annie jump cannon
... brightness changes of these stars can range from a thousandth of a magnitude to as much as twenty magnitudes over periods of a fraction of a second to years, depending on the type of variable star.” ...
... brightness changes of these stars can range from a thousandth of a magnitude to as much as twenty magnitudes over periods of a fraction of a second to years, depending on the type of variable star.” ...
Milky Way
... star forming regions. Some are clearly massive supernovae (hypernovae?) because spectra are seen. • Short gamma-ray bursts (< 2 sec): Found in young and old regions. Thought to be two merging neutron stars or a neutron star plus a black hole. ...
... star forming regions. Some are clearly massive supernovae (hypernovae?) because spectra are seen. • Short gamma-ray bursts (< 2 sec): Found in young and old regions. Thought to be two merging neutron stars or a neutron star plus a black hole. ...
M - Physics.cz
... Observations: The X-ray radiation is absorbed by Earth atmosphere and must be studied using detectors on orbiting satellites representing rather expensive research tool. On the other hand, it provides a unique chance to probe effects in the strong-gravity-field region (GM/r~c^2) and test extremal im ...
... Observations: The X-ray radiation is absorbed by Earth atmosphere and must be studied using detectors on orbiting satellites representing rather expensive research tool. On the other hand, it provides a unique chance to probe effects in the strong-gravity-field region (GM/r~c^2) and test extremal im ...
The Night Sky
... Billions of stars also light our night sky. Stars are huge balls of hot, glowing gas that shine throughout our universe. The Sun is not the brightest star, but it seems like it to us because it’s the closest one to Earth. All of the stars in our galaxy belong to a group called the Milky Way. It’ ...
... Billions of stars also light our night sky. Stars are huge balls of hot, glowing gas that shine throughout our universe. The Sun is not the brightest star, but it seems like it to us because it’s the closest one to Earth. All of the stars in our galaxy belong to a group called the Milky Way. It’ ...
File
... From here on earth it is difficult to fathom the huge distances that exist between the stars and planets. The circumference of the earth (38,500 km) may seem like a long way to us but is an insignificant distance in space. The nearest celestial object to earth, the moon, is approximately 400, 000 km ...
... From here on earth it is difficult to fathom the huge distances that exist between the stars and planets. The circumference of the earth (38,500 km) may seem like a long way to us but is an insignificant distance in space. The nearest celestial object to earth, the moon, is approximately 400, 000 km ...
If Earth had no tilt, what else would happen?
... •The poles would receive less direct light and thus be colder making the survival rate there lower as well. •The species would have evolved differently (micro-evolution), thus different life would be on Earth. •But we would have a habitable zone between the poles and the equator, but unfortunately i ...
... •The poles would receive less direct light and thus be colder making the survival rate there lower as well. •The species would have evolved differently (micro-evolution), thus different life would be on Earth. •But we would have a habitable zone between the poles and the equator, but unfortunately i ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... galaxy a collection of stars, dust, and gas bound together by gravity • Galaxies are the major building blocks of the universe. Astronomers estimate that the universe contains hundreds of billions of galaxies. • A typical galaxy, such as the Milky Way, has a diameter of bout 100,000 light-years and ...
... galaxy a collection of stars, dust, and gas bound together by gravity • Galaxies are the major building blocks of the universe. Astronomers estimate that the universe contains hundreds of billions of galaxies. • A typical galaxy, such as the Milky Way, has a diameter of bout 100,000 light-years and ...
Document
... Why larger semi-major axes now? Kepler’s third law implies longer period, so requires monitoring for many years to determine ‘wobble’ precisely Amplitude of wobble smaller (at fixed mP ); benefit of improved spectroscopic precision ...
... Why larger semi-major axes now? Kepler’s third law implies longer period, so requires monitoring for many years to determine ‘wobble’ precisely Amplitude of wobble smaller (at fixed mP ); benefit of improved spectroscopic precision ...
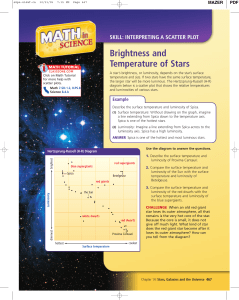
Brightness and Temperature of Stars
... Describe the surface temperature and luminosity of Spica. (1) Surface temperature: Without drawing on the graph, imagine a line extending from Spica down to the temperature axis. Spica is one of the hottest stars. (2) Luminosity: Imagine a line extending from Spica across to the ...
... Describe the surface temperature and luminosity of Spica. (1) Surface temperature: Without drawing on the graph, imagine a line extending from Spica down to the temperature axis. Spica is one of the hottest stars. (2) Luminosity: Imagine a line extending from Spica across to the ...
The Celestial E-Sphere
... stars’ positions were plotted using simple spherical geometry. They are modeled using a single star texture mapped to the relevant size depending on apparent magnitude. They are coloured according to their spectral type. The textured stars are ‘bill-boarded’ that is their two dimensional image alway ...
... stars’ positions were plotted using simple spherical geometry. They are modeled using a single star texture mapped to the relevant size depending on apparent magnitude. They are coloured according to their spectral type. The textured stars are ‘bill-boarded’ that is their two dimensional image alway ...
CS3_Ch 3 - Leon County Schools
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
Stars and Galaxies - La Salle Elementary Public Schools No 122
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
Venus - QZAB Teachers
... Crater-A bowl-shaped depression at the mouth of a volcano or geyser Absolute magnitude- Magnitude that a star would appear to have if it were at a distance of 10 pc from the Sun Astrology- A system in which the positions of the Sun, Moon, and Planets are supposed to exert an influence on events on ...
... Crater-A bowl-shaped depression at the mouth of a volcano or geyser Absolute magnitude- Magnitude that a star would appear to have if it were at a distance of 10 pc from the Sun Astrology- A system in which the positions of the Sun, Moon, and Planets are supposed to exert an influence on events on ...
Navigation - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... As people ventured further (the Hawaiians 3000BC could travel over 1000km between islands) they needed to find other landmarks so they turned to the stars. ...
... As people ventured further (the Hawaiians 3000BC could travel over 1000km between islands) they needed to find other landmarks so they turned to the stars. ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.