ANHB1102 Basic Principles of the Nervous System • The nervous
... - Cerebellum is the major regulator of coordination and timing of movements (damage to this area doesn’t stop movement, but movement becomes erratic and slow). - The temporal lobe is responsible for auditory processing. It contains the hippocampus which is responsible for storing long-term memories. ...
... - Cerebellum is the major regulator of coordination and timing of movements (damage to this area doesn’t stop movement, but movement becomes erratic and slow). - The temporal lobe is responsible for auditory processing. It contains the hippocampus which is responsible for storing long-term memories. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Tamalpais Union High School District
... • Divided into right and left cerebral hemispheres • Covered by folds called convolutions/gyri and grooves called sulci (little groves) and fissures (big grooves) • Connected by the corpus callosum • It has a cortex: an outer covering about 2 mm thick • Gray matter vs. white matter ...
... • Divided into right and left cerebral hemispheres • Covered by folds called convolutions/gyri and grooves called sulci (little groves) and fissures (big grooves) • Connected by the corpus callosum • It has a cortex: an outer covering about 2 mm thick • Gray matter vs. white matter ...
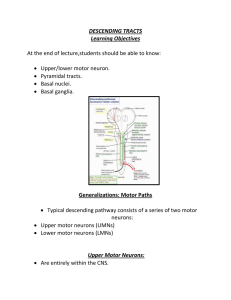
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Anterior corticospinal tract: Made up of uncrossed corticospinal fibers of synapse with LMNs. Supply neck and upper limbs. ...
... Anterior corticospinal tract: Made up of uncrossed corticospinal fibers of synapse with LMNs. Supply neck and upper limbs. ...
Motor activity induced by disinhibition of the primary motor cortex of
... after stimulation of the infragranular layers of the motor cortex with low impedance electrodes which produce large current spreads. The rate of the spontaneous EMG activity was approximately of 0.8 + 0.2 Hz. Even though the anesthesia used (ketamine) is a NMDA receptor antagonist we applied another ...
... after stimulation of the infragranular layers of the motor cortex with low impedance electrodes which produce large current spreads. The rate of the spontaneous EMG activity was approximately of 0.8 + 0.2 Hz. Even though the anesthesia used (ketamine) is a NMDA receptor antagonist we applied another ...
Part 1: From Ion Channels to behavior, HT2009 Course
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
Pain
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
... The cognition concept Localization of cognitive functions in the brain Examples of specific dysfunctions after brain lesions Learning and memory Examples of declarative and implicit memory Major brain areas involved in learning and memory Language Characteristics of language and support for a geneti ...
11.3: The Central Nervous System The nervous system consists of
... The Brain is the major centre that receives, integrates, stores, and retrieves information. The Brain and its network of interneurons provide the basis for our voluntary movements, consciousness, behaviour, emotions, learning, reasoning, language and memory. The brain contains grey and white matter, ...
... The Brain is the major centre that receives, integrates, stores, and retrieves information. The Brain and its network of interneurons provide the basis for our voluntary movements, consciousness, behaviour, emotions, learning, reasoning, language and memory. The brain contains grey and white matter, ...
博士論文
... linguistic factors, such as semantic information of sentences and lexical/contextual information, still remain unclear. It is thus important to clarify how syntactic and other linguistic processes are temporally and spatially integrated in the left frontal cortex. For this purpose, I investigated th ...
... linguistic factors, such as semantic information of sentences and lexical/contextual information, still remain unclear. It is thus important to clarify how syntactic and other linguistic processes are temporally and spatially integrated in the left frontal cortex. For this purpose, I investigated th ...
nervous system
... b.) Motor neurons: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands c.) Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them 3. Neuron Parts and Function a.) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm; location of cellular metabolic activi ...
... b.) Motor neurons: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands c.) Interneurons: connect sensory and motor neurons and carry impulses between them 3. Neuron Parts and Function a.) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm; location of cellular metabolic activi ...
corticospinal tract
... • The rubrospinal tract – 2ndairy motor system responsible for large muscle movement such as the arms and the legs (flexor and extension, ...
... • The rubrospinal tract – 2ndairy motor system responsible for large muscle movement such as the arms and the legs (flexor and extension, ...
nervous system
... dendrite, cell body, axon • Distinguish among sensory, motor and interneuron with respect to structure and function • Contrast the locations and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems • Differentiate between the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the auton ...
... dendrite, cell body, axon • Distinguish among sensory, motor and interneuron with respect to structure and function • Contrast the locations and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems • Differentiate between the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the auton ...
Motor system - Brain Facts
... parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the same direction but without a specific aim, or in relation to a pass ...
... parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the same direction but without a specific aim, or in relation to a pass ...
Testing upper motor neuron function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
... investigate upper motor neuron function has proved useful and applicable as a measure of efficacy in clinical trials, despite some enthusiasm for the threshold tracking transcranial magnetic stimulation as a marker of early diagnosis. EMG is also not the preferred method for assessing upper motor ne ...
... investigate upper motor neuron function has proved useful and applicable as a measure of efficacy in clinical trials, despite some enthusiasm for the threshold tracking transcranial magnetic stimulation as a marker of early diagnosis. EMG is also not the preferred method for assessing upper motor ne ...
The Brain
... responsible for combining sounds into words and arranging words into meaningful sentences? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... responsible for combining sounds into words and arranging words into meaningful sentences? A. B. C. D. E. ...
5. hierarchical multimodal language modeling
... Figure 6. System state of the model of cortical language areas after simulation step 13. The ‘_blank’ representing the word border between words “bot” and “put” is recognized in area A2 which activates the ‘OFF’ representation in af-A4 which deactivates area A4 for one simulation step. Immediately a ...
... Figure 6. System state of the model of cortical language areas after simulation step 13. The ‘_blank’ representing the word border between words “bot” and “put” is recognized in area A2 which activates the ‘OFF’ representation in af-A4 which deactivates area A4 for one simulation step. Immediately a ...
AP Ψ - nrappsychology
... e. Terminal buttons- tiny bulblike structures at the end of the axon, which contain neurotransmitters that carry the neuron’s message into the synapse 5. Action potential: The abrupt wave of electrochemical changes traveling down an axon when a neuron becomes depolarized. Recently discovered that de ...
... e. Terminal buttons- tiny bulblike structures at the end of the axon, which contain neurotransmitters that carry the neuron’s message into the synapse 5. Action potential: The abrupt wave of electrochemical changes traveling down an axon when a neuron becomes depolarized. Recently discovered that de ...
Chapter 9 Part 3 Central Nervous System
... axons from the motor areas down through the brain stem to the spinal cord Other pathways go from the cerebral cortex to the basal ganglia and lower brain regions Descending motor pathways cross over to the opposite side of the body Damage to a motor area manifests as paralysis or loss of function on ...
... axons from the motor areas down through the brain stem to the spinal cord Other pathways go from the cerebral cortex to the basal ganglia and lower brain regions Descending motor pathways cross over to the opposite side of the body Damage to a motor area manifests as paralysis or loss of function on ...
Document
... Cerebellum and motor learning • In a well-known model of cerebellum motor learning, climbing fiber activity represents error signals (difference between expected and actual sensory inputs, e.g., the template and the actual drawing). • Experimentally, simultaneous activation of climbing fibers and p ...
... Cerebellum and motor learning • In a well-known model of cerebellum motor learning, climbing fiber activity represents error signals (difference between expected and actual sensory inputs, e.g., the template and the actual drawing). • Experimentally, simultaneous activation of climbing fibers and p ...
Nervous System Outline
... message along its way. Some neurons can have very long axons, such as an axon traveling from your foot to your spinal cord. 2. Nerve - When there are a group of neurons (specifically their axons) bundled together in the peripheral (anywhere but brain and spinal cord) part of your body, it is termed ...
... message along its way. Some neurons can have very long axons, such as an axon traveling from your foot to your spinal cord. 2. Nerve - When there are a group of neurons (specifically their axons) bundled together in the peripheral (anywhere but brain and spinal cord) part of your body, it is termed ...
1. Brain Parts Song Worksheet—3 min Use the word bank to
... 11The _________________ lobe is the center for memory and learning. 12The _________________ lobe is probably the most important for defining us for who we are, personality, social behavior, decision making center, voluntary movement. 13At the back are the two lobes of the _________________. Allows u ...
... 11The _________________ lobe is the center for memory and learning. 12The _________________ lobe is probably the most important for defining us for who we are, personality, social behavior, decision making center, voluntary movement. 13At the back are the two lobes of the _________________. Allows u ...
6. Peripheral Nervous System
... Effector Tissue is Skeletal Muscle Neurotransmitter is ACh (released from somatic motor neurons) Receptors are Nicotinic (response is always excitatory) Control is Voluntary (except reflexes) ...
... Effector Tissue is Skeletal Muscle Neurotransmitter is ACh (released from somatic motor neurons) Receptors are Nicotinic (response is always excitatory) Control is Voluntary (except reflexes) ...
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT - Welcome to Smart Start
... Anatomical studies of brain development show Occipital lobes show earliest pruning Frontal and Temporal lobes show growth of neural connections longer than other areas of the brain…through 3 years old Frontal and Temporal lobes show pruning of connections longer than other areas of the brain ...
... Anatomical studies of brain development show Occipital lobes show earliest pruning Frontal and Temporal lobes show growth of neural connections longer than other areas of the brain…through 3 years old Frontal and Temporal lobes show pruning of connections longer than other areas of the brain ...