February 6
... http://www.geographyalltheway.com/ks3_geography/maps_atlases/longitude_latitude.htm ...
... http://www.geographyalltheway.com/ks3_geography/maps_atlases/longitude_latitude.htm ...
30.2 PowerPoint Stellar Evolution
... the core of the star The energy from fusion balances the force of gravity and makes it a very stable stage ...
... the core of the star The energy from fusion balances the force of gravity and makes it a very stable stage ...
1) The following questions refer to the HR diagram
... A) it amplifies the contrast with red giants. B) they are both very hot and very small. C) they are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity wh ...
... A) it amplifies the contrast with red giants. B) they are both very hot and very small. C) they are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity wh ...
PH709-assn-answers
... 1. Suppose that two exoplanets are observed to transit the same star. They are both in circular orbits with an inclination of 90 degrees. One produces periodic dips with a period of 4 days and the other produces periodic dips with a period of 108 days. The decrease in luminosity caused by both exopl ...
... 1. Suppose that two exoplanets are observed to transit the same star. They are both in circular orbits with an inclination of 90 degrees. One produces periodic dips with a period of 4 days and the other produces periodic dips with a period of 108 days. The decrease in luminosity caused by both exopl ...
Click on image to content
... The never-before-seen surface of the distant planet Pluto is resolved in these NASA ...
... The never-before-seen surface of the distant planet Pluto is resolved in these NASA ...
What is a planet? Why? How?
... • Think long orbital period comets that never get close to the Sun ...
... • Think long orbital period comets that never get close to the Sun ...
9binary1i
... Spectroscopic Binary Motion What information can we get about the orbit if we can’t see it? Can get the velocity of the orbit from the Doppler shift More shifted the lines the faster the star is moving in its orbit ...
... Spectroscopic Binary Motion What information can we get about the orbit if we can’t see it? Can get the velocity of the orbit from the Doppler shift More shifted the lines the faster the star is moving in its orbit ...
Star Search Game: Constructing a Hertzsprung
... Inspired by: Ian Christie (VSSEC); Activity created by: Nandita Bajaj Introduction: Star Search is an online game developed by the Victorian Space Science Education Centre (VSSEC) that allows the user to go on a simulated journey into space using a spacecraft in search of various stars. The user is ...
... Inspired by: Ian Christie (VSSEC); Activity created by: Nandita Bajaj Introduction: Star Search is an online game developed by the Victorian Space Science Education Centre (VSSEC) that allows the user to go on a simulated journey into space using a spacecraft in search of various stars. The user is ...
ScienceHelpNotes-UnitE1 - JA Williams High School
... Humans have always been fascinated by entities in the sky. Many ancient tribes created stories to explain the presence and movement of objects in space. The people of the First Nation saw a distinct pattern of stars they called the Great Bear. The Egyptians built the pyramids in alignment with the ...
... Humans have always been fascinated by entities in the sky. Many ancient tribes created stories to explain the presence and movement of objects in space. The people of the First Nation saw a distinct pattern of stars they called the Great Bear. The Egyptians built the pyramids in alignment with the ...
THE BIRTH AND DEATH OF A LOW/MEDIUM MASS STAR
... • THE STAGE WHEN A STAR IS IN IT’S “BEST” LIFE CYCLE • OUR SUN IS A MAIN SEQUENCE STAR • MAIN SEQUENCE STARS HAVE MOSTLY HYDROGEN. • THE HYDROGEN EXPLODES, GIVING OFF LIGHT AND HEAT • AS IT EXPLODES, THE HYDROGEN TURNS TO HELIUM. • HELIUM IS LIGHTER THAN HYDROGEN. • OUR SUN IS 4.6 BILLION YEARS OLD. ...
... • THE STAGE WHEN A STAR IS IN IT’S “BEST” LIFE CYCLE • OUR SUN IS A MAIN SEQUENCE STAR • MAIN SEQUENCE STARS HAVE MOSTLY HYDROGEN. • THE HYDROGEN EXPLODES, GIVING OFF LIGHT AND HEAT • AS IT EXPLODES, THE HYDROGEN TURNS TO HELIUM. • HELIUM IS LIGHTER THAN HYDROGEN. • OUR SUN IS 4.6 BILLION YEARS OLD. ...
Inner and Outer Planets
... • Pluto is much like the inner planets because it is made of rock and metal. • Pluto has only one moon and takes about 249 years to orbit the sun. • Part of Pluto’s orbit passes inside that of Neptune, so at times Neptune is the planet farthest from the sun. • Pluto was located and named in 1930, bu ...
... • Pluto is much like the inner planets because it is made of rock and metal. • Pluto has only one moon and takes about 249 years to orbit the sun. • Part of Pluto’s orbit passes inside that of Neptune, so at times Neptune is the planet farthest from the sun. • Pluto was located and named in 1930, bu ...
Email Template - Personal.psu.edu
... (a) Jovian (b) Inferior (c) Inner (d) Minor (3) Compared to terrestrial planets, Jovian planets have a A. lower density. B. more rapid rotation. C. more rocky composition. D. larger size. E. [More than one of the above.] (4) The only planet whose orbit is more eccentric than Mercury's is A. Pluto. B ...
... (a) Jovian (b) Inferior (c) Inner (d) Minor (3) Compared to terrestrial planets, Jovian planets have a A. lower density. B. more rapid rotation. C. more rocky composition. D. larger size. E. [More than one of the above.] (4) The only planet whose orbit is more eccentric than Mercury's is A. Pluto. B ...
Test#1
... Groups of galaxies seen clustered in the night sky. b. Groups of stars that make an apparent pattern in the sky. ...
... Groups of galaxies seen clustered in the night sky. b. Groups of stars that make an apparent pattern in the sky. ...
12.4 Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun
... • Massive stars become hot enough to fuse carbon, then heavier elements all the way to iron. At the end, the core collapses and rebounds as a Type II supernova. • Type I supernova is a carbon explosion, occurring when too much mass falls onto a white dwarf. • All heavy elements are formed in stellar ...
... • Massive stars become hot enough to fuse carbon, then heavier elements all the way to iron. At the end, the core collapses and rebounds as a Type II supernova. • Type I supernova is a carbon explosion, occurring when too much mass falls onto a white dwarf. • All heavy elements are formed in stellar ...
Stellar Evolution Test Answers
... 20. When the central material in our huge rotating cloud of gas and dust comes together and reaches about _________million degrees, a protostar is formed. a) 200 b) 100 c) 20 d) 2 21. The most common type star in the universe is the a) brown dwarf b) white dwarf c) yellow dwarf d) red dwarf 22. A st ...
... 20. When the central material in our huge rotating cloud of gas and dust comes together and reaches about _________million degrees, a protostar is formed. a) 200 b) 100 c) 20 d) 2 21. The most common type star in the universe is the a) brown dwarf b) white dwarf c) yellow dwarf d) red dwarf 22. A st ...
01 - Ionia Public Schools
... Directed Reading – 30.2 Section: Stellar Evolution _____ 1. Why are astronomers not able to observe the entire life of any star? a. because of the movement of stars b. because a star typically exists for billions of years c. because the light of stars reaches Earth millions of years later d. because ...
... Directed Reading – 30.2 Section: Stellar Evolution _____ 1. Why are astronomers not able to observe the entire life of any star? a. because of the movement of stars b. because a star typically exists for billions of years c. because the light of stars reaches Earth millions of years later d. because ...
Earth - jennydebellis
... 3. Main-sequence stage – main part of a star’s life – the sun is in this stage – lifespan of sun is about 10 billion yers – it’s about ½ way through life, so as about 5 billion more years to go 4. Red Giant stage – all of the hydrogen is gone in the core, so the star expands, the surface cools, and ...
... 3. Main-sequence stage – main part of a star’s life – the sun is in this stage – lifespan of sun is about 10 billion yers – it’s about ½ way through life, so as about 5 billion more years to go 4. Red Giant stage – all of the hydrogen is gone in the core, so the star expands, the surface cools, and ...
eneb_form
... • Radiation (light) being emitted by stars can also effect material outside of a star. When dust absorbs the light, dust particles respond by moving away from the star. ...
... • Radiation (light) being emitted by stars can also effect material outside of a star. When dust absorbs the light, dust particles respond by moving away from the star. ...
Document
... notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planets. Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed a heliocentric model of planetary motion. Simpler and more elegant. Model could order planets e.g. Mercury and Venus are never seen more than 28 and 47deg. E or W of the Sun => inside orb ...
... notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planets. Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed a heliocentric model of planetary motion. Simpler and more elegant. Model could order planets e.g. Mercury and Venus are never seen more than 28 and 47deg. E or W of the Sun => inside orb ...
PHYSICS 1500 - ASTRONOMY TOTAL: 100 marks Section A Please
... of gravitational interactions between ring particles. a density wave confines them. the magnetic field holds them in place. Uranus and Neptune are much smaller than Saturn. they are shepherded by small moons. ...
... of gravitational interactions between ring particles. a density wave confines them. the magnetic field holds them in place. Uranus and Neptune are much smaller than Saturn. they are shepherded by small moons. ...
E5 stellar processes and stellar evolution (HL only)
... • If the core is above 1.4 solar masses (the Chandrasekhar limit) Electrons are forced into protons producing neutrons. • The core is only made of neutrons and contracting rapidly. ...
... • If the core is above 1.4 solar masses (the Chandrasekhar limit) Electrons are forced into protons producing neutrons. • The core is only made of neutrons and contracting rapidly. ...
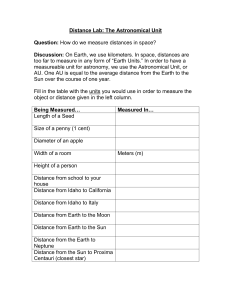
Distance Lab: The Astronomical Unit
... Sun over the course of one year. Fill in the table with the units you would use in order to measure the object or distance given in the left column. ...
... Sun over the course of one year. Fill in the table with the units you would use in order to measure the object or distance given in the left column. ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.