THERMODYNAMICS. Elements of Physical Chemistry. By P. Atkins
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
THERMODYNAMICS. Elements of Physical Chemistry. By P. Atkins
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
... CONSERVATION OF ENERGY – states that: ...
Chapter 1 Introduction and Definition of Terms
... external influences acting on the system to cause a change in the system and the tendency of the system to resist change. The fixing of the pressure of the gas at P1 and the temperature T1 determines the state of the system and hence fixes the volume at the value V1. If, by suitable decrease in the ...
... external influences acting on the system to cause a change in the system and the tendency of the system to resist change. The fixing of the pressure of the gas at P1 and the temperature T1 determines the state of the system and hence fixes the volume at the value V1. If, by suitable decrease in the ...
PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I Ground Rules Thermodynamics
... temperature until all of the water has been changed into steam. Only then will the steam increase in temperature. Because the water stays at the same temperature, regardless of how fast it is boiling, the potatoes will not cook any faster. How can you cook the potatoes faster? ...
... temperature until all of the water has been changed into steam. Only then will the steam increase in temperature. Because the water stays at the same temperature, regardless of how fast it is boiling, the potatoes will not cook any faster. How can you cook the potatoes faster? ...
Chapter 2 Classical Thermodynamics: The Second Law 2.1 Heat
... common theme, and one we will explore in much more detail later is that an increase in entropy means an increase in disorder. We will see that the entropy of the universe always increases during spontaneous changes (typical example are the flow of heat from a hotter to a cooler body and the free exp ...
... common theme, and one we will explore in much more detail later is that an increase in entropy means an increase in disorder. We will see that the entropy of the universe always increases during spontaneous changes (typical example are the flow of heat from a hotter to a cooler body and the free exp ...
Chapter 20 - NUS Physics Department
... Transfer variables are zero unless a process occurs in which energy is transferred across the boundary of a system Transfer variables are not associated with any given state of the system, only with changes in the state ...
... Transfer variables are zero unless a process occurs in which energy is transferred across the boundary of a system Transfer variables are not associated with any given state of the system, only with changes in the state ...
Biological Thermodynamics
... “…the term energy is difficult to define precisely, but one possible definition might be the capacity to produce an effect” ...
... “…the term energy is difficult to define precisely, but one possible definition might be the capacity to produce an effect” ...
3.1 Thermal concepts (PPT)
... • The interior of roasted meat can never reach temperatures higher than the boiling point of water until all the water is cooked out of it, at which point it would resemble shoe leather. The outside is quickly dried out, however, and can reach the temperature of the surrounding cooking medium. • Coc ...
... • The interior of roasted meat can never reach temperatures higher than the boiling point of water until all the water is cooked out of it, at which point it would resemble shoe leather. The outside is quickly dried out, however, and can reach the temperature of the surrounding cooking medium. • Coc ...
How long does it take to boil an egg?
... instantaneously, the water temperature. This temperature will be homogeneous provided that convection in the water bath due to boiling is sufficiently intense. So, we are faced with the heating of an object with initial internal homogeneous temperature T0 and surface temperature Ts imposed by the wa ...
... instantaneously, the water temperature. This temperature will be homogeneous provided that convection in the water bath due to boiling is sufficiently intense. So, we are faced with the heating of an object with initial internal homogeneous temperature T0 and surface temperature Ts imposed by the wa ...
Chapter 2: Energy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
... Most closed systems remain stationary during a process and, thus, experience no change in their kinetic and potential energies. The change in the stored energy is identical to the change in internal energy for stationary systems. If KE = PE = 0, ...
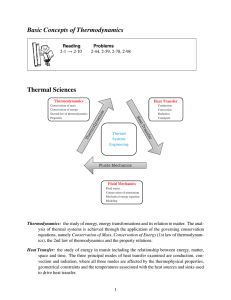
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Thermal Sciences
... • P, V, T, and m are important because they are measurable quantities. Many other thermodynamic quantities can only be calculated and used in calculations when they are related to P, V, T, and m – Pressure (P ) and Temperature (T ) are easily measured intensive properties. Note: They are not always ...
... • P, V, T, and m are important because they are measurable quantities. Many other thermodynamic quantities can only be calculated and used in calculations when they are related to P, V, T, and m – Pressure (P ) and Temperature (T ) are easily measured intensive properties. Note: They are not always ...
1 - WordPress.com
... The mass of a hot air balloon and its cargo (not including the air inside) is 200 kg. The air outside is at a temperature of 10° C and a pressure of 1 ATM = 105 N/m2 . The volume of the balloon is 400 m3 . To what temperature must the air in the balloon be heated before the balloon will lift off? (A ...
... The mass of a hot air balloon and its cargo (not including the air inside) is 200 kg. The air outside is at a temperature of 10° C and a pressure of 1 ATM = 105 N/m2 . The volume of the balloon is 400 m3 . To what temperature must the air in the balloon be heated before the balloon will lift off? (A ...
Heat

In physics, heat is energy in a process of transfer between a system and its surroundings, other than as work or with the transfer of matter. When there is a suitable physical pathway, heat flows from a hotter body to a colder one. The pathway can be direct, as in conduction and radiation, or indirect, as in convective circulation.Because it refers to a process of transfer between two systems, the system of interest, and its surroundings considered as a system, heat is not a state or property of a single system. If heat transfer is slow and continuous, so that the temperature of the system of interest remains well defined, it can sometimes be described by a process function.Kinetic theory explains heat as a macroscopic manifestation of the motions and interactions of microscopic constituents such as molecules and photons.In calorimetry, sensible heat is defined with respect to a specific chosen state variable of the system, such as pressure or volume. Sensible heat transferred into or out of the system under study causes change of temperature while leaving the chosen state variable unchanged. Heat transfer that occurs with the system at constant temperature and that does change that particular state variable is called latent heat with respect to that variable. For infinitesimal changes, the total incremental heat transfer is then the sum of the latent and sensible heat increments. This is a basic paradigm for thermodynamics, and was important in the historical development of the subject.The quantity of energy transferred as heat is a scalar expressed in an energy unit such as the joule (J) (SI), with a sign that is customarily positive when a transfer adds to the energy of a system. It can be measured by calorimetry, or determined by calculations based on other quantities, relying on the first law of thermodynamics.