence each type of solar activity discussed in class (sunspots, plages, prominences, solar flares, coronal mass ejections)? Why is it important for us to be able to predict such events? What causes the Sun to leave the M ...
Grade 9 Science – Unit 4 Space Quiz
... b. Galaxies are moving away from Earth in all directions at a constant rate c. Remnant heat from the original very hot expansion has been measured d. All of the above 18. What type of star forms after a Supernova explosion? In this star, the centre collapses so that protons and electrons combine to ...
... b. Galaxies are moving away from Earth in all directions at a constant rate c. Remnant heat from the original very hot expansion has been measured d. All of the above 18. What type of star forms after a Supernova explosion? In this star, the centre collapses so that protons and electrons combine to ...
Final Review Sheet - Astronomy Part 2
... 24.What units do I use to describe distance in space? List them from smallest to ...
... 24.What units do I use to describe distance in space? List them from smallest to ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • “Absolute magnitude” is a measure of true brightness. It’s what the apparent magnitude would be if the star were 33 light-years away. Sun’s absolute magnitude is about 5. • The formulas that relate magnitudes to brightnesses (in watts or W/m2) are complicated and not so important. ...
... • “Absolute magnitude” is a measure of true brightness. It’s what the apparent magnitude would be if the star were 33 light-years away. Sun’s absolute magnitude is about 5. • The formulas that relate magnitudes to brightnesses (in watts or W/m2) are complicated and not so important. ...
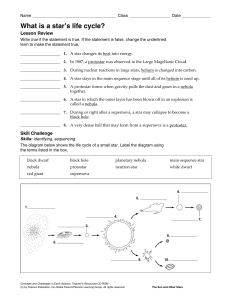
Stellar Evolution
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
PowerPoint Presentation - ASTR498E High energy
... The efficiency of the fusion The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
... The efficiency of the fusion The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
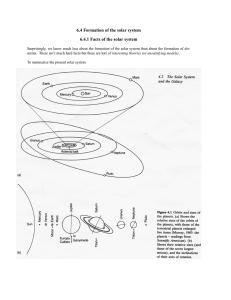
Formation of the solar system
... The result would be a protosun with a disk outside it - several possible mechanisms. This creates a tendency for particles to be drawn by gravity to the midplane. The disk is a turbulent region so that angular momentum can be easily transferred away from the protosun. In the disk, material starts to ...
... The result would be a protosun with a disk outside it - several possible mechanisms. This creates a tendency for particles to be drawn by gravity to the midplane. The disk is a turbulent region so that angular momentum can be easily transferred away from the protosun. In the disk, material starts to ...
Jeopardy Questions
... A: Nova – Material falls on WD, fuses in small burst of energy. Type Ia Supernova – Material falls on WD, builds up until Chandrasekhar limit, and then everything explodes. Core-collapse Supernova – Massive star goes through shell burning until iron, can’t support its own weight, and collapses, leav ...
... A: Nova – Material falls on WD, fuses in small burst of energy. Type Ia Supernova – Material falls on WD, builds up until Chandrasekhar limit, and then everything explodes. Core-collapse Supernova – Massive star goes through shell burning until iron, can’t support its own weight, and collapses, leav ...
No Slide Title
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
... The neutron star may continue to gain mass from nearby stars. At a critical moment, it becomes so dense it collapses in on itself, becoming a single point of zero size! Its gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape from inside a certain boundary - the EVENT HORIZON. The star is now a BLACK ...
Ecliptic 1 2 3 Three tell tale visual characteristics a planet:
... Shifting position of a planet against the starry backdrop. In this case, Mars moves in front of the stars of Cancer, ...
... Shifting position of a planet against the starry backdrop. In this case, Mars moves in front of the stars of Cancer, ...
Final Exam Review (Word doc)
... 30. From Earth, Mercury is difficult to see mostly because it always appears near the Sun. 31. Synchrotron radiation is produced by electrons moving rapidly (whirling) in a magnetic field. 32. One way in which Uranus is peculiar because its axis of rotation is in the ecliptic plane. 33. Why do Mercu ...
... 30. From Earth, Mercury is difficult to see mostly because it always appears near the Sun. 31. Synchrotron radiation is produced by electrons moving rapidly (whirling) in a magnetic field. 32. One way in which Uranus is peculiar because its axis of rotation is in the ecliptic plane. 33. Why do Mercu ...
Unit 4 CSI Letter Solar System - Home of the Super Stingrays!!!
... Sun: The star at the center of our solar system Constellation: A pattern of stars that form an imaginary picture or design in the sky Galaxy: A huge system of gases, dust, and many stars Universe: Everything that exists in space ...
... Sun: The star at the center of our solar system Constellation: A pattern of stars that form an imaginary picture or design in the sky Galaxy: A huge system of gases, dust, and many stars Universe: Everything that exists in space ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.