Receptor Theory and Biological Constraints on Value
... economic quantity, which is represented by a scalar quantity. There are two ways that utility can be interpreted in the context of Equation 2. The first is to interpret utility as z, the exogenous entity, and treat it as if it were a physical quantity that is transformed into a cellular response. Th ...
... economic quantity, which is represented by a scalar quantity. There are two ways that utility can be interpreted in the context of Equation 2. The first is to interpret utility as z, the exogenous entity, and treat it as if it were a physical quantity that is transformed into a cellular response. Th ...
A neuropsychological theory of metaphor
... Whereas Hayek speaks of co-classification of impulses that occur repeatedly together, Hebb (1949) more specifically states, ÔWhen an axon of cell A is near enough to excite B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells ...
... Whereas Hayek speaks of co-classification of impulses that occur repeatedly together, Hebb (1949) more specifically states, ÔWhen an axon of cell A is near enough to excite B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells ...
Gray matters: How neuroscience can inform economics
... Bayesian updating — provided similar “as if” tools which sidestep cognitive detail. Economists then spent decades developing mathematical techniques to make economic predictions without having to measure thoughts or feelings directly. But now neuroscience, the study of the brain and nervous system, ...
... Bayesian updating — provided similar “as if” tools which sidestep cognitive detail. Economists then spent decades developing mathematical techniques to make economic predictions without having to measure thoughts or feelings directly. But now neuroscience, the study of the brain and nervous system, ...
How does alcohol affect the teenage brain?
... It has been more than eight years since Volkmann took his last drink. And while there’s no telling whether his drinking habits during his teens and early twenties impacted his brain function over the long term, experts claim that the incompletely developed brain is remarkably resilient. So theoretic ...
... It has been more than eight years since Volkmann took his last drink. And while there’s no telling whether his drinking habits during his teens and early twenties impacted his brain function over the long term, experts claim that the incompletely developed brain is remarkably resilient. So theoretic ...
blue_brain2 - 123seminarsonly.com
... The neocortex is thought to be responsible for the cognitive functions of language, learning, memory and complex thought. The simulated neurons will be interconnected with rules the team has worked out about how the brain functions. ...
... The neocortex is thought to be responsible for the cognitive functions of language, learning, memory and complex thought. The simulated neurons will be interconnected with rules the team has worked out about how the brain functions. ...
A Step by Step Guide to Understanding and Managing Traumatic
... is a metabolically high cost organ consuming about 20% of the body’s metabolic energy providing further evidence of its complex operations. Further, most energy use is devoted to being ready to think and respond rather than thinking per se. It is this readiness that is often so adversely impacted wh ...
... is a metabolically high cost organ consuming about 20% of the body’s metabolic energy providing further evidence of its complex operations. Further, most energy use is devoted to being ready to think and respond rather than thinking per se. It is this readiness that is often so adversely impacted wh ...
USC Brain Project Specific Aims
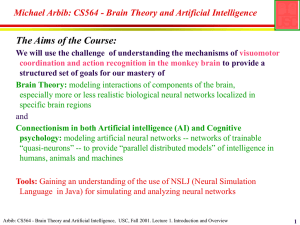
... Michael A Arbib, and Jeffrey Grethe, Editors, 2001, Computing the Brain: A Guide to Neuroinformatics, San Diego: Academic Press (in press) Arbib: CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, USC, Fall 2001. Lecture 1. Introduction and Overview ...
... Michael A Arbib, and Jeffrey Grethe, Editors, 2001, Computing the Brain: A Guide to Neuroinformatics, San Diego: Academic Press (in press) Arbib: CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, USC, Fall 2001. Lecture 1. Introduction and Overview ...
Nativism Versus Neuroconstructivism: Rethinking the Study of
... using an uneven profile automatically to assume the existence in the brain of independently functioning, domain-specific modules. Question (d) underlines the crucial role of developmental time in developmental disorders (Karmiloff-Smith, 1992, 1998, 2007). Paradoxically, numerous studies of developm ...
... using an uneven profile automatically to assume the existence in the brain of independently functioning, domain-specific modules. Question (d) underlines the crucial role of developmental time in developmental disorders (Karmiloff-Smith, 1992, 1998, 2007). Paradoxically, numerous studies of developm ...
Sound Medicine: Using State-of-the
... aware, but not yet in action mode. Alpha is an ideal state to access when participating in martial arts and sports. It is the main reason to consider meditation or relaxation as part of a daily practice, especially for those of us who are “too busy to relax.” Beta frequencies range from 15 to 30 cyc ...
... aware, but not yet in action mode. Alpha is an ideal state to access when participating in martial arts and sports. It is the main reason to consider meditation or relaxation as part of a daily practice, especially for those of us who are “too busy to relax.” Beta frequencies range from 15 to 30 cyc ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... closed and do not allow positively charged ions in. negatively charged ions are on the inside. Electrical activity must get past the threshold to fire. ...
... closed and do not allow positively charged ions in. negatively charged ions are on the inside. Electrical activity must get past the threshold to fire. ...
Are Bigger Brains Better?
... While some increases in brain size will affect cognitive capacity, many increases in certain brain areas — especially those involved in sensory and motor processing — produce only quantitative improvements: more detail, finer resolution, higher sensitivity, greater precision — in other words, more o ...
... While some increases in brain size will affect cognitive capacity, many increases in certain brain areas — especially those involved in sensory and motor processing — produce only quantitative improvements: more detail, finer resolution, higher sensitivity, greater precision — in other words, more o ...
Preview Sample 2
... Common directional terms must be established before undertaking a description of the nervous system. The anatomical directional terms may become confusing due to a 90degree bend in the neuraxis of humans. Comparing the use of the terms between a fourlegged animal and a human is a very useful tool to ...
... Common directional terms must be established before undertaking a description of the nervous system. The anatomical directional terms may become confusing due to a 90degree bend in the neuraxis of humans. Comparing the use of the terms between a fourlegged animal and a human is a very useful tool to ...
Convergent evolution of complex brains and high intelligence
... several lobes that are involved in the control of feeding, locomotion and colour change, and a dorsal portion exerting sensory information processing and higher cognitive functions [21–23]. The brain receives visual afferents from the eyes and the subsequent optic lobes as well as tactile–chemosenso ...
... several lobes that are involved in the control of feeding, locomotion and colour change, and a dorsal portion exerting sensory information processing and higher cognitive functions [21–23]. The brain receives visual afferents from the eyes and the subsequent optic lobes as well as tactile–chemosenso ...
Some Neurobiological Aspects of Psychotherapy
... dates back to mid-century. The neuroanatomist Ramón y Cajal1 had earlier discovered that information could be stored by modifying the connections between communicating nerve cells in order to form associations. In 1949 this idea was formalized by Hebb,2 who suggested that such modifications should t ...
... dates back to mid-century. The neuroanatomist Ramón y Cajal1 had earlier discovered that information could be stored by modifying the connections between communicating nerve cells in order to form associations. In 1949 this idea was formalized by Hebb,2 who suggested that such modifications should t ...
chapter 9: nervous system
... Learning Outcome 7: Describe the general structure of a neuron. 1. Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines a. Give an overview of neuron structure. b. Introduce the major components of a neuron, including the cell body, neurofibrils, Nissl bodies, dendrites, axons, Schwann cells, myelin sheath, neurilemm ...
... Learning Outcome 7: Describe the general structure of a neuron. 1. Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines a. Give an overview of neuron structure. b. Introduce the major components of a neuron, including the cell body, neurofibrils, Nissl bodies, dendrites, axons, Schwann cells, myelin sheath, neurilemm ...
A biologically constrained learning mechanism in networks of formal
... L. Personnaz, 1 I. Guyon, ~ G. Dreyfus, ~ and G. Toulouse ~ Received November 27, 1985; final December 12, 1985 ...
... L. Personnaz, 1 I. Guyon, ~ G. Dreyfus, ~ and G. Toulouse ~ Received November 27, 1985; final December 12, 1985 ...
Learning: On the Multiple Facets of a Colloquial Concept
... a bunch of different abilities based on special linguistic, mathematical, sportive, musical, etc. skills as ascribed by Howard Gardner to the phenomenon of “multiple intelligences” (Gardner 1985; 1999). If we go along with Gardner, it is clear that not only cognitive aspects account for intelligence ...
... a bunch of different abilities based on special linguistic, mathematical, sportive, musical, etc. skills as ascribed by Howard Gardner to the phenomenon of “multiple intelligences” (Gardner 1985; 1999). If we go along with Gardner, it is clear that not only cognitive aspects account for intelligence ...
LTMReinforce
... Waltz, J. A., & Gold, J. M. (2007). Probabilistic reversal learning impairments in schizophrenia: further evidence of orbitofrontal dysfunction. Schizophrenia Research, 93(1-3), 296-303. Waltz, J. A., Schweitzer, J. B., Gold, J. M., Kurup, P. K., Ross, T. J., Salmeron, B. J., et al. (2009). Patients ...
... Waltz, J. A., & Gold, J. M. (2007). Probabilistic reversal learning impairments in schizophrenia: further evidence of orbitofrontal dysfunction. Schizophrenia Research, 93(1-3), 296-303. Waltz, J. A., Schweitzer, J. B., Gold, J. M., Kurup, P. K., Ross, T. J., Salmeron, B. J., et al. (2009). Patients ...
Brain Fun and Exploration for Kids
... The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain interactive module which includes: a great little video Make a Mad, Mad, Mad, Neuron: an instructional video of Neurons, Synapses, Neurotransmitters; plus, The Other Brain Cells- great info about glial cells ...
... The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain interactive module which includes: a great little video Make a Mad, Mad, Mad, Neuron: an instructional video of Neurons, Synapses, Neurotransmitters; plus, The Other Brain Cells- great info about glial cells ...