32) What spacecraft mission crashed because the NASA contractor
... No notes, No books. You can use a calculator 1) The order of the eight planets from closest to farthest from the Sun is A) Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune B) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, Uranus C) Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Saturn, Jupiter, U ...
... No notes, No books. You can use a calculator 1) The order of the eight planets from closest to farthest from the Sun is A) Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune B) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, Uranus C) Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Saturn, Jupiter, U ...
Astrophysics
... b) (2 points) Find Rs in parsecs for an O star if Φ=1049 photons/s, n = 10 atoms/cm3 , and α = 2 × 10−13 . c) (2 points) Find Rs in parsecs for the sun if Φ = 5×1023 photons/s, while n and α remain the same. d) (3 points) Could the cloud around the sun be seen by an astronomer on α-Centauri (distanc ...
... b) (2 points) Find Rs in parsecs for an O star if Φ=1049 photons/s, n = 10 atoms/cm3 , and α = 2 × 10−13 . c) (2 points) Find Rs in parsecs for the sun if Φ = 5×1023 photons/s, while n and α remain the same. d) (3 points) Could the cloud around the sun be seen by an astronomer on α-Centauri (distanc ...
32) What spacecraft mission crashed because the NASA contractor
... No notes, No books. You can use a calculator 1) The order of the eight planets from closest to farthest from the Sun is A) Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune B) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune C) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, N ...
... No notes, No books. You can use a calculator 1) The order of the eight planets from closest to farthest from the Sun is A) Mars, Venus, Earth, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune B) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune C) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, N ...
300 MHz - 3 GHz Yes, we`re interested
... Assembly and Evolution • HI: heard several times about billion galaxies to z=1.5. And further… • Diffuse HI (cosmic web) - IGM-galaxy feedback poorly understood aspect of galaxy formation • Local HI mass function, probe low-mass end, in various environments HVC/dwarfs ...
... Assembly and Evolution • HI: heard several times about billion galaxies to z=1.5. And further… • Diffuse HI (cosmic web) - IGM-galaxy feedback poorly understood aspect of galaxy formation • Local HI mass function, probe low-mass end, in various environments HVC/dwarfs ...
Solar System Test Review - Garnet Valley School District
... 10. _________________________ is the movement of an object around another, i.e., the earth going around the sun or the moon going around the earth. 11. The _________________________ states the sun, earth and other objects in the solar system formed from a rotating cloud of gas, called a nebula, abou ...
... 10. _________________________ is the movement of an object around another, i.e., the earth going around the sun or the moon going around the earth. 11. The _________________________ states the sun, earth and other objects in the solar system formed from a rotating cloud of gas, called a nebula, abou ...
Fig. 16-7, p.363
... from a disk around the Sun as it formed; such protoplanetary disks are seen around many young stars • Planets like Earth are believed therefore to form as normal byproducts of stars forming • There are two types of planets in our solar system, Earth-like and Jupiter-like, results of a process we thi ...
... from a disk around the Sun as it formed; such protoplanetary disks are seen around many young stars • Planets like Earth are believed therefore to form as normal byproducts of stars forming • There are two types of planets in our solar system, Earth-like and Jupiter-like, results of a process we thi ...
Lesson 1 | Scientific Inquiry
... 1. The inner planets are those closest to the Sun. 2. The inner planets are made of rocky and metallic materials. a. Because of its small mass, Mercury’s gravity is not strong enough to hold gases to its surface. b. Venus is covered by a thick layer of clouds. c. The high temperatures on Venus are c ...
... 1. The inner planets are those closest to the Sun. 2. The inner planets are made of rocky and metallic materials. a. Because of its small mass, Mercury’s gravity is not strong enough to hold gases to its surface. b. Venus is covered by a thick layer of clouds. c. The high temperatures on Venus are c ...
Astronomical Distance Determination
... • A sixth magnitude star is thus 100 times less “bright” than a first magnitude star. Larger magnitude is ...
... • A sixth magnitude star is thus 100 times less “bright” than a first magnitude star. Larger magnitude is ...
SW - Calculating Magnitudes
... Here, ‘intensity’, also knowns as ‘counts’, refers to the amount of light that is emitted from the object and received by the CCD (see ‘Photometry in Astronomy’ worksheet). However, it’s a bit of an archaic system in that the brighter an object, the lower its apparent magnitude value. Objects that a ...
... Here, ‘intensity’, also knowns as ‘counts’, refers to the amount of light that is emitted from the object and received by the CCD (see ‘Photometry in Astronomy’ worksheet). However, it’s a bit of an archaic system in that the brighter an object, the lower its apparent magnitude value. Objects that a ...
astronomy - Scioly.org
... 47. RR Lyrae variable stars are typically _________ giant stars? (fill in the blank with a color) 48. Variable stars are stars in which the _______ changes over time. A. Size B. Color C. Shape D. brightness 49. A planet orbits the Sun at 3 AU. How long (in years) does it take to orbit the Sun? (Hint ...
... 47. RR Lyrae variable stars are typically _________ giant stars? (fill in the blank with a color) 48. Variable stars are stars in which the _______ changes over time. A. Size B. Color C. Shape D. brightness 49. A planet orbits the Sun at 3 AU. How long (in years) does it take to orbit the Sun? (Hint ...
here - Next Wave
... the subject of worldwide astronomical research, advancing at a breakneck pace. In less than a decade we may well know whether we’re the cosmos’ first and only living progeny, or if there are others. Since the 1990s, we have known what we had long suspected: our solar system is not unique. There are ...
... the subject of worldwide astronomical research, advancing at a breakneck pace. In less than a decade we may well know whether we’re the cosmos’ first and only living progeny, or if there are others. Since the 1990s, we have known what we had long suspected: our solar system is not unique. There are ...
types of stars, luminosity, and brightness
... 13. You would NOT expect the same distribution of stars on the HR diagram if Apparent Brightness versus Temperature were plotted, because apparent brightness depends on the distance to each star, and every star is located at a different distance from us. So, some stars APPEAR dimmer, even though th ...
... 13. You would NOT expect the same distribution of stars on the HR diagram if Apparent Brightness versus Temperature were plotted, because apparent brightness depends on the distance to each star, and every star is located at a different distance from us. So, some stars APPEAR dimmer, even though th ...
File
... • The outer shells of the core contain all elements lighter than iron. These are now targets for the neutrons. • These elements capture neutrons until they are swollen up to isotopes like 250Fe! Then they decay into copper, gold, lead, etc. - all the remaining elements in the ...
... • The outer shells of the core contain all elements lighter than iron. These are now targets for the neutrons. • These elements capture neutrons until they are swollen up to isotopes like 250Fe! Then they decay into copper, gold, lead, etc. - all the remaining elements in the ...
Unit 60 to 79
... 7) Which of the following events will not leave any remnant? a. Type I supernova b. Type II supernova c. Nova 8) The Sun will likely never become a nova because this only happens to stars a. Much more massive than the Sun b. Much less massive than the Sun c. In close binary pairs d. That have no pla ...
... 7) Which of the following events will not leave any remnant? a. Type I supernova b. Type II supernova c. Nova 8) The Sun will likely never become a nova because this only happens to stars a. Much more massive than the Sun b. Much less massive than the Sun c. In close binary pairs d. That have no pla ...
AST301.Ch22.NeutGammBH - University of Texas Astronomy
... was enormous. As we’ll see later, because the universe is expanding, redshift can be used to get distance. Resulting distance for this gamma ray burst was 2 billion parsecs! By now we have seen ~10 afterglows from gamma ray bursts (and their parent galaxies) and they are all extremely distant extr ...
... was enormous. As we’ll see later, because the universe is expanding, redshift can be used to get distance. Resulting distance for this gamma ray burst was 2 billion parsecs! By now we have seen ~10 afterglows from gamma ray bursts (and their parent galaxies) and they are all extremely distant extr ...
Planets and Small Objects in the Solar System Worksheet
... 6. Asteroids and meteoroids are chunks of rocks left over from the formation of the early Solar System. Which of the following describes the difference between these? A) Asteroids are round and meteoroids are irregular shaped B) Asteroids are much larger than meteoroids C) Asteroids are located much ...
... 6. Asteroids and meteoroids are chunks of rocks left over from the formation of the early Solar System. Which of the following describes the difference between these? A) Asteroids are round and meteoroids are irregular shaped B) Asteroids are much larger than meteoroids C) Asteroids are located much ...
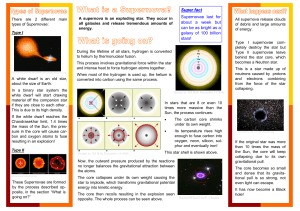
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... material off the companion star if they are close to each other . This is due to its high density. ...
... material off the companion star if they are close to each other . This is due to its high density. ...
Midterm Exam: Chs. 1-3, 7-11
... + 8. Galileo disproved Ptolemy’s model of the solar system by observing the phases of ____ Venus through a telescope. O 9. The greenhouse effect is the absorption of solar ultraviolet planetary infrared ____ radiation by gases in planetary atmospheres leading to atmospheric heating. O 10. Because of ...
... + 8. Galileo disproved Ptolemy’s model of the solar system by observing the phases of ____ Venus through a telescope. O 9. The greenhouse effect is the absorption of solar ultraviolet planetary infrared ____ radiation by gases in planetary atmospheres leading to atmospheric heating. O 10. Because of ...
Characteristics of Stars (Ph)
... Characteristics of Stars Imagine you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. To travel from Earth to the sun would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is much farther away—a trip to Proxima Centauri would take 4.2 years! ...
... Characteristics of Stars Imagine you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. To travel from Earth to the sun would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is much farther away—a trip to Proxima Centauri would take 4.2 years! ...
Stars - Sun
... the Sun that we can see from a distance is called the photosphere, which means “sphere of light.” • Just above it is the chromosphere. • This is a very hot layer of plasma, a high-energy state of matter. ...
... the Sun that we can see from a distance is called the photosphere, which means “sphere of light.” • Just above it is the chromosphere. • This is a very hot layer of plasma, a high-energy state of matter. ...
1 - Stellar Life Cycle
... center of the new star, this heats stops the rest of the star from collapsing. The balance between gravity trying to make the star shrink and heat holding it up is called Thermodynamic Equilibrium. The star then stays almost exactly the same for a long time (about 10 billion years for a star lik ...
... center of the new star, this heats stops the rest of the star from collapsing. The balance between gravity trying to make the star shrink and heat holding it up is called Thermodynamic Equilibrium. The star then stays almost exactly the same for a long time (about 10 billion years for a star lik ...
CyclesOfTheSky
... Explain why the Earth undergoes seasons. Explain why it is hot in the summer. Explain why the Sun appears high in the sky during the summer but low in winter? Define equinox and solstice? Sketch the Sun, Earth, and Earth’s orbit. On the sketch, draw Earth and label the location of Earth at the solst ...
... Explain why the Earth undergoes seasons. Explain why it is hot in the summer. Explain why the Sun appears high in the sky during the summer but low in winter? Define equinox and solstice? Sketch the Sun, Earth, and Earth’s orbit. On the sketch, draw Earth and label the location of Earth at the solst ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.