A new Cosmos – a novel Physics
... A third critique of Copernican theory was a quite sophisticated argument which included precise astronomical measurements already available in the mid 16th century: If the earth rotates around the sun, which is located in the center of the universe, then one should observe a small variation of the s ...
... A third critique of Copernican theory was a quite sophisticated argument which included precise astronomical measurements already available in the mid 16th century: If the earth rotates around the sun, which is located in the center of the universe, then one should observe a small variation of the s ...
large PDF file
... • A high-mass star dies in a violent cataclysm in which its core collapses and most of its matter is ejected into space at high speeds • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, movin ...
... • A high-mass star dies in a violent cataclysm in which its core collapses and most of its matter is ejected into space at high speeds • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, movin ...
summary - guideposts
... The planets are divided into two types. The inner four are terrestrial planets—small, rocky, dense Earthlike worlds. The next four outward are Jovian planets that are large and low density. All four of the Jovian worlds have ring systems and large families of moons. Jupiter’s Galilean satellites wer ...
... The planets are divided into two types. The inner four are terrestrial planets—small, rocky, dense Earthlike worlds. The next four outward are Jovian planets that are large and low density. All four of the Jovian worlds have ring systems and large families of moons. Jupiter’s Galilean satellites wer ...
Class II Supernova
... Stars with anywhere from 3-9 solar masses have hydrogen in their core. When the hydrogen combines with the helium, it produces thermal energy. This is how the star is maintained. When the star runs out or stops producing hydrogen the thermal energy doesn’t maintain the star anymore. ...
... Stars with anywhere from 3-9 solar masses have hydrogen in their core. When the hydrogen combines with the helium, it produces thermal energy. This is how the star is maintained. When the star runs out or stops producing hydrogen the thermal energy doesn’t maintain the star anymore. ...
ASTR 5340: Radio Astronomy Problem Set 1 Due: 13 September
... The star Betelgeuse is an excellent candidate. Betelgeuse (aka α Orionis because it is the brightest star visible in the Orion constellation) is the red star that defines the left shoulder of Orion. It is an extremely luminous (bolometric luminosity L ≈ 105 L⊙ , where the ⊙ subscript refers to the S ...
... The star Betelgeuse is an excellent candidate. Betelgeuse (aka α Orionis because it is the brightest star visible in the Orion constellation) is the red star that defines the left shoulder of Orion. It is an extremely luminous (bolometric luminosity L ≈ 105 L⊙ , where the ⊙ subscript refers to the S ...
Lecture 17, PPT version
... between 0.03 and 0.3 seconds (meaning they rotate between 3 and 30 times per seconds) The fastest known pulsars have periods of milliseconds and are rotating at speeds approaching ...
... between 0.03 and 0.3 seconds (meaning they rotate between 3 and 30 times per seconds) The fastest known pulsars have periods of milliseconds and are rotating at speeds approaching ...
Earth in Space - Learning Outcomes
... 6.4 x 106 m. The mass of Mars is 0.11 times the mass of the Earth. (a) How does the mean density of Mars compare with that of the Earth? (b) Calculate the value of “g” on the surface of Mars. (c) Calculate the escape velocity on Mars. ...
... 6.4 x 106 m. The mass of Mars is 0.11 times the mass of the Earth. (a) How does the mean density of Mars compare with that of the Earth? (b) Calculate the value of “g” on the surface of Mars. (c) Calculate the escape velocity on Mars. ...
What is the sun?
... The Earth moves in another way,too. If it travels round the sun in an orbit towards the sun, it is summer on that part of the Earth , Half a year later, the Earth goes round to the other side of its orbit. That part of the earth is now farther away from the sun and has it winter and the other part h ...
... The Earth moves in another way,too. If it travels round the sun in an orbit towards the sun, it is summer on that part of the Earth , Half a year later, the Earth goes round to the other side of its orbit. That part of the earth is now farther away from the sun and has it winter and the other part h ...
Earth is the third planet from the Sun. It is a rocky planet and the fifth
... one moon and no rings. © www.thecurriculumcorner.com ...
... one moon and no rings. © www.thecurriculumcorner.com ...
Oct 06, 2001
... evolutionary track of a 1 solar mass star to the right to answer the following 5 questions ...
... evolutionary track of a 1 solar mass star to the right to answer the following 5 questions ...
8 Grade/Comp.Sci.III adv Course Code: 2002110
... Essential Questions: What makes up the universe? (2-1) What are the properties of stars? (2-2) How have people modeled the solar system? (3-1) Why is gravity important in the solar system? (3-2) What are the properties of the sun? (3-3) What is known about the terrestrial planets? (3-4) What is know ...
... Essential Questions: What makes up the universe? (2-1) What are the properties of stars? (2-2) How have people modeled the solar system? (3-1) Why is gravity important in the solar system? (3-2) What are the properties of the sun? (3-3) What is known about the terrestrial planets? (3-4) What is know ...
005 Astrophysics problems
... 6.4 x 106 m. The mass of Mars is 0.11 times the mass of the Earth. (a) How does the mean density of Mars compare with that of the Earth? (b) Calculate the value of “g” on the surface of Mars. (c) Calculate the escape velocity on Mars. ...
... 6.4 x 106 m. The mass of Mars is 0.11 times the mass of the Earth. (a) How does the mean density of Mars compare with that of the Earth? (b) Calculate the value of “g” on the surface of Mars. (c) Calculate the escape velocity on Mars. ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... (in parsecs) = 1/p (in arcseconds), the method of spectroscopic parallax and the Cepheids method for determining distances in astronomy? Can you define the parsec? Can you state the definitions of apparent brightness, b = L/4πd2 , and apparent and absolute magnitude, b/b0 = 100-m/5 = 2.512-m? ...
... (in parsecs) = 1/p (in arcseconds), the method of spectroscopic parallax and the Cepheids method for determining distances in astronomy? Can you define the parsec? Can you state the definitions of apparent brightness, b = L/4πd2 , and apparent and absolute magnitude, b/b0 = 100-m/5 = 2.512-m? ...
Stars are made of very hot gas. This gas is mostly hydrogen and
... Blue giant stars die in a spectacular way They grow larger just like the Sun sized stars, but then instead of shrinking and forming a planetary nebula they explode in what is called a super nova. Super nova explosions can be brighter than an entire galaxy, and can be seen from very far away ...
... Blue giant stars die in a spectacular way They grow larger just like the Sun sized stars, but then instead of shrinking and forming a planetary nebula they explode in what is called a super nova. Super nova explosions can be brighter than an entire galaxy, and can be seen from very far away ...
More on Stars and the Sky
... objects appear stationary. Why? What is the typical parallax of a nearby star? Why is it not possible to measure the parallax better than 0.01” from ground based instruments, but can be done from space? What is the precession of the Earth. Which of the following would change due to precession celest ...
... objects appear stationary. Why? What is the typical parallax of a nearby star? Why is it not possible to measure the parallax better than 0.01” from ground based instruments, but can be done from space? What is the precession of the Earth. Which of the following would change due to precession celest ...
Stellar Structure - McMurry University
... the flashes (“pulses”) of light happen many times a second. When observed with telescopes, these rapidly flashing (“pulsing”) objects were originally called pulsars. Pulsars are just neutron stars that are easy to observe because the pulsing makes them stand out. ...
... the flashes (“pulses”) of light happen many times a second. When observed with telescopes, these rapidly flashing (“pulsing”) objects were originally called pulsars. Pulsars are just neutron stars that are easy to observe because the pulsing makes them stand out. ...
Topic 3 Assignment - Science 9 Portfolio
... The significance of the spectral lines was discovered about 50 years later when Kirschoff and Bunsen, two chemists used a spectroscope to observe various chemicals when they were heated. They found some of the lines missing in some of the chemicals. Each particular element had its own unique spectra ...
... The significance of the spectral lines was discovered about 50 years later when Kirschoff and Bunsen, two chemists used a spectroscope to observe various chemicals when they were heated. They found some of the lines missing in some of the chemicals. Each particular element had its own unique spectra ...
Falling Stars
... speedy flight of light flash by, and you are left trying to describe what you saw and felt. You stare at the dark space, hoping another will streak across the sky. ...
... speedy flight of light flash by, and you are left trying to describe what you saw and felt. You stare at the dark space, hoping another will streak across the sky. ...
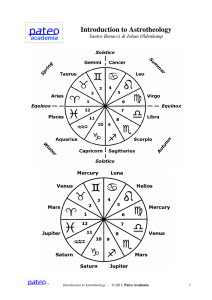
Introduction to Astrotheology
... birth. This relation is based on the three decanates (or decans for short) per Zodiac sign. A decan is the division of the full period of a Zodiac sign (of 30 degrees of arc) into three equal periods (of 10 degrees of arc). Roughly, we can say that the people who were born on the day numbers of 21 a ...
... birth. This relation is based on the three decanates (or decans for short) per Zodiac sign. A decan is the division of the full period of a Zodiac sign (of 30 degrees of arc) into three equal periods (of 10 degrees of arc). Roughly, we can say that the people who were born on the day numbers of 21 a ...
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2
... are meteorites, the bits of meteoroids that survive passing through the Earth’s atmosphere and land on our planet’s surface. Radioactive age-dating of meteorites, reveals that they are all nearly the same age, about 4.56 billion ...
... are meteorites, the bits of meteoroids that survive passing through the Earth’s atmosphere and land on our planet’s surface. Radioactive age-dating of meteorites, reveals that they are all nearly the same age, about 4.56 billion ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.