Stars in Motion
... stars for which distances and motions are available. Velocities of stars in the Milky Way are on the order of 3 × 104 m · s−1 , though some can be as high as 105 m · s−1 . The Sun’s motion through space with respect to the neighboring stars is 2 × 104 m · s−1 . ...
... stars for which distances and motions are available. Velocities of stars in the Milky Way are on the order of 3 × 104 m · s−1 , though some can be as high as 105 m · s−1 . The Sun’s motion through space with respect to the neighboring stars is 2 × 104 m · s−1 . ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... few comments on the overall judging: The quality of images entered into this years competition was of a high standard making it challenging to judge. In the Artistic/Misc and Newcomers categories, I was mainly looking for well composed natural looking images that stood out from the rest and unique i ...
... few comments on the overall judging: The quality of images entered into this years competition was of a high standard making it challenging to judge. In the Artistic/Misc and Newcomers categories, I was mainly looking for well composed natural looking images that stood out from the rest and unique i ...
The Earth`s orbit and an exoplanetary orbit 1 Creating the objects 2
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
The Earth`s orbit and an exoplanetary orbit 1 Creating
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
Lab 5 - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy
... and structure and morphology of the HII region. Estimate the electron density form the size and surface brightness of the H-alpha emission. Estimate the extinction from the H-alpa / H-beta ratio, which is about 3.0 for un-reddened emission by hydrogen. From the de-reddened emission, calculate the lu ...
... and structure and morphology of the HII region. Estimate the electron density form the size and surface brightness of the H-alpha emission. Estimate the extinction from the H-alpa / H-beta ratio, which is about 3.0 for un-reddened emission by hydrogen. From the de-reddened emission, calculate the lu ...
arXiv:1404.0641v2 [astro
... complex life at optimal conditions equivalent to ones established on the Earth. From this point of view, most (if not all) known habitable planets can only potentially serve as places for developing biota but can hardly carry it currently. This conclusion follows from the fact that all habitable pla ...
... complex life at optimal conditions equivalent to ones established on the Earth. From this point of view, most (if not all) known habitable planets can only potentially serve as places for developing biota but can hardly carry it currently. This conclusion follows from the fact that all habitable pla ...
chapter01lecturecdl
... • Apparent groupings of stars into constellations seen on celestial sphere are not true, physical groupings. ...
... • Apparent groupings of stars into constellations seen on celestial sphere are not true, physical groupings. ...
13.1 Introduction 13.2 The Red Giant Branch
... An important process experienced by stars while they are in the red giant phase is mass loss. As the stellar luminosity and radius increase while a star evolves along the giant branch, the envelope becomes loosely bound and it is relatively easy for the large photon flux to remove mass from the stel ...
... An important process experienced by stars while they are in the red giant phase is mass loss. As the stellar luminosity and radius increase while a star evolves along the giant branch, the envelope becomes loosely bound and it is relatively easy for the large photon flux to remove mass from the stel ...
Part 1 - Cura
... plane of Ecliptic. At the same time, all these Heavenly objects experience the same influence, the Galactic Center and other Galactic objects exert to them, e.g. from the Southern Pole of Ecliptic (See below). From this point of view, the Solar System (SS) as the whole is called the Heliosphere [8]. ...
... plane of Ecliptic. At the same time, all these Heavenly objects experience the same influence, the Galactic Center and other Galactic objects exert to them, e.g. from the Southern Pole of Ecliptic (See below). From this point of view, the Solar System (SS) as the whole is called the Heliosphere [8]. ...
arXiv:0905.3008v1 [astro-ph.EP] 19 May 2009
... In this paper, we considered the secular increase of astronomical unit recently reported by Krasinsky and Brumberg (2004), and suggested a possible explanation for this secular trend by means of the conservation law of total angular momentum. Assuming the existence of some tidal interactions that tr ...
... In this paper, we considered the secular increase of astronomical unit recently reported by Krasinsky and Brumberg (2004), and suggested a possible explanation for this secular trend by means of the conservation law of total angular momentum. Assuming the existence of some tidal interactions that tr ...
The Origin, Structure, and Evolution of the Stars
... diagram. Our calculations indicate that the more massive stars “burn” their fuel so rapidly they cannot last very long. Some of these bright stars must have been formed more recently than the earth, perhaps some even as recently as the appearance of early man. By the same arguments, there must have ...
... diagram. Our calculations indicate that the more massive stars “burn” their fuel so rapidly they cannot last very long. Some of these bright stars must have been formed more recently than the earth, perhaps some even as recently as the appearance of early man. By the same arguments, there must have ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) ISSN: 2278-4861.
... This method of analysis has shown to be a simple method of verifying the new intensity formula by using atomic and stellar data. By using this method together with the new intensity formula it has been possible to determine the mean electron temperature in different laboratory plasmas and in the opt ...
... This method of analysis has shown to be a simple method of verifying the new intensity formula by using atomic and stellar data. By using this method together with the new intensity formula it has been possible to determine the mean electron temperature in different laboratory plasmas and in the opt ...
THREE INTRIGUER NEBULAE IN CONSTELLATION CARINA
... Astronomical Twilight. The first step was to identify constellation Antlia whose stars, although faint, were clearly visible to the naked eye. Once the constellation was identified I focused on the region where the cluster lies. To make this possible it is necessary to fix our view on the eastern pa ...
... Astronomical Twilight. The first step was to identify constellation Antlia whose stars, although faint, were clearly visible to the naked eye. Once the constellation was identified I focused on the region where the cluster lies. To make this possible it is necessary to fix our view on the eastern pa ...
MAIN SEQUENCE STARS, Red Giants and White Dwarfs
... He BURNING MAIN SEQUENCE -- which is visible on an H-R diagram as the HORIZONTAL BRANCH (lower L but higher Ts than during the He flash). o Stars are again in HYDROSTATIC EQUILIBRIUM throughout: the thermostat works again o These are still RGs, and on HB the higher masses are to the left part of the ...
... He BURNING MAIN SEQUENCE -- which is visible on an H-R diagram as the HORIZONTAL BRANCH (lower L but higher Ts than during the He flash). o Stars are again in HYDROSTATIC EQUILIBRIUM throughout: the thermostat works again o These are still RGs, and on HB the higher masses are to the left part of the ...
Quiz Reviews - Orion Observatory
... 1. How did scientists first look for extrasolar planets? Why were their discoveries false? 2. How were their first extrasolar planets found? Why were scientists less interested in them? 3. How was the first extrasolar planet orbiting a main sequence star found? Who discovered it? Why was this discov ...
... 1. How did scientists first look for extrasolar planets? Why were their discoveries false? 2. How were their first extrasolar planets found? Why were scientists less interested in them? 3. How was the first extrasolar planet orbiting a main sequence star found? Who discovered it? Why was this discov ...
the galaxy in which we live - Cosmos
... gravitationally bound forming a much larger structure: our Milky Way Galaxy. There are huge numbers of galaxies apart from our own, constituting the basic structural units of the Universe. ...
... gravitationally bound forming a much larger structure: our Milky Way Galaxy. There are huge numbers of galaxies apart from our own, constituting the basic structural units of the Universe. ...
S1-4-03 - Celestial Navigation
... Begin by showing students a star trails photograph of how stars move across the night sky in the northern hemisphere. Try to draw out more in-depth reasoning for the circular pattern and the star in the middle, explaining that the picture is of star trails due to the earth's rotation. Guide the stud ...
... Begin by showing students a star trails photograph of how stars move across the night sky in the northern hemisphere. Try to draw out more in-depth reasoning for the circular pattern and the star in the middle, explaining that the picture is of star trails due to the earth's rotation. Guide the stud ...
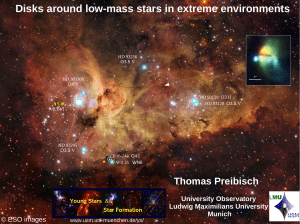
Disks around low-mass stars in extreme environments
... Problem of many injection scenarios: In most clusters (e.g., Orion Nebula Cluster), all stars formed at ~ the same time. When the first supernova happens (after > 4 Myr), most low-mass stars have already largely dispersed their disks (i.e. planetesimal formation is already finished). ...
... Problem of many injection scenarios: In most clusters (e.g., Orion Nebula Cluster), all stars formed at ~ the same time. When the first supernova happens (after > 4 Myr), most low-mass stars have already largely dispersed their disks (i.e. planetesimal formation is already finished). ...
Slide 1
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
Chapter 20
... form complex molecules, primitive life may well have arisen not only on the Earth but also in other locations. The appearance of very simple organisms in Earth rocks that are 3.5 billion years old, and indirect evidence for life as far back as 3.8 billion years (not long after the end of the bombard ...
... form complex molecules, primitive life may well have arisen not only on the Earth but also in other locations. The appearance of very simple organisms in Earth rocks that are 3.5 billion years old, and indirect evidence for life as far back as 3.8 billion years (not long after the end of the bombard ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.








![arXiv:0905.3008v1 [astro-ph.EP] 19 May 2009](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017089867_1-59d3a66da8f73e76d7a42b1bdf6b26f3-300x300.png)