Question Title
... a)Some planetoids will collide with such high energies that they do not break into pieces. Instead they meld to form one planetoid. b)Other planetoids will break into smaller pieces. In this case, the smaller pieces will likely be pulled in by the gravitational force of the largest remaining piece, ...
... a)Some planetoids will collide with such high energies that they do not break into pieces. Instead they meld to form one planetoid. b)Other planetoids will break into smaller pieces. In this case, the smaller pieces will likely be pulled in by the gravitational force of the largest remaining piece, ...
tremaine_lecture_1
... one of the oldest problems in theoretical physics what is the fate of the Earth? why are there so few planets in the solar system? can we calibrate geological timescale over the last 50 Myr? how do dynamical systems behave over very long times? can we explain the properties of extrasolar planetary s ...
... one of the oldest problems in theoretical physics what is the fate of the Earth? why are there so few planets in the solar system? can we calibrate geological timescale over the last 50 Myr? how do dynamical systems behave over very long times? can we explain the properties of extrasolar planetary s ...
Solar System Formation
... buildup of terrestrial planets took ~ 100 Myr slow accumulation of small bodies not much mass involved buildup of giant planets took ~ 10 Myr (need to have gas around) all giant planets have roughly the same heavy element mass… 5, 15, 300, 300 X solar heavy/light element ratios in J/S/U/N H and He t ...
... buildup of terrestrial planets took ~ 100 Myr slow accumulation of small bodies not much mass involved buildup of giant planets took ~ 10 Myr (need to have gas around) all giant planets have roughly the same heavy element mass… 5, 15, 300, 300 X solar heavy/light element ratios in J/S/U/N H and He t ...
Scattering (and the blue sky)
... Emission and Absorption Spectra More accurately, a gas cloud is only opaque within spectral lines, while a star is opaque at all wavelengths. The brightness of each depends on the usual T4 relation. If, as is usually the case, the cloud is colder than the star (or the star’s atmosphere is colder th ...
... Emission and Absorption Spectra More accurately, a gas cloud is only opaque within spectral lines, while a star is opaque at all wavelengths. The brightness of each depends on the usual T4 relation. If, as is usually the case, the cloud is colder than the star (or the star’s atmosphere is colder th ...
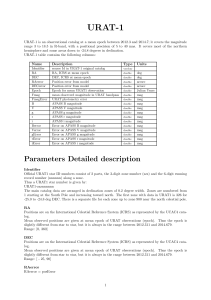
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... slightly different from star to star, but it is always in the range between 2012.311 and 2014.679. Range: [0, 360] DEC Positions are on the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) as represented by the UCAC4 catalog. Mean observed positions are given at mean epoch of URAT observations (epoch ...
... slightly different from star to star, but it is always in the range between 2012.311 and 2014.679. Range: [0, 360] DEC Positions are on the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) as represented by the UCAC4 catalog. Mean observed positions are given at mean epoch of URAT observations (epoch ...
PP 23-The Solar System
... The chromosphere (which means "colored sphere") is a transparent layer, just above the photosphere. ...
... The chromosphere (which means "colored sphere") is a transparent layer, just above the photosphere. ...
Powerpoint file
... Short period M dwarfs are very active and we would have seen Ca II emission from the binary stars and X-ray emission ...
... Short period M dwarfs are very active and we would have seen Ca II emission from the binary stars and X-ray emission ...
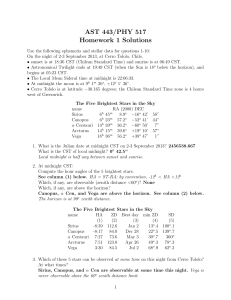
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
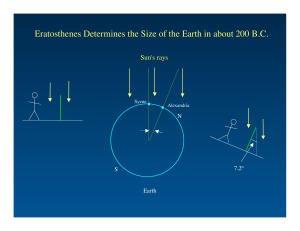
Eratosthenes Determines the Size of the Earth in about 200 B.C.
... • The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. • Rotation axis inclined 23.5° away from the perpendicular to the orbital plane. => This causes solar illumination and number of daylight hours to vary at any location throughout the year. ...
... • The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. • Rotation axis inclined 23.5° away from the perpendicular to the orbital plane. => This causes solar illumination and number of daylight hours to vary at any location throughout the year. ...
Worksheet
... 4. Solar Neutrinos - Many of the thermonuclear fusion reactions predicted to occur in the core of our Sun produce a sub-atomic particle, known as a neutrino. As its name implies, it has no charge, and its main property is that it does not interact with other matter very much (doing so through the we ...
... 4. Solar Neutrinos - Many of the thermonuclear fusion reactions predicted to occur in the core of our Sun produce a sub-atomic particle, known as a neutrino. As its name implies, it has no charge, and its main property is that it does not interact with other matter very much (doing so through the we ...
Starbirth and Interstellar Matter
... 23. In the very young open cluster of bright blue stars, which have already evolved to the main sequence? A. The more massive stars. B. The less massive stars. C. The less luminous stars. D. The coolest stars. 24. On the H-R diagram, where do the first stars to form fall on the main sequence? A. Upp ...
... 23. In the very young open cluster of bright blue stars, which have already evolved to the main sequence? A. The more massive stars. B. The less massive stars. C. The less luminous stars. D. The coolest stars. 24. On the H-R diagram, where do the first stars to form fall on the main sequence? A. Upp ...
EXPLORING THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... south to north and ending in an impact crater called Gusev. The valley looks like a dried-up river bed, and if it was once a river then there could once have been a lake inside Gusev. With that in mind, NASA landed a rover called Spirit inside Gusev in January 2004, and it spent five years exploring ...
... south to north and ending in an impact crater called Gusev. The valley looks like a dried-up river bed, and if it was once a river then there could once have been a lake inside Gusev. With that in mind, NASA landed a rover called Spirit inside Gusev in January 2004, and it spent five years exploring ...
Surveys of Stars, The interstellar medium
... ISM and stars are the components of the “machine” that makes the universe evolve: the cycle of star formation and death, and the chemical enrichment of the cosmos. ISM also “disturbs” observations, since it absorbs light and ...
... ISM and stars are the components of the “machine” that makes the universe evolve: the cycle of star formation and death, and the chemical enrichment of the cosmos. ISM also “disturbs” observations, since it absorbs light and ...
cifutielu`s Astronomy Test 2014
... 8. Which variable will, within a few million years, expel its outer envelope as a planetary nebula and become a white dwarf? 9. Which variable is found mainly in globular clusters? ...
... 8. Which variable will, within a few million years, expel its outer envelope as a planetary nebula and become a white dwarf? 9. Which variable is found mainly in globular clusters? ...
Slide 1
... • "I will explain," says Hooke, in a communication to the Royal Society in 1666, "a system of the world very different from any yet received. It is founded on the following positions. 1. That all the heavenly bodies have not only a gravitation of their parts to their own proper centre, but that they ...
... • "I will explain," says Hooke, in a communication to the Royal Society in 1666, "a system of the world very different from any yet received. It is founded on the following positions. 1. That all the heavenly bodies have not only a gravitation of their parts to their own proper centre, but that they ...
Aquarius sign scorpio rising
... The Sign rising over the horizon at the time of your birth is the Ascendant, or Rising Sign. This changes every two hours, approximately (see note below table). Find out more about the astrology and the 12 Signs of the Zodiac. Learn about what your sign means and how if affects your life. Informatio ...
... The Sign rising over the horizon at the time of your birth is the Ascendant, or Rising Sign. This changes every two hours, approximately (see note below table). Find out more about the astrology and the 12 Signs of the Zodiac. Learn about what your sign means and how if affects your life. Informatio ...
IND 6 - 1 Stars and Stellar Evolution In order to better understand
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
Galileo & the Telescope—Sept 21
... in a few days she was reduced to a semicircle. She maintained this shape for many days, all the while, however, growing in size. At present, she is becoming sickle-shaped… ...
... in a few days she was reduced to a semicircle. She maintained this shape for many days, all the while, however, growing in size. At present, she is becoming sickle-shaped… ...
Slide 1
... • 1) Timing of gas loss – Presence of gas tends to cause planets to spiral inwards, hence timing of gas loss is important – Since outer planets can accrete gas if large enough, the relative timescales of planetary growth and gas loss are important ...
... • 1) Timing of gas loss – Presence of gas tends to cause planets to spiral inwards, hence timing of gas loss is important – Since outer planets can accrete gas if large enough, the relative timescales of planetary growth and gas loss are important ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.