Nervous System - Aurora City Schools
... information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - ar ...
... information from the eyes. • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - ar ...
Neurophysiology and Psycho-Pharmacology Final Exam General
... Studies of dismissive mothers demonstrate left hemisphere brain activation inst of right hemispheric active (consistent with retrieval of autobiographical memories) ...
... Studies of dismissive mothers demonstrate left hemisphere brain activation inst of right hemispheric active (consistent with retrieval of autobiographical memories) ...
CHAPTER 39 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS
... b. The vertebrate brain is customarily divided into the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. 1) A well-developed hindbrain regulates organs below a level of consciousness; in humans it regulates lung and heart function even when sleeping; also, it coordinates motor activity. 2) The optic lobes are pa ...
... b. The vertebrate brain is customarily divided into the hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain. 1) A well-developed hindbrain regulates organs below a level of consciousness; in humans it regulates lung and heart function even when sleeping; also, it coordinates motor activity. 2) The optic lobes are pa ...
The aging brain: The cognitive reserve hypothesis
... high correlation between the two variables in haplorhine primates, and when taken on their own, in humans and the great apes (Allman et al., 1993a). In other words, although humans are exceptional within primates for brain size and lifespan length, they are not exceptional in the quantitative relati ...
... high correlation between the two variables in haplorhine primates, and when taken on their own, in humans and the great apes (Allman et al., 1993a). In other words, although humans are exceptional within primates for brain size and lifespan length, they are not exceptional in the quantitative relati ...
Ch. 7 - Nervous System
... A minimum stimulus (threshold) is needed to start an impulse If the threshold is met, a nerve impulse starts, and continues over the entire axon (all or none response) ...
... A minimum stimulus (threshold) is needed to start an impulse If the threshold is met, a nerve impulse starts, and continues over the entire axon (all or none response) ...
CHAPTER 14 –NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of
... Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission of nerve impulses. Describe the central nervous system. Describe the peripheral nervous system. Describe the autonomic nervous system Analyze, build, spell, and pronounce medical words. C ...
... Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission of nerve impulses. Describe the central nervous system. Describe the peripheral nervous system. Describe the autonomic nervous system Analyze, build, spell, and pronounce medical words. C ...
Fridtjof Nansen Science Symposium 2011
... on the editorial board for Current Opinion of Neurobiology, Journal of Neurophysiology, and Neural Development among others. His is a member of the Nobel Assembly and his work has been acknowledged by the Schellenberg Prize and an endowed Söderberg’s professorship. ...
... on the editorial board for Current Opinion of Neurobiology, Journal of Neurophysiology, and Neural Development among others. His is a member of the Nobel Assembly and his work has been acknowledged by the Schellenberg Prize and an endowed Söderberg’s professorship. ...
Social regulation of allostasis: Commentary on “Mentalizing
... input from the social environment. This is often framed as the nature vs. nurture debate. In their paper, Fotopoulou and Tsakiris confront this debate head on, and propose a hypothesis by which the most fundamental neural features are not predetermined, but instead are shaped after birth by social i ...
... input from the social environment. This is often framed as the nature vs. nurture debate. In their paper, Fotopoulou and Tsakiris confront this debate head on, and propose a hypothesis by which the most fundamental neural features are not predetermined, but instead are shaped after birth by social i ...
NIH Public Access
... Toward the end of the 1990s, technological and methodological advances allowed for more precise measurement of cortical thickness (Fischl and Dale 2000; Kabani et al. 2001), which is considered to reflect the packing density of neurons, as well as other components of the neuropil. Similar to volume, ...
... Toward the end of the 1990s, technological and methodological advances allowed for more precise measurement of cortical thickness (Fischl and Dale 2000; Kabani et al. 2001), which is considered to reflect the packing density of neurons, as well as other components of the neuropil. Similar to volume, ...
Endocrine and Nervous Systems
... When you are hot or exercise strenuously, you lose water through sweat. If you lose too much water, your pituitary gland releases a hormone called ADH. Your blood carries the ADH to your kidneys, where it signals the kidneys to slow the removal of water from the blood. You also feel thirsty and tak ...
... When you are hot or exercise strenuously, you lose water through sweat. If you lose too much water, your pituitary gland releases a hormone called ADH. Your blood carries the ADH to your kidneys, where it signals the kidneys to slow the removal of water from the blood. You also feel thirsty and tak ...
Environmental Causes of Central Nervous System Maldevelopment
... has been shown in animals that were exposed as neonates to triethyltin.12 An example of a widespread environmental hazard with antimitotic properties is methylmercury. Data from environmental disasters in Japan13 and Iraq14 led to the conclusion that children in utero are much more sensitive to this ...
... has been shown in animals that were exposed as neonates to triethyltin.12 An example of a widespread environmental hazard with antimitotic properties is methylmercury. Data from environmental disasters in Japan13 and Iraq14 led to the conclusion that children in utero are much more sensitive to this ...
HORMONES AND BEHAVIOR 1. The Neuroendocrine System: Sum
... many of the hormones found in the body. This is usually regulated through “multi-step” signaling mechanisms (_____________) all the way to the various glands in the body that synthesize hormones. In turn, many hormones reach back to the brain and influence various cognitive and behavioral functions. ...
... many of the hormones found in the body. This is usually regulated through “multi-step” signaling mechanisms (_____________) all the way to the various glands in the body that synthesize hormones. In turn, many hormones reach back to the brain and influence various cognitive and behavioral functions. ...
TEACHER`S GUIDE
... Learning Objectives After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send informati ...
... Learning Objectives After viewing this video students should understand the following concepts: 1. The brain is a structure that controls many different functions; areas within the brain are highly specialized to control specific functions, but they are also interconnected. 2. Neurons send informati ...
The triune organism – an abstract
... externally with their environment, in multidimensional patterns, which create meaningful wholes. What is the ontological status of the patterns that connect all these parts? Do we merely interpret them into the phenomena? Or do they belong to nature? If they do belong to nature, how can such pattern ...
... externally with their environment, in multidimensional patterns, which create meaningful wholes. What is the ontological status of the patterns that connect all these parts? Do we merely interpret them into the phenomena? Or do they belong to nature? If they do belong to nature, how can such pattern ...
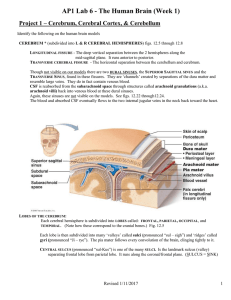
Lab Activity Sheets
... responsible for conscious perception of sensory info. also conscious thought, reasoning, problem solving, etc. also conscious control of motor messages to skeletal muscles for body movement and speech. BASAL NUCLEI (not visible on our models) (commonly but mistakenly called “basal ganglia”) ...
... responsible for conscious perception of sensory info. also conscious thought, reasoning, problem solving, etc. also conscious control of motor messages to skeletal muscles for body movement and speech. BASAL NUCLEI (not visible on our models) (commonly but mistakenly called “basal ganglia”) ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BSc Counselling Psychology
... 80. One groove called the _____________, divides each hemisphere vertically. a. Cortex c. Central sulcus b. Lateral fissure d. Brain stem 81. One groove called the _____________, divides each hemisphere horizontally. a. Cortex c. Central sulcus b. Lateral fissure d. Brain stem 82. In humans, the ___ ...
... 80. One groove called the _____________, divides each hemisphere vertically. a. Cortex c. Central sulcus b. Lateral fissure d. Brain stem 81. One groove called the _____________, divides each hemisphere horizontally. a. Cortex c. Central sulcus b. Lateral fissure d. Brain stem 82. In humans, the ___ ...
Untitled
... In this photograph, the pituitary gland has been removed to reveal the hypothalamus.Note that the floor of the midbrain consists of the two cerebral peduncles (Latin: pedunculus = stem) separatedby an interpeduncularspace. These peduncles disappear under the surface of the pons (Latin: pontis =bridg ...
... In this photograph, the pituitary gland has been removed to reveal the hypothalamus.Note that the floor of the midbrain consists of the two cerebral peduncles (Latin: pedunculus = stem) separatedby an interpeduncularspace. These peduncles disappear under the surface of the pons (Latin: pontis =bridg ...
Neil Bossenger - The power of upper cervical
... Over 8 years lost ability to work. Chronic daily headaches. Wore sunglasses indoors. Chronic fatigue. Loss of strength on RHS. Slow mental processing. After 25 medical practitioners, diagnosed as “psychosomatic”. ...
... Over 8 years lost ability to work. Chronic daily headaches. Wore sunglasses indoors. Chronic fatigue. Loss of strength on RHS. Slow mental processing. After 25 medical practitioners, diagnosed as “psychosomatic”. ...
Phys Chapter 59 [4-20
... So a grand mall attack involves abnormal activation of the thalamus, cerebral cortex, and subthalamic brainstem parts of the brain activating system o Most people who have grand mal attacks have a hereditary predisposition to epilepsy In these people, things that can increase the excitability enou ...
... So a grand mall attack involves abnormal activation of the thalamus, cerebral cortex, and subthalamic brainstem parts of the brain activating system o Most people who have grand mal attacks have a hereditary predisposition to epilepsy In these people, things that can increase the excitability enou ...
Lecture 1 Psycholinguistics Overview Psycholinguistics Definitions
... for programming the motor cortex to move the tongue, lips and speech muscles to articulate words. ...
... for programming the motor cortex to move the tongue, lips and speech muscles to articulate words. ...
English - Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Berlin
... How successful busy bees are in their search for food depends largely on how well they can, based on their odors, detect nectarrich flowers from a distance and distinguish them from less promising plants. How do bees memorize the connection between the odor of a flower and whether or not it bears ne ...
... How successful busy bees are in their search for food depends largely on how well they can, based on their odors, detect nectarrich flowers from a distance and distinguish them from less promising plants. How do bees memorize the connection between the odor of a flower and whether or not it bears ne ...
What Is Psychology?
... theories as a new approach to therapy, based on Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theory. These theories are based on the belief that unlocking the unconscious mind is the key to understanding human behaviour and relationships. Calling your new love interest by your ex’s name—a Freudian slip—would lead ...
... theories as a new approach to therapy, based on Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theory. These theories are based on the belief that unlocking the unconscious mind is the key to understanding human behaviour and relationships. Calling your new love interest by your ex’s name—a Freudian slip—would lead ...
Chapter 3—The Brain and Behavior
... voluntary muscles, personality and intelligence is associated with the frontal lobe. The parietal lobe is involved in body sensation. The corpus callosum is a large bundle of axons connecting the two cerebral hemispheres. Speech and grammar are localized to the left hemisphere, which mainly controls ...
... voluntary muscles, personality and intelligence is associated with the frontal lobe. The parietal lobe is involved in body sensation. The corpus callosum is a large bundle of axons connecting the two cerebral hemispheres. Speech and grammar are localized to the left hemisphere, which mainly controls ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 21) Compare the structure and functions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 22) Distinguish between the functions of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. 23) Describe the embryonic development of the vertebrate brain. 24) Describe the structure an ...
... 21) Compare the structure and functions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 22) Distinguish between the functions of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. 23) Describe the embryonic development of the vertebrate brain. 24) Describe the structure an ...