2 Measurements in Astronomy
... Measurements in Astronomy Astronomical unit: distance from Earth to the Sun (about 150,000,000 kilometers, or 93,000,000 miles). Used for measuring distances within our solar system. Light year: the distance light travels in one year (nearly 10 trillion kilometers or 6 trillion miles). Used for ...
... Measurements in Astronomy Astronomical unit: distance from Earth to the Sun (about 150,000,000 kilometers, or 93,000,000 miles). Used for measuring distances within our solar system. Light year: the distance light travels in one year (nearly 10 trillion kilometers or 6 trillion miles). Used for ...
Luminosity
... • Luminosity=intrinsic brightness =total energy emitted • Diameter and Mass • And to define a typical star ...
... • Luminosity=intrinsic brightness =total energy emitted • Diameter and Mass • And to define a typical star ...
Lecture 5: The H-R diagram, standard candles and cosmic distances
... and forth in wavelength due to the Doppler effect, as the orbits of the stars carry them first toward then away from the Earth • Analysis of these spectral shifts allows velocity and period to be derived, and hence M1+M2 ...
... and forth in wavelength due to the Doppler effect, as the orbits of the stars carry them first toward then away from the Earth • Analysis of these spectral shifts allows velocity and period to be derived, and hence M1+M2 ...
09astrophysics_2007Nov
... •“Spectroscopic Binaries” are so close together you only see one star, but we can see the spectral lines split and converge as the starts orbit. ...
... •“Spectroscopic Binaries” are so close together you only see one star, but we can see the spectral lines split and converge as the starts orbit. ...
Document
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
Earth and Stars
... certainly do better in the matter of accuracy. Yet, in spite of all these flaws, it worked fine: around 250 BC, Earth had at last a size. ...
... certainly do better in the matter of accuracy. Yet, in spite of all these flaws, it worked fine: around 250 BC, Earth had at last a size. ...
Celestial Distances - Wayne State University
... To define the period-luminosity relation with actual numbers (to calibrate it), astronomers first had to measure the actual distances to a few nearby cepheids (in other clusters of stars) in another way 1 August 2005 ...
... To define the period-luminosity relation with actual numbers (to calibrate it), astronomers first had to measure the actual distances to a few nearby cepheids (in other clusters of stars) in another way 1 August 2005 ...
SECTION 8: STARS- OBSERVING CONSTELLATIONS INTRODUCTION
... A light year is a unit of measure for distance in space and equals the distance light travels in 1 year. Light travels 300,000 km (186,000 miles) per second. It takes 8 ½ minutes for light to reach us from our Sun and 4.5 light years for light to reach us from the next closest star, Centauri Proxima ...
... A light year is a unit of measure for distance in space and equals the distance light travels in 1 year. Light travels 300,000 km (186,000 miles) per second. It takes 8 ½ minutes for light to reach us from our Sun and 4.5 light years for light to reach us from the next closest star, Centauri Proxima ...
File
... From here on earth it is difficult to fathom the huge distances that exist between the stars and planets. The circumference of the earth (38,500 km) may seem like a long way to us but is an insignificant distance in space. The nearest celestial object to earth, the moon, is approximately 400, 000 km ...
... From here on earth it is difficult to fathom the huge distances that exist between the stars and planets. The circumference of the earth (38,500 km) may seem like a long way to us but is an insignificant distance in space. The nearest celestial object to earth, the moon, is approximately 400, 000 km ...
Celestial Distances
... Motion of the star relative to the Sun (Ch. 16): radial motion: star moves along line of sight proper motion: star moves across celestial sphere February 14, 2006 ...
... Motion of the star relative to the Sun (Ch. 16): radial motion: star moves along line of sight proper motion: star moves across celestial sphere February 14, 2006 ...
E3 STELLAR DISTANCES E4 COSMOLOGY
... A main sequence star emits most of its energy at λ = 2.4 x 10-7 m. Its apparent brightness is measure at 4.3 x 10-9 W m-2. How far away is the star? [28 pc] ...
... A main sequence star emits most of its energy at λ = 2.4 x 10-7 m. Its apparent brightness is measure at 4.3 x 10-9 W m-2. How far away is the star? [28 pc] ...
here - ScienceA2Z.com
... Moving cluster parallax is a technique where the motions of individual stars in a nearby star cluster can be used to find the distance to the cluster. Only open clusters are near enough for this technique to be useful. In particular the distance obtained for the Hyades has been an important step in ...
... Moving cluster parallax is a technique where the motions of individual stars in a nearby star cluster can be used to find the distance to the cluster. Only open clusters are near enough for this technique to be useful. In particular the distance obtained for the Hyades has been an important step in ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... Because of Earth’s movement around the sun Apparent Magnitude – What is it? How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
... Because of Earth’s movement around the sun Apparent Magnitude – What is it? How bright a star appears to be to an observer on Earth. ...
ppt - Astronomy & Physics
... Given measured ∆λ, and the wavelength of the atomic line were are looking at, l, we can then get velocity v of object using the speed of light c ...
... Given measured ∆λ, and the wavelength of the atomic line were are looking at, l, we can then get velocity v of object using the speed of light c ...
Document
... Also in the early 1900’s, Lindblad was doing the first kinematic studies of the MW •Estimated mass in MW from all stars in Kapteyn’s model •Determined velocities of GCs to be as high as 250 km/s - much higher than escape velocity of Kapteyn model Lindblad (1927) developed first detailed kinematic m ...
... Also in the early 1900’s, Lindblad was doing the first kinematic studies of the MW •Estimated mass in MW from all stars in Kapteyn’s model •Determined velocities of GCs to be as high as 250 km/s - much higher than escape velocity of Kapteyn model Lindblad (1927) developed first detailed kinematic m ...
Distance in Space and the Birth of Stars
... 0 Parallax is measuring the apparent motion of a nearby ...
... 0 Parallax is measuring the apparent motion of a nearby ...
Absolute magnitude of type Ia supernovae
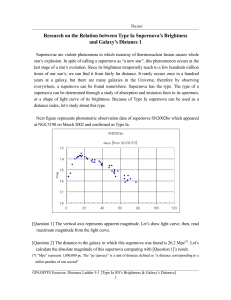
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
measure
... takes light more than 4 years to travel this distance. If the distance from the Earth to the Sun were the width of this screen, the next nearest star would be in Rome. ...
... takes light more than 4 years to travel this distance. If the distance from the Earth to the Sun were the width of this screen, the next nearest star would be in Rome. ...
Parallax
... shift, but will not appear to move as much as it did when it was closer. The same thing happens to stars. The closer stars appear to shift more than the farther stars. The "fixed" background stars are not really fixed; they are just so far away that we cannot distinguish their apparent shift. ...
... shift, but will not appear to move as much as it did when it was closer. The same thing happens to stars. The closer stars appear to shift more than the farther stars. The "fixed" background stars are not really fixed; they are just so far away that we cannot distinguish their apparent shift. ...
ASTR-1020 Exam 2 Review Questions
... 8. What is the difference between an observational and theoretical H-R diagram? What is meant by spectroscopic parallax? 9. What are the strongest spectral features in A stars? What are the strongest spectral features in M stars? What are the strongest optical spectral lines in the Sun? 10. What thr ...
... 8. What is the difference between an observational and theoretical H-R diagram? What is meant by spectroscopic parallax? 9. What are the strongest spectral features in A stars? What are the strongest spectral features in M stars? What are the strongest optical spectral lines in the Sun? 10. What thr ...
Topic E: Astrophysics
... Other important units. Astronomical unit (AU) – the average distance between the Sun and Earth 1AU = 1.5 x 1011m Used to measure distances inside our solar system ...
... Other important units. Astronomical unit (AU) – the average distance between the Sun and Earth 1AU = 1.5 x 1011m Used to measure distances inside our solar system ...
4 Distances in Astronomy
... In 1989–1993 the Hipparcos satellite measured the parallax for 120,000 stars with precision as good as 0.001 arcsec, and for another million stars with lower precision. An angle of 0.001 arcsec is comparable to the angular diameter of a golf ball viewed across the Atlantic Ocean, and corresponds to ...
... In 1989–1993 the Hipparcos satellite measured the parallax for 120,000 stars with precision as good as 0.001 arcsec, and for another million stars with lower precision. An angle of 0.001 arcsec is comparable to the angular diameter of a golf ball viewed across the Atlantic Ocean, and corresponds to ...
Astronomy 242: Review Questions #1 Distributed: February 10
... 12. You observe a sample of Cepheid variable stars in a nearby galaxy. Plotting the average apparent K-band magnitude of each one against the period of pulsation yields Fig. 3. The straight line, a least-squares fit to the data, has the equation mK = 16.40 − 3.53 log(P/day). (a) Does it seem reasona ...
... 12. You observe a sample of Cepheid variable stars in a nearby galaxy. Plotting the average apparent K-band magnitude of each one against the period of pulsation yields Fig. 3. The straight line, a least-squares fit to the data, has the equation mK = 16.40 − 3.53 log(P/day). (a) Does it seem reasona ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.