VNS Worksheet - Rice CAAM Department
... 4. Why is the locus coeruleus (LC) called the "blue spot." 5. How many neurons are contained in the blue spot. 6. If the volume of a typical LC neuron is 50,000 cubic microns and there are 2.54 cm in one inch what is the volume of such a cell in cubic inches? 7. What important molecule is delivered ...
... 4. Why is the locus coeruleus (LC) called the "blue spot." 5. How many neurons are contained in the blue spot. 6. If the volume of a typical LC neuron is 50,000 cubic microns and there are 2.54 cm in one inch what is the volume of such a cell in cubic inches? 7. What important molecule is delivered ...
Congenital Malformation & Hydrocephalus
... Prenatal or perinatal insults may either cause: ◦ failure of normal CNS development ◦ tissue destruction ...
... Prenatal or perinatal insults may either cause: ◦ failure of normal CNS development ◦ tissue destruction ...
“Definitions” section of your binder Central nervous system
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
... Somatic Nervous System (SNS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles Autonomic nervous system (ANS): the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal biological functions ...
Body Systems - Nervous System
... c. It conducts electricity better than other areas of your body d. It contains more neurotransmitters than other areas of your body 8. Where in your body can you find nerve cells? Choose the best answer. a. In your brain b. In your spinal cord c. In your neurons d. Everywhere 9. A disorder called CI ...
... c. It conducts electricity better than other areas of your body d. It contains more neurotransmitters than other areas of your body 8. Where in your body can you find nerve cells? Choose the best answer. a. In your brain b. In your spinal cord c. In your neurons d. Everywhere 9. A disorder called CI ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here
... b. Beta waves have a higher frequency than alpha waves and are less regular, usually occurring when the brain is mentally focused. c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but ...
... b. Beta waves have a higher frequency than alpha waves and are less regular, usually occurring when the brain is mentally focused. c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but ...
Impact of Neuroscience in Human Development
... function of the brain? What are the reasons behind these brain diseases? How can we cure them? These are but some of the questions being asked, and neuroscience is in the frontier of disciplines seeking the answers. Except for satisfying curiosity and the constant hunger for knowledge, a more signif ...
... function of the brain? What are the reasons behind these brain diseases? How can we cure them? These are but some of the questions being asked, and neuroscience is in the frontier of disciplines seeking the answers. Except for satisfying curiosity and the constant hunger for knowledge, a more signif ...
SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION GUIDE
... (which is the inability to remember new information and experiences though previously-stored memories remain intact). The hippocampus and the medial temporal cortical areas which project to it are critical for long-term memory. The rat hippocampus is probably the single most studied brain structure ...
... (which is the inability to remember new information and experiences though previously-stored memories remain intact). The hippocampus and the medial temporal cortical areas which project to it are critical for long-term memory. The rat hippocampus is probably the single most studied brain structure ...
Language Processing in the Brain
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
Local Copy - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... of hundreds of billions of neurons, which fall into perhaps hundreds of different classes, defined by their shape and the molecules they contain. Each computes in concert with thousands of others, its activity dynamically changing on the millisecond timescale. In many diseases, specific computations ...
... of hundreds of billions of neurons, which fall into perhaps hundreds of different classes, defined by their shape and the molecules they contain. Each computes in concert with thousands of others, its activity dynamically changing on the millisecond timescale. In many diseases, specific computations ...
The relationship between heart-brain dynamics, positive emotions
... 5) Asthma (Robert Wood Johnson Medical School), over 50% of patients experienced a decrease in airway impedance, symptom severity and medication consumption The Electrophysiology of Intuition Dean Radin (1997): ‘Sometimes if a future event is sufficiently important, novel, or emotional, it may pre ...
... 5) Asthma (Robert Wood Johnson Medical School), over 50% of patients experienced a decrease in airway impedance, symptom severity and medication consumption The Electrophysiology of Intuition Dean Radin (1997): ‘Sometimes if a future event is sufficiently important, novel, or emotional, it may pre ...
The Nervous System - teacheroftruth.net
... despite having had his medical licence revoked. He had diluted the neurotoxin before injecting it into himself and three patients. The incident is described in the Journal of the American Medical Association by doctors at the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta. The researchers ...
... despite having had his medical licence revoked. He had diluted the neurotoxin before injecting it into himself and three patients. The incident is described in the Journal of the American Medical Association by doctors at the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta. The researchers ...
Exam 5 Objectives Bio241
... mechanism of action of cocaine? SSRIs? 8. Be familiar (do not memorize chemical structures) with the neurotransmitters: ACh, serotonin, norepinepherine, dopamine, glutamate, and GABA. Understand the different classes of molecules that can function as neurotransmitters (chemicals, polypeptides, gasse ...
... mechanism of action of cocaine? SSRIs? 8. Be familiar (do not memorize chemical structures) with the neurotransmitters: ACh, serotonin, norepinepherine, dopamine, glutamate, and GABA. Understand the different classes of molecules that can function as neurotransmitters (chemicals, polypeptides, gasse ...
Biopsychology – Paper 2
... Sensory neurons are also known as afferent neurons, meaning moving towards a central organ or point, that is they move impulses towards the CNS . This type of neuron receives information or stimuli from sensory receptors found in various locations in the body, for example the eyes, ears, tongue, sk ...
... Sensory neurons are also known as afferent neurons, meaning moving towards a central organ or point, that is they move impulses towards the CNS . This type of neuron receives information or stimuli from sensory receptors found in various locations in the body, for example the eyes, ears, tongue, sk ...
Chapter 12 Nervous System
... IV. Brain – Fig 8-2, & 8-3 “encephalo” = “in head” 4 main parts A. Cerebrum 1. Separated by fissure into 2 hemispheres 2. Convoluted surface: ridges called gyri, depressions called sulci, or fissures if deeper 3. NRF lobes, but realize that functions are localized 4. Outer layer of gray matter = ce ...
... IV. Brain – Fig 8-2, & 8-3 “encephalo” = “in head” 4 main parts A. Cerebrum 1. Separated by fissure into 2 hemispheres 2. Convoluted surface: ridges called gyri, depressions called sulci, or fissures if deeper 3. NRF lobes, but realize that functions are localized 4. Outer layer of gray matter = ce ...
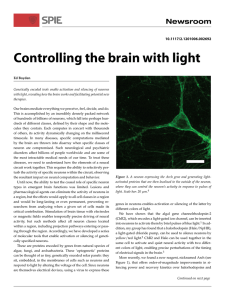
Neurons: A fish-eye view of the brain
... “death-ray.” The light would burn opaque organisms, but shines right through the seethrough zebrafish. Using this technique, scientists can watch and measure the growth, development, and activity of specific neurons without harming the living fish. Researchers in the Smith lab also use zebrafish eng ...
... “death-ray.” The light would burn opaque organisms, but shines right through the seethrough zebrafish. Using this technique, scientists can watch and measure the growth, development, and activity of specific neurons without harming the living fish. Researchers in the Smith lab also use zebrafish eng ...
Lesson Overview - Diman Regional
... of these regions regulates the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body. ...
... of these regions regulates the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body. ...
Nervous system - Effingham County Schools
... • picks up sensory information and delivers it to the CNS Motor Division • carries information to muscles and glands Divisions of the Motor Division • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
... • picks up sensory information and delivers it to the CNS Motor Division • carries information to muscles and glands Divisions of the Motor Division • Somatic – carries information to skeletal muscle • Autonomic – carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands ...
PAPER #3: EMBARGOED PRESS RELEASE STRICTLY UNDER
... between activation of the ventral subiculum (the brain's addiction center) and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons tha ...
... between activation of the ventral subiculum (the brain's addiction center) and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons tha ...
The Nervous System WS-11A Review Quest
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
Section: Nervous system
... THE SPINAL CORD 32. The spinal cord is protected by _______________ . 33. The spinal cord is made of ________________ and ________________. 34. Nerve fibers in your spinal cord allow your brain to communicate with your _____________ nervous system. 35. A spinal cord injury may block all information ...
... THE SPINAL CORD 32. The spinal cord is protected by _______________ . 33. The spinal cord is made of ________________ and ________________. 34. Nerve fibers in your spinal cord allow your brain to communicate with your _____________ nervous system. 35. A spinal cord injury may block all information ...
Introduction to Psychology The Nervous System: Biological Control
... from the cell body and transmit them to the next neuron. The messages usually stem from the dendrite through the axon, but can go the opposite direction. The human nervous system is made up of 100 billion neurons. The human body contains trillions of neural connections, most of them in the brain. ...
... from the cell body and transmit them to the next neuron. The messages usually stem from the dendrite through the axon, but can go the opposite direction. The human nervous system is made up of 100 billion neurons. The human body contains trillions of neural connections, most of them in the brain. ...
Jeopardy - Zion-Benton Township High School
... neurotransmitters into the spaces called synapses between neurons. The axon is the long threadlike fiber that transmits the message. ...
... neurotransmitters into the spaces called synapses between neurons. The axon is the long threadlike fiber that transmits the message. ...