doc - Pocket Stars
... The LOPs (Line of Position) Page is used to calculate an improved fix from two or more LOPs. You can select from amongst the previously acquired observations by checking the associated checkbox. The results are shown in red text in the lower left corner. These include: - Corrected Assumed Position - ...
... The LOPs (Line of Position) Page is used to calculate an improved fix from two or more LOPs. You can select from amongst the previously acquired observations by checking the associated checkbox. The results are shown in red text in the lower left corner. These include: - Corrected Assumed Position - ...
Lyman Break Galaxies at z~ 5: Luminosity Function
... Since their first discovery in the late 1990s, the Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) at z ∼ 3 have been extensively investigated in various ways and knowledge on their nature has been accumulated. Their rest UV spectra resemble those of nearby active star-forming galaxies (Steidel et al. 1996b). On-going ...
... Since their first discovery in the late 1990s, the Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) at z ∼ 3 have been extensively investigated in various ways and knowledge on their nature has been accumulated. Their rest UV spectra resemble those of nearby active star-forming galaxies (Steidel et al. 1996b). On-going ...
this PDF file
... In the first attempt only template spectra (with no I2 gas cell inserted) were used for the analysis. However, I2 molecular absorption affects the spectrum up to 660 nm only, so it does not influence 7Li line region. Hence, in the final analysis it was also possible to use the “red” spectra obtained ...
... In the first attempt only template spectra (with no I2 gas cell inserted) were used for the analysis. However, I2 molecular absorption affects the spectrum up to 660 nm only, so it does not influence 7Li line region. Hence, in the final analysis it was also possible to use the “red” spectra obtained ...
Self-similarity in the chemical evolution of galaxies and the delay
... W15 sample. Here, we did not impose the additional cut based on the 1σ scatter of the Johansson et al. (2012) massage relation (see Section 6.3.1 of Y13). This additional cut would have removed those low mass model galaxies that we know are too old and red, due to efficient stripping and SN feedback ...
... W15 sample. Here, we did not impose the additional cut based on the 1σ scatter of the Johansson et al. (2012) massage relation (see Section 6.3.1 of Y13). This additional cut would have removed those low mass model galaxies that we know are too old and red, due to efficient stripping and SN feedback ...
4. Star Formation
... cloud core would lead to the buildup of a quasi-static 1/r2 density structure that contracts on times scales of the order of the ambipolar diffusion timescale. This is called quasi-static since τ AD >> τ f f . When a singularity is formed in the centre, the system becomes unstable and undergoes an i ...
... cloud core would lead to the buildup of a quasi-static 1/r2 density structure that contracts on times scales of the order of the ambipolar diffusion timescale. This is called quasi-static since τ AD >> τ f f . When a singularity is formed in the centre, the system becomes unstable and undergoes an i ...
Measuring the Rotational Speed of Spiral Galaxies and
... electrons later drop back down to lower energy levels. When an electron jumps from the n=3 level to the n=2 level, the H-alpha emission line at 6563 Angstroms (Å; 1 Å = 10-9 m) is emitted. This emission line is in the red region of the visible spectrum. Hydrogen is abundant in the universe, so this ...
... electrons later drop back down to lower energy levels. When an electron jumps from the n=3 level to the n=2 level, the H-alpha emission line at 6563 Angstroms (Å; 1 Å = 10-9 m) is emitted. This emission line is in the red region of the visible spectrum. Hydrogen is abundant in the universe, so this ...
LET THE STARS GET IN YOUR EYES SKY MOTIONS
... telescope the more light it gathers. The ability to gather light becomes crucial when magnifying objects because enlarging them makes dimmer objects harder to see. The "f" focal ratio of a telescope is found by dividing the telescope's focal length by the aperture. It is important to note telescopes ...
... telescope the more light it gathers. The ability to gather light becomes crucial when magnifying objects because enlarging them makes dimmer objects harder to see. The "f" focal ratio of a telescope is found by dividing the telescope's focal length by the aperture. It is important to note telescopes ...
Nucleosynthesis, the r-Process, Abundances and Jim Truran
... and Hydrodynamic Models of the Nova Outburst Cameron & Truran (1977) The Supernova Trigger for the Formation of the Solar System Truran, Cowan & Cameron (1978) The Helium Driven rProcess in Supernovae Truran (1981) A New Interpretation of the Heavy Element Abundances in Metal-deficient Stars Cowan, ...
... and Hydrodynamic Models of the Nova Outburst Cameron & Truran (1977) The Supernova Trigger for the Formation of the Solar System Truran, Cowan & Cameron (1978) The Helium Driven rProcess in Supernovae Truran (1981) A New Interpretation of the Heavy Element Abundances in Metal-deficient Stars Cowan, ...
Observational Evidence for Dark Matter Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC XXXIX SLAC Summer Institute
... By measuring the velocity (dispersion) of the galaxies in the Coma cluster, Zwicky could infer its total mass. However, the luminous mass (the galaxies in the cluster) was far smaller! ...
... By measuring the velocity (dispersion) of the galaxies in the Coma cluster, Zwicky could infer its total mass. However, the luminous mass (the galaxies in the cluster) was far smaller! ...
The SAMI Pilot Survey: The Fundamental and Mass Planes in Three
... plane with coefficients similar, but not identical, to those in the optical. La Barbera et al. (2010) compared the optical and NIR FPs in a large, homogeneous sample of galaxies, finding only small variations in the FP coefficients with wavelength. Another source of variation in the FP coefficients ...
... plane with coefficients similar, but not identical, to those in the optical. La Barbera et al. (2010) compared the optical and NIR FPs in a large, homogeneous sample of galaxies, finding only small variations in the FP coefficients with wavelength. Another source of variation in the FP coefficients ...
Review for final
... 7. Explain azimuth and altitude as parts of a celestial coordinate system. Include when are they useful 8. Find objects in the sky by computing altitude and azimuth using your hand o If your fist fits 9 times between the horizon and the zenith, it covers 10o. Explain why o find how many degrees a ha ...
... 7. Explain azimuth and altitude as parts of a celestial coordinate system. Include when are they useful 8. Find objects in the sky by computing altitude and azimuth using your hand o If your fist fits 9 times between the horizon and the zenith, it covers 10o. Explain why o find how many degrees a ha ...
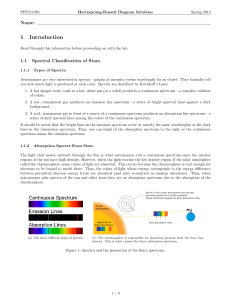
1 Introduction - High Point University
... Table 6: Fill in the empty fields above. 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of al ...
... Table 6: Fill in the empty fields above. 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of al ...
21_Testbank
... 28) Where are the X rays produced that are emitted by quasars and other active galactic nuclei? A) in hot gas in an accretion disk around a central black hole B) in ionization nebulae of interstellar gas that surround the accretion disk C) in dust grains in molecular clouds that encircle the active ...
... 28) Where are the X rays produced that are emitted by quasars and other active galactic nuclei? A) in hot gas in an accretion disk around a central black hole B) in ionization nebulae of interstellar gas that surround the accretion disk C) in dust grains in molecular clouds that encircle the active ...
–1– 1. Stellar Evolution For Massive Stars 1.1. The Importance of
... during the main sequence phase is proportional to ∆M/M ∝ M 1.8 . Because of this strong dependence on mass, mass loss becomes very important for high mass stars. If high mass 0Z stars really do have very weak winds, they will not be very effective at polluting the ISM with nuclear processed material ...
... during the main sequence phase is proportional to ∆M/M ∝ M 1.8 . Because of this strong dependence on mass, mass loss becomes very important for high mass stars. If high mass 0Z stars really do have very weak winds, they will not be very effective at polluting the ISM with nuclear processed material ...
The Magellan 20 Telescope Science Goals
... 300,000 in the single-DM adaptive mode. The vast increase in volume is critical in being able to define large samples of galaxies with particular properties (for example environment, luminosity, or isophotal characteristics). The current state-of-the-art produces measurements of high order moments o ...
... 300,000 in the single-DM adaptive mode. The vast increase in volume is critical in being able to define large samples of galaxies with particular properties (for example environment, luminosity, or isophotal characteristics). The current state-of-the-art produces measurements of high order moments o ...
Possible origin of the Damocloids
... On 2010 March 10, we discovered a new asteroid moving along a very eccentric orbit, designated as 2010 EJ104. We observed this rapidly moving object using the 1.04/1.20 m Schmidt Telescope (Near Earth Object Survey Telescope) at the Xuyi station of Purple Mountain Observatory (PMO) (Zhao et al. 2008 ...
... On 2010 March 10, we discovered a new asteroid moving along a very eccentric orbit, designated as 2010 EJ104. We observed this rapidly moving object using the 1.04/1.20 m Schmidt Telescope (Near Earth Object Survey Telescope) at the Xuyi station of Purple Mountain Observatory (PMO) (Zhao et al. 2008 ...
Kepler`s Laws of Planetary Motion
... 1. The orbit of each planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus. 2. Each planet moves so that an imaginary line drawn from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets about the sun is equal to the ratio ...
... 1. The orbit of each planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus. 2. Each planet moves so that an imaginary line drawn from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets about the sun is equal to the ratio ...
Gemini IFU Observations of Feedback from Radio
... RL objects are rare, what about RQ quasars? RQ quasars at highest luminosity commonly have outflows that are galaxy-wide, round, and likely ...
... RL objects are rare, what about RQ quasars? RQ quasars at highest luminosity commonly have outflows that are galaxy-wide, round, and likely ...
The Milky Way thin disk structure as revealed by stars and young
... experienced quite a significant burst of activity. This is mostly because of the failure of HI studies, that cannot go much beyond the detection of gas density peaks in the velocity space (McClure-Griffiths et al. 2004; Dame et al 2011), and struggle in the process of translating these velocities into ...
... experienced quite a significant burst of activity. This is mostly because of the failure of HI studies, that cannot go much beyond the detection of gas density peaks in the velocity space (McClure-Griffiths et al. 2004; Dame et al 2011), and struggle in the process of translating these velocities into ...
The old globular cluster system of the dIrr galaxy NGC 1427A in the
... that all three dwarf galaxy types host a population of old GCs with very similar (V − I) colors. The mean color of this population is almost identical to the (V − I) colors of the blue GC population in massive early-type galaxies. One way to address the evolutionary connection between dE, dSph, dIrr ...
... that all three dwarf galaxy types host a population of old GCs with very similar (V − I) colors. The mean color of this population is almost identical to the (V − I) colors of the blue GC population in massive early-type galaxies. One way to address the evolutionary connection between dE, dSph, dIrr ...
- Cosmotography
... dwarfs have been identified observationally (Stinson et al. 2009), but it is not clear if these stars were accreted, or formed in-situ. Star formation in dwarfs is thought to occur in stochastic episodes (Tolstoy et al. 2009; Weisz et al. 2011), which could be triggered by accretion events. An iconi ...
... dwarfs have been identified observationally (Stinson et al. 2009), but it is not clear if these stars were accreted, or formed in-situ. Star formation in dwarfs is thought to occur in stochastic episodes (Tolstoy et al. 2009; Weisz et al. 2011), which could be triggered by accretion events. An iconi ...
Galaxy Image Classification using Non
... compared and evaluated the behavior of 10 artificial neural networks based classifiers based on selected sets of galaxy features derived from image analysis and principle component analysis features (PCA). The support vector machine (SVM) based classifier provides the best results about 99.5%. [7], ...
... compared and evaluated the behavior of 10 artificial neural networks based classifiers based on selected sets of galaxy features derived from image analysis and principle component analysis features (PCA). The support vector machine (SVM) based classifier provides the best results about 99.5%. [7], ...
The nature of the faint galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field
... by mergers (67 per cent of the mergers in Fig. 1 have B - V < 0.5) and cover a range of U - B colours ( - 1 < U - B < 1), locating them at different redshifts. These are reasonably well fitted by our galaxy models, shifted to high redshifts (z'" 1.5-3). According to these models, most of the mergers ...
... by mergers (67 per cent of the mergers in Fig. 1 have B - V < 0.5) and cover a range of U - B colours ( - 1 < U - B < 1), locating them at different redshifts. These are reasonably well fitted by our galaxy models, shifted to high redshifts (z'" 1.5-3). According to these models, most of the mergers ...
IAC_L5_bulge_GALAH
... The disk took ~ 2 Gyr to evolve chemically and dynamically before going unstable and buckling into the peanut structure, so the components A-E are trapped relics of the Galactic disk and halo from that time. The instability process generated a mapping of the stars of the early disk into the boxy/pea ...
... The disk took ~ 2 Gyr to evolve chemically and dynamically before going unstable and buckling into the peanut structure, so the components A-E are trapped relics of the Galactic disk and halo from that time. The instability process generated a mapping of the stars of the early disk into the boxy/pea ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.