Kepler`s laws - FSU High Energy Physics
... where a = semimajor axis of the ellipse distance in 3rd law is really semimajor axis a circle is a special case of an ellipse, where the semimajor and semimajor axes are equal: a = b = r excentricity of ellipse = (distance of focus from center) divided by (semimajor axis) excentricity of a circle = ...
... where a = semimajor axis of the ellipse distance in 3rd law is really semimajor axis a circle is a special case of an ellipse, where the semimajor and semimajor axes are equal: a = b = r excentricity of ellipse = (distance of focus from center) divided by (semimajor axis) excentricity of a circle = ...
The Bigger Picture - Astronomy and Astrophysics
... • Imagine a star with a relatively cool (4000k) atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of t ...
... • Imagine a star with a relatively cool (4000k) atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of t ...
INTERSTELLAR MedLab
... Emission – a gas cloud that receives energy from a hot star(s), allowing the nebula to give off radiation in emission. Reflection – dust clouds that reflect (scatter) a star’s light to us Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. ...
... Emission – a gas cloud that receives energy from a hot star(s), allowing the nebula to give off radiation in emission. Reflection – dust clouds that reflect (scatter) a star’s light to us Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. ...
Contents
... 3. The Energy Generation Inside the Central Core of the Sun Nuclear fusion inside the central core of the Sun The Sun as a star in the main sequence Evolutionary path of the Sun ...
... 3. The Energy Generation Inside the Central Core of the Sun Nuclear fusion inside the central core of the Sun The Sun as a star in the main sequence Evolutionary path of the Sun ...
Structure of the solar system
... Earth (A), its lines will be blue-shifted. As they two stars are moving horizontally with respect to the Earth, the spectral lines are normal. Then B moves towards Earth and A moves away. The spectral lines move apart then come together twice per revolution. See the simplified animation ...
... Earth (A), its lines will be blue-shifted. As they two stars are moving horizontally with respect to the Earth, the spectral lines are normal. Then B moves towards Earth and A moves away. The spectral lines move apart then come together twice per revolution. See the simplified animation ...
Order of the Planets
... Using information in The Sun, verify whether the following statements are true or false. Check your answers in the book. List the page where you found the information that proves you are correct. ...
... Using information in The Sun, verify whether the following statements are true or false. Check your answers in the book. List the page where you found the information that proves you are correct. ...
Solar System Formation
... Pluto, usually the ninth planet from the Sun, is the smallest planet in our solar system. Some scientists believe that Pluto once was one of Neptune’s moons, and that it pulled out away from Neptune and made its own orbit. ...
... Pluto, usually the ninth planet from the Sun, is the smallest planet in our solar system. Some scientists believe that Pluto once was one of Neptune’s moons, and that it pulled out away from Neptune and made its own orbit. ...
Solar System - eNetLearning
... Pluto, usually the ninth planet from the Sun, is the smallest planet in our solar system. Some scientists believe that Pluto once was one of Neptune’s moons, and that it pulled out away from Neptune and made its own orbit. ...
... Pluto, usually the ninth planet from the Sun, is the smallest planet in our solar system. Some scientists believe that Pluto once was one of Neptune’s moons, and that it pulled out away from Neptune and made its own orbit. ...
Star Light, Star Bright
... The following suggestions are intended to help identify major concepts covered in the activity that may need extra reinforcement. The goal is to provide opportunities to assess student progress without creating the need for a separate, formal assessment session (or activity) for each of the 40 hands ...
... The following suggestions are intended to help identify major concepts covered in the activity that may need extra reinforcement. The goal is to provide opportunities to assess student progress without creating the need for a separate, formal assessment session (or activity) for each of the 40 hands ...
Document
... The star, Procyon A, is 11.4 light years away from Earth. If there is intelligent life on a planet in that solar system, which is looking at Earth with a special telescope, what are they able to see? A ...
... The star, Procyon A, is 11.4 light years away from Earth. If there is intelligent life on a planet in that solar system, which is looking at Earth with a special telescope, what are they able to see? A ...
Celestial Motions - Georgia State University
... – We can see over 2,000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along the horizon • Why do stars rise and set? – Becau ...
... – We can see over 2,000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along the horizon • Why do stars rise and set? – Becau ...
Science Project
... asteroids that orbit larger asteroids. They are not as clearly distinguished as planetary moons, sometimes being almost as large as their partners. The asteroid belt also contains main-belt comets, which may have been the source of Earth's water. • Trojan asteroids are located in either of Jupiter's ...
... asteroids that orbit larger asteroids. They are not as clearly distinguished as planetary moons, sometimes being almost as large as their partners. The asteroid belt also contains main-belt comets, which may have been the source of Earth's water. • Trojan asteroids are located in either of Jupiter's ...
Nebulae - Innovative Teachers BG
... are stellar clusters. The Galactic Stellar Clusters have a relatively small number (a few hundreds) of bright hot stars. These astronomical objects are observed in the spirals of the galactic plane and are realtively young – hundred millions years. Oposite to them are Globular Clusters found as a ru ...
... are stellar clusters. The Galactic Stellar Clusters have a relatively small number (a few hundreds) of bright hot stars. These astronomical objects are observed in the spirals of the galactic plane and are realtively young – hundred millions years. Oposite to them are Globular Clusters found as a ru ...
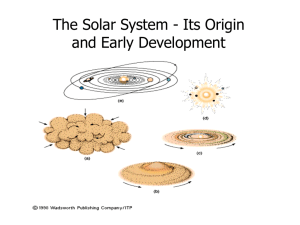
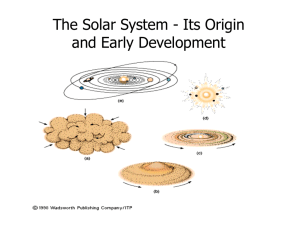
Observational Constraints The Nebular Hypothesis
... In the Solar System we can identify a few trends in physical and orbital characteristics. 1. Giant planets exist at large radial distances (> 5 AU). 2. The mass of the giant planets decreases with orbital distance. 3. Heavy element enrichment increases with decreasing mass. Outside of the Solar Syst ...
... In the Solar System we can identify a few trends in physical and orbital characteristics. 1. Giant planets exist at large radial distances (> 5 AU). 2. The mass of the giant planets decreases with orbital distance. 3. Heavy element enrichment increases with decreasing mass. Outside of the Solar Syst ...
Week 4
... Sun, the faster it goes. • The square of the orbital period is proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis: P2 = a3. (P is how long it takes to make one orbit in years. a is distance in AU) ...
... Sun, the faster it goes. • The square of the orbital period is proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis: P2 = a3. (P is how long it takes to make one orbit in years. a is distance in AU) ...
The first cool rocky/icy exoplanet
... host star. But because these planets had to be large to cause an observable Doppler shift, the planetary systems revealed were unlike the solar system; astronomers were faced with massive gas giants in close orbits around their host star. By January 2006, about 170 extrasolar planets were known, of ...
... host star. But because these planets had to be large to cause an observable Doppler shift, the planetary systems revealed were unlike the solar system; astronomers were faced with massive gas giants in close orbits around their host star. By January 2006, about 170 extrasolar planets were known, of ...
Exercises - Leiden Observatory
... In other words the anisotropy of radiation in the stellar interior is very small. This is why radiation in the solar interior is close to that of a black body. (c) Verify that a gas element in the solar interior, which radiates as a black body, emits ...
... In other words the anisotropy of radiation in the stellar interior is very small. This is why radiation in the solar interior is close to that of a black body. (c) Verify that a gas element in the solar interior, which radiates as a black body, emits ...
Universal Gravitation
... distance from the Earth the less it will weigh. No matter how great the distance Earth’s gravity does not drop to zero. The gravitational influence of every object is exerted through all space. ...
... distance from the Earth the less it will weigh. No matter how great the distance Earth’s gravity does not drop to zero. The gravitational influence of every object is exerted through all space. ...
Probeseiten 2 PDF
... be discovered in this part of the solar system? It was indeed curious that, even in the most powerful of telescopes, the new celestial objects remained little points of light, like stars, while all other planets were resolved as small, round disks. This could only mean one thing: Ceres and Pallas co ...
... be discovered in this part of the solar system? It was indeed curious that, even in the most powerful of telescopes, the new celestial objects remained little points of light, like stars, while all other planets were resolved as small, round disks. This could only mean one thing: Ceres and Pallas co ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.