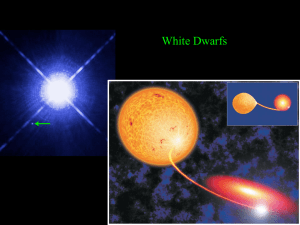
white dwarf supernova
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
Slide 1
... low mass, hard to detect Kuiper belt like discs. Observations find hot, dusty discs within tidal radius Can we link the two populations? Maybe the Kuiper-belts provide the reservoir of material required to replenish the hot discs? We just need a mechanism to move the ...
... low mass, hard to detect Kuiper belt like discs. Observations find hot, dusty discs within tidal radius Can we link the two populations? Maybe the Kuiper-belts provide the reservoir of material required to replenish the hot discs? We just need a mechanism to move the ...
Beyond Pluto
... planets on his bedroom wall. On it, Pluto was depicted as ―this crazy and very eccentric planet,‖ he says. ―It was everyone‘s favorite crazy planet.‖ Brown still recalls the mnemonic he learned for the names of the planets: Martha visits every Monday and—a for asteroids—just stays until noon, period ...
... planets on his bedroom wall. On it, Pluto was depicted as ―this crazy and very eccentric planet,‖ he says. ―It was everyone‘s favorite crazy planet.‖ Brown still recalls the mnemonic he learned for the names of the planets: Martha visits every Monday and—a for asteroids—just stays until noon, period ...
Grade 9 Botony: plant nutrition
... The sun is a star. It is our closest star, which is why it seems so different from the tiny stars we see at night. The sun is one of the stars in the Milky Way galaxy. Like other stars, the sun is a ball of burning gas made up of different layers. It has a core in the middle which is extreme ...
... The sun is a star. It is our closest star, which is why it seems so different from the tiny stars we see at night. The sun is one of the stars in the Milky Way galaxy. Like other stars, the sun is a ball of burning gas made up of different layers. It has a core in the middle which is extreme ...
Local group
... • Our galactic neighborhood consists of one more 'giant' spiral (M31, Andromeda), a smaller spiral M33 and lots of (>35 galaxies), most of which are dwarf ellipticals and irregulars with low mass; most are satellites of MW, M31 or M33 • The gravitational interaction between these systems is complex ...
... • Our galactic neighborhood consists of one more 'giant' spiral (M31, Andromeda), a smaller spiral M33 and lots of (>35 galaxies), most of which are dwarf ellipticals and irregulars with low mass; most are satellites of MW, M31 or M33 • The gravitational interaction between these systems is complex ...
A Planetary Overview
... now a dwarf planet, along with the asteroid Ceres and Eris, an object a bit larger than Pluto in the Kuiper belt. The IAU will establish a process to assign borderline objects into either dwarf planet or other categories. The third category above includes most of the asteroids, most of the objects b ...
... now a dwarf planet, along with the asteroid Ceres and Eris, an object a bit larger than Pluto in the Kuiper belt. The IAU will establish a process to assign borderline objects into either dwarf planet or other categories. The third category above includes most of the asteroids, most of the objects b ...
Grade 5 Unit 6
... that occurs between each object and the Earth. In addition, students should use their observations as evidence to support an argument that the gravitational force exerted by the Earth on objects is directed “down” (towards the center of the Earth), no matter the height or location from which an obje ...
... that occurs between each object and the Earth. In addition, students should use their observations as evidence to support an argument that the gravitational force exerted by the Earth on objects is directed “down” (towards the center of the Earth), no matter the height or location from which an obje ...
Star Formation in Bok Globules - European Southern Observatory
... Figure 2 shows a blue IDS spectrum from the ESO 3.6-m telescope of Sernes 135. It is noteworthy that the Hß line at A 4861 has a central emission peak which is displaced bluewards, indicating outflow of malter with over 100 km/sec. Optical and infrared photometry shows that over 80 % of the radiatio ...
... Figure 2 shows a blue IDS spectrum from the ESO 3.6-m telescope of Sernes 135. It is noteworthy that the Hß line at A 4861 has a central emission peak which is displaced bluewards, indicating outflow of malter with over 100 km/sec. Optical and infrared photometry shows that over 80 % of the radiatio ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... Individual objects show a variety of characteristics that do not always track the “standard model.” Collectively, SNRs can affect star formation and galactic evolution ...
... Individual objects show a variety of characteristics that do not always track the “standard model.” Collectively, SNRs can affect star formation and galactic evolution ...
p35-KIDS_Layout 1
... was probably once a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt. It is close enough to Neptune to be locked into asynchronous rotation, and it is slowly spiralling inward because of tidal acceleration. It will eventually be torn apart, in about 3.6 billion years, when it reaches the Roche limit. In 1989, Triton ...
... was probably once a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt. It is close enough to Neptune to be locked into asynchronous rotation, and it is slowly spiralling inward because of tidal acceleration. It will eventually be torn apart, in about 3.6 billion years, when it reaches the Roche limit. In 1989, Triton ...
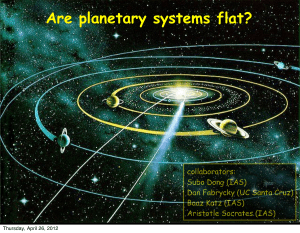
Are planetary systems flat?
... • circular orbits cannot remain circular, and are excited to high inclination and eccentricity •circular orbits are chaotic ...
... • circular orbits cannot remain circular, and are excited to high inclination and eccentricity •circular orbits are chaotic ...
Measuring the Stars Section 29.2
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
Terrestrial Planets
... timescales is achieved by: • passing stellar light through a cell containing iodine, imprinting large number of additional lines of known wavelength into the spectrum • with the calibrating data suffering identical instrumental distortions as the data ...
... timescales is achieved by: • passing stellar light through a cell containing iodine, imprinting large number of additional lines of known wavelength into the spectrum • with the calibrating data suffering identical instrumental distortions as the data ...
Chapter 9 - Astronomy
... moons, have eccentric orbits, dark surfaces, and are probably captured asteroids. 2. Io, the Galilean moon closest to Jupiter, has active volcanoes. Voyager images suggested that Io’s lava flows were mostly molten sulfur but Galileo observed flows at 1800 K (much higher than sulfur’s vaporization te ...
... moons, have eccentric orbits, dark surfaces, and are probably captured asteroids. 2. Io, the Galilean moon closest to Jupiter, has active volcanoes. Voyager images suggested that Io’s lava flows were mostly molten sulfur but Galileo observed flows at 1800 K (much higher than sulfur’s vaporization te ...
Review Sheet and Study Hints - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... Draw and label it Include magnitude (M), luminosity (L/Lo), color or color index (B-V), spectral type OBAFGKM and temperature. Point towards increasing luminosity, temperature, radius, redder color. Point arrows towards increasing main-sequence-radius and m.-s.-mass. Evolutionary Tracks draw ...
... Draw and label it Include magnitude (M), luminosity (L/Lo), color or color index (B-V), spectral type OBAFGKM and temperature. Point towards increasing luminosity, temperature, radius, redder color. Point arrows towards increasing main-sequence-radius and m.-s.-mass. Evolutionary Tracks draw ...
Life Cycle of the Stars
... These nebulae are very large and have very low density Their size means that their masses are large despite the low density. ...
... These nebulae are very large and have very low density Their size means that their masses are large despite the low density. ...
Nucleosynthesis and the death of stars
... • For the majority of stars (~95%, corresponding to stars with initial masses of less than 8 M-Sun), direct nuclear fusion does not proceed beyond helium, and carbon is never fused. • Most of the nucleosynthesis occurs through slow neutron capture during the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), a brief ph ...
... • For the majority of stars (~95%, corresponding to stars with initial masses of less than 8 M-Sun), direct nuclear fusion does not proceed beyond helium, and carbon is never fused. • Most of the nucleosynthesis occurs through slow neutron capture during the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), a brief ph ...
PHYS3380_110215_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the heat capacity. The relatively low temperature in this region simultaneously causes the opacity due to heavier elements to be high enough to produc ...
... •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the heat capacity. The relatively low temperature in this region simultaneously causes the opacity due to heavier elements to be high enough to produc ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.