Timing of Impulses From the Central Amygdala and Bed Nucleus of
... the stria terminalis (BNST) are thought to subserve distinct functions, with the former mediating rapid fear responses to discrete sensory cues and the latter longer “anxiety-like” states in response to diffuse environmental contingencies. However, these structures are reciprocally connected and the ...
... the stria terminalis (BNST) are thought to subserve distinct functions, with the former mediating rapid fear responses to discrete sensory cues and the latter longer “anxiety-like” states in response to diffuse environmental contingencies. However, these structures are reciprocally connected and the ...
Final Paper Outline: Effects of Meditation on the Brain
... consciousness (Pinel, 2006). For example, alpha waves are high-amplitude waves which are most associated with a relaxed state of wakefulness, while delta waves are the slowest and largest waves associated with deep states of relaxation and sleep (Pinel, 2006). With that being said, several studies ...
... consciousness (Pinel, 2006). For example, alpha waves are high-amplitude waves which are most associated with a relaxed state of wakefulness, while delta waves are the slowest and largest waves associated with deep states of relaxation and sleep (Pinel, 2006). With that being said, several studies ...
Psychosurgery: past, present, and future
... the surgery fell to the hands of non-surgeons as well as nonphysicians. Electroconvulsive treatment (another controversial somatic therapy in psychiatry) was used for anesthesia, and then an instrument resembling an ice pick was inserted into the orbital roof and swept across the prefrontal cortex. ...
... the surgery fell to the hands of non-surgeons as well as nonphysicians. Electroconvulsive treatment (another controversial somatic therapy in psychiatry) was used for anesthesia, and then an instrument resembling an ice pick was inserted into the orbital roof and swept across the prefrontal cortex. ...
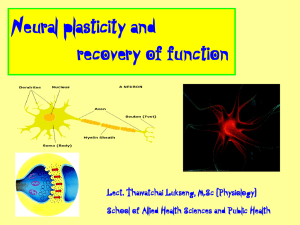
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve cells) in the brain to compensate for injury and disease and to adjust their activitie ...
... • Plastic (adj.) = soft enough to be changed into a new shape • Neuroplasticity, brain plasticity or brain malleability • The brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections • Neurons (nerve cells) in the brain to compensate for injury and disease and to adjust their activitie ...
FUNCTIONAL COGNITIVE NETWORKS IN PRIMATES
... The fundamental computational building block of the brain is the neuron, which contains dendrites for the input of information and an axon for the dissemination of the results of the neuron's analysis. Neurons arose in primitive invertebrates at least six-hundred million years ago. Typical early inv ...
... The fundamental computational building block of the brain is the neuron, which contains dendrites for the input of information and an axon for the dissemination of the results of the neuron's analysis. Neurons arose in primitive invertebrates at least six-hundred million years ago. Typical early inv ...
FREE Sample Here
... communicate directly without sending chemical messengers. Their operation has not been fully understood by researchers. Plasticity The brain can adapt or modify itself, a process known as plasticity. Plasticity helps to account for the brain’s ability to compensate for injury. It also accoun ...
... communicate directly without sending chemical messengers. Their operation has not been fully understood by researchers. Plasticity The brain can adapt or modify itself, a process known as plasticity. Plasticity helps to account for the brain’s ability to compensate for injury. It also accoun ...
14.FARS 3.Synthetic PET(2001) - University of Southern California
... As a computational plus (going beyond the imaging technology), we can also collect the contributions of the excitatory and inhibitory synapses separately, based on evaluating the integral in (1) over one set of synapses or the other. Michael Arbib CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, US ...
... As a computational plus (going beyond the imaging technology), we can also collect the contributions of the excitatory and inhibitory synapses separately, based on evaluating the integral in (1) over one set of synapses or the other. Michael Arbib CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence, US ...
The Nervous System
... the understanding of the structure and function of the nervous system, and to the understanding of biological, psychological and social factors that influence learning and memory. Use these tables as checklists when revising. Tick off each dot point when you are satisfied that you have thoroughly co ...
... the understanding of the structure and function of the nervous system, and to the understanding of biological, psychological and social factors that influence learning and memory. Use these tables as checklists when revising. Tick off each dot point when you are satisfied that you have thoroughly co ...
the neurobiology of emotion
... defensive or protective acts that serve to promote survival. These behaviors include fleeing or withdrawing from a situation, freezing to remain inconspicuous, or fighting. Nature vs. Nurture Fear behavior is essential for survival and much of its development appears to be innate. In humans, behavio ...
... defensive or protective acts that serve to promote survival. These behaviors include fleeing or withdrawing from a situation, freezing to remain inconspicuous, or fighting. Nature vs. Nurture Fear behavior is essential for survival and much of its development appears to be innate. In humans, behavio ...
The Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... complex intellectual functions requiring verbal, analytical, and computational skills. ...
... complex intellectual functions requiring verbal, analytical, and computational skills. ...
Altered States of Consciousness
... • Spontaneous shifts attention away from the here and now into a makebelieve world • Urge to daydream peaks about every 90 minutes and is highest between 12:00 and 2:00pm • Almost half of your waking hours? ...
... • Spontaneous shifts attention away from the here and now into a makebelieve world • Urge to daydream peaks about every 90 minutes and is highest between 12:00 and 2:00pm • Almost half of your waking hours? ...
The Potential of Treating Alzheimer`s disease with Intranasal Light
... pathogen entering the brain via olfactory pathways allowed by a dysfunctional olfactory bulb. ...
... pathogen entering the brain via olfactory pathways allowed by a dysfunctional olfactory bulb. ...
Ch 16 - Motivation - Head
... Neurons in the medial preoptic area of the hypothalamus Somatic motor (behavioral) responses Neurons of lateral hypothalamic area Slide 26 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... Neurons in the medial preoptic area of the hypothalamus Somatic motor (behavioral) responses Neurons of lateral hypothalamic area Slide 26 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3rd Ed, Bear, Connors, and Paradiso Copyright © 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Brain Tumor
... diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), have been widely used to evaluate such tumors. Diffusion-weighted MR image Diffusion-weighted imaging is based on the random or Brownian motion of water molecules in relation to their thermal energy. DWI has been used to assess bra ...
... diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), have been widely used to evaluate such tumors. Diffusion-weighted MR image Diffusion-weighted imaging is based on the random or Brownian motion of water molecules in relation to their thermal energy. DWI has been used to assess bra ...
Craving, Desire, and Addiction
... abuse of addictive substances. These studies have shown how repeated drug use can target key molecules (both common and specific for various drug types) and brain circuits, and eventually disrupt the higher order processes that underlie emotions, cognition, and behavior, and enable an individual to ...
... abuse of addictive substances. These studies have shown how repeated drug use can target key molecules (both common and specific for various drug types) and brain circuits, and eventually disrupt the higher order processes that underlie emotions, cognition, and behavior, and enable an individual to ...
The Biology
... Because it evolved very early, the [a] _______________ of the brain is referred to as the old brain. It is composed of the medulla, which controls functions like breathing and heartbeat; the pons, which transmits information helping to coordinate muscle activity on the right and left halves of the b ...
... Because it evolved very early, the [a] _______________ of the brain is referred to as the old brain. It is composed of the medulla, which controls functions like breathing and heartbeat; the pons, which transmits information helping to coordinate muscle activity on the right and left halves of the b ...
Task-induced brain activity in aphasic stroke
... It is claimed that one-third of all stroke patients have an aphasic deficit as part of their presenting symptoms (Laska et al., 2001; Pedersen et al., 2004; Lazar et al., 2008). Although half of these patients recover much or all of their language function, the remainder are left with a persisting a ...
... It is claimed that one-third of all stroke patients have an aphasic deficit as part of their presenting symptoms (Laska et al., 2001; Pedersen et al., 2004; Lazar et al., 2008). Although half of these patients recover much or all of their language function, the remainder are left with a persisting a ...
Genetic basis of human brain evolution
... in the part of brain that translates intended speech into specific muscle movements [27]. Interestingly, FOXP2 is implicated in verbal communication in other species including mice and songbirds [28–31]. Despite near-perfect amino-acid-sequence conservation in mammals, FOXP2 shows two non-synonymous ...
... in the part of brain that translates intended speech into specific muscle movements [27]. Interestingly, FOXP2 is implicated in verbal communication in other species including mice and songbirds [28–31]. Despite near-perfect amino-acid-sequence conservation in mammals, FOXP2 shows two non-synonymous ...
Nuclear medicine in psychiatry
... a prevalence of about 1% and significant disablement. RN neuroimaging is focused on receptor research, with few results, mostly ...
... a prevalence of about 1% and significant disablement. RN neuroimaging is focused on receptor research, with few results, mostly ...
Article Review - Make up assignment
... 12. In the case of acids what specific chemical causes depolarization? Which type of taste is this phenomenon associated with? ...
... 12. In the case of acids what specific chemical causes depolarization? Which type of taste is this phenomenon associated with? ...
mechanisms of neurotransmitter receptor biogenesis and trafficking
... these findings have yet to translate into effective treatments for many neurological disorders and psychiatric conditions. Thus, while unravelling the complexities of the brain and its dysfunction will be a key to treating devastating brain disorders, there will likely be a long time lag between und ...
... these findings have yet to translate into effective treatments for many neurological disorders and psychiatric conditions. Thus, while unravelling the complexities of the brain and its dysfunction will be a key to treating devastating brain disorders, there will likely be a long time lag between und ...
A Moderate Approach to Embodied Cognitive Science
... circuitry for a variety of cognitive purposes is a central organizing principle of the brain. In other words, it is common for neural circuits originally established for one purpose to be exapted (exploited, recycled, redeployed) during evolution or normal development and put to different uses, with ...
... circuitry for a variety of cognitive purposes is a central organizing principle of the brain. In other words, it is common for neural circuits originally established for one purpose to be exapted (exploited, recycled, redeployed) during evolution or normal development and put to different uses, with ...
FREE Sample Here
... The process of lateralization results in a division of functions between the cerebral hemispheres. In most people (right-handed more than left) the left hemisphere handles most of the language functions, including speaking, writing, reading, speech comprehension, and comprehension of the logic o ...
... The process of lateralization results in a division of functions between the cerebral hemispheres. In most people (right-handed more than left) the left hemisphere handles most of the language functions, including speaking, writing, reading, speech comprehension, and comprehension of the logic o ...
Ajna Light Theory and Science Guy Harriman June 2015 The Ajna
... photoreceptors. In addition, ipRGCs convey contrast (irradiance) information via the optic nerve to influence several functions. These nerve cell's dendrites are either shared or run alongside the optic nerve cell fibers. It is now known that photoreception in the mammalian retina occurs outside of ...
... photoreceptors. In addition, ipRGCs convey contrast (irradiance) information via the optic nerve to influence several functions. These nerve cell's dendrites are either shared or run alongside the optic nerve cell fibers. It is now known that photoreception in the mammalian retina occurs outside of ...