Paradigms in Personality Psychology
... 1. Broadly understand what personality psychology is about 2. Define “Personality” 3. Consider the relevance of personality for the study of behavior more broadly 4. Overview of Approaches/Paradigms of Personality 5. Provide a general framework for understanding personality in context. 6. Overview o ...
... 1. Broadly understand what personality psychology is about 2. Define “Personality” 3. Consider the relevance of personality for the study of behavior more broadly 4. Overview of Approaches/Paradigms of Personality 5. Provide a general framework for understanding personality in context. 6. Overview o ...
week 3 ppt
... terminal disease was first described by a German psychiatrist and neuropathologist Alois Alzheimer in 1906 and was named after him. • Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a slowly progressive neurodegenerative disorder of the brain mostly affects the elderly and characterized by impairment of memory and even ...
... terminal disease was first described by a German psychiatrist and neuropathologist Alois Alzheimer in 1906 and was named after him. • Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a slowly progressive neurodegenerative disorder of the brain mostly affects the elderly and characterized by impairment of memory and even ...
Can Digital Games Be a Way of Improving the Neuroplasticity in
... ognize that the brain continues to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections during the life [3]. This phenomenon is called neuroplasticity that refers to the potential which the brain has to reorganize by creating new neural pathways to adapt, as it needs. Those studies arise anyways, whi ...
... ognize that the brain continues to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections during the life [3]. This phenomenon is called neuroplasticity that refers to the potential which the brain has to reorganize by creating new neural pathways to adapt, as it needs. Those studies arise anyways, whi ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s own track to the cerebral cortex • Audition has it own tra ...
... brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s own track to the cerebral cortex • Audition has it own tra ...
skinner theory of operent conditioning and shaping
... Shaping is a conditioning paradigm used primarily in the experimental analysis of behaviour. Skinner proved this using a Bird in a Cage. Skinner says,” it is constructed by a continual process of differential reinforcement from undifferentiated behavior, just as the sculptor shapes his figure ...
... Shaping is a conditioning paradigm used primarily in the experimental analysis of behaviour. Skinner proved this using a Bird in a Cage. Skinner says,” it is constructed by a continual process of differential reinforcement from undifferentiated behavior, just as the sculptor shapes his figure ...
Computational models of reinforcement learning
... (Fig. 1; Sutton and Barto 1998; Freeman 2007). On the biological side, it has also become clear that there is no single brain area responsible for the implementation of RL and that learning and reward processing are highly distributed functions involving dozens of dynamically interacting brain struc ...
... (Fig. 1; Sutton and Barto 1998; Freeman 2007). On the biological side, it has also become clear that there is no single brain area responsible for the implementation of RL and that learning and reward processing are highly distributed functions involving dozens of dynamically interacting brain struc ...
Vestibular senses
... Review visual receptive field concept; opponent colors are perceived, respectively by the center and surround fields of a ganglion cell - for example, red illumination in the center field of one ganglion cell will increase its activity, but green illumination on its surround field will inhibit the s ...
... Review visual receptive field concept; opponent colors are perceived, respectively by the center and surround fields of a ganglion cell - for example, red illumination in the center field of one ganglion cell will increase its activity, but green illumination on its surround field will inhibit the s ...
Brain development
... • (2) Brain a collection of genetically-specified modules • (3) Each module processes a specific kind of information & works independently of other modules • (4) In evolution: modules get added to the “collection” • (5) In development: genes that code for modules are expressed and modules develop ac ...
... • (2) Brain a collection of genetically-specified modules • (3) Each module processes a specific kind of information & works independently of other modules • (4) In evolution: modules get added to the “collection” • (5) In development: genes that code for modules are expressed and modules develop ac ...
Chapter 1
... The same content can be represented either by descriptions (abstract, language-like propositional representations) or depictions (picture-like representations). Some of the differences between the two types of formats are listed. A “relation” specifies how entities are combined, and an “argument” is ...
... The same content can be represented either by descriptions (abstract, language-like propositional representations) or depictions (picture-like representations). Some of the differences between the two types of formats are listed. A “relation” specifies how entities are combined, and an “argument” is ...
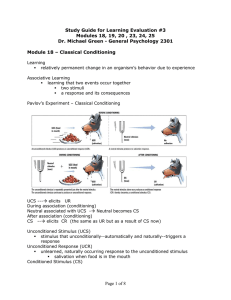
Study Guide for Learning Evaluation #4
... Spontaneous Recovery reappearance, after a rest period, of an extinguished CR Discrimination in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal a UCS ...
... Spontaneous Recovery reappearance, after a rest period, of an extinguished CR Discrimination in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a CS and other stimuli that do not signal a UCS ...
Symptoms: visual disturbances, ______, loss of
... iv. Important in embryonic nervous tissue and some brain regions f. Chemical synapses i. Specialized in the ___________ of neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled spa ...
... iv. Important in embryonic nervous tissue and some brain regions f. Chemical synapses i. Specialized in the ___________ of neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled spa ...
Brain Development
... Human nervous system development takes longer in the embryonic stage than other species The lower regions of the central nervous system develop specific attributes earlier while higher level (and area ) brain development may be formed w/less detail initially ...
... Human nervous system development takes longer in the embryonic stage than other species The lower regions of the central nervous system develop specific attributes earlier while higher level (and area ) brain development may be formed w/less detail initially ...
THE BASAL GANGLIA - Selam Higher Clinic
... areas of the brainstem Contribute chiefly to: postural control ...
... areas of the brainstem Contribute chiefly to: postural control ...
Recovery of consciousness after brain injury: a mesocircuit hypothesis
... to MCS within the first 3 months after injuries will recover past MCS by 10 months. Two to five year outcomes can include recovery past the level of severe disability even for patients who remain in MCS for greater than 6 months or a year. Rare cases that demonstrate endpoints of very late recovery ...
... to MCS within the first 3 months after injuries will recover past MCS by 10 months. Two to five year outcomes can include recovery past the level of severe disability even for patients who remain in MCS for greater than 6 months or a year. Rare cases that demonstrate endpoints of very late recovery ...
Amsterdam Brn Adapt View P3
... be brought about by experience. It also suggests that multiple forms of plasticity may occur at the synapse. In short, while memory researchers largely focus on naturallyand artificially-induced changes in synaptic connectivity, the brains of real animals (and presumably people) in realworld situati ...
... be brought about by experience. It also suggests that multiple forms of plasticity may occur at the synapse. In short, while memory researchers largely focus on naturallyand artificially-induced changes in synaptic connectivity, the brains of real animals (and presumably people) in realworld situati ...
Recovery of consciousness after brain injury: a
... to MCS within the first 3 months after injuries will recover past MCS by 10 months. Two to five year outcomes can include recovery past the level of severe disability even for patients who remain in MCS for greater than 6 months or a year. Rare cases that demonstrate endpoints of very late recovery ...
... to MCS within the first 3 months after injuries will recover past MCS by 10 months. Two to five year outcomes can include recovery past the level of severe disability even for patients who remain in MCS for greater than 6 months or a year. Rare cases that demonstrate endpoints of very late recovery ...
Optogenetics
... an excitatory neuron-specific promoter; this cell type specificity will result in a more direct inhibition, and thus less side-effects, compared with electrode-based DBS. Depression. DBS to the subgenual cingulate area 25 (Cg25) appears to alleviate depression symptoms. NpHR could be introduced into ...
... an excitatory neuron-specific promoter; this cell type specificity will result in a more direct inhibition, and thus less side-effects, compared with electrode-based DBS. Depression. DBS to the subgenual cingulate area 25 (Cg25) appears to alleviate depression symptoms. NpHR could be introduced into ...
MOTIVATION Motivating people is not an easy task. What motivates
... to their disadvantage, people adapt their behavior to reduce that inequity. An extension of equity theory is the procedural justice theory proposed by Folger and his colleagues6. It also takes into account the justice of the decision process. Various studies have shown that people only react against ...
... to their disadvantage, people adapt their behavior to reduce that inequity. An extension of equity theory is the procedural justice theory proposed by Folger and his colleagues6. It also takes into account the justice of the decision process. Various studies have shown that people only react against ...
Behaviorism: Its all in the action
... "conditioned reflex,"different from an innate reflex, such as yanking a hand back from a flame, in that it had to be learned. Pavlov called this learning process “conditioning” He thought that conditioned reflexes could explain the behavior of people. ...
... "conditioned reflex,"different from an innate reflex, such as yanking a hand back from a flame, in that it had to be learned. Pavlov called this learning process “conditioning” He thought that conditioned reflexes could explain the behavior of people. ...
PSY 402
... Adjunctive behaviors are behaviors that occur naturally as part of a species-specific natural behavior system (e.g., for eating). When an operant schedule provides frequent reward, the drinking occurs as an adjunct to eating, so rats wind up drinking too much. ...
... Adjunctive behaviors are behaviors that occur naturally as part of a species-specific natural behavior system (e.g., for eating). When an operant schedule provides frequent reward, the drinking occurs as an adjunct to eating, so rats wind up drinking too much. ...
Classical Conditioning
... Contains information from our sensory store that our brain has deemed relevant (at least for the time being). Information can be stored in this stage of memory from anywhere between 10 seconds to a few days (some scientists even argue that this can last up to 6 years). After that, the memories store ...
... Contains information from our sensory store that our brain has deemed relevant (at least for the time being). Information can be stored in this stage of memory from anywhere between 10 seconds to a few days (some scientists even argue that this can last up to 6 years). After that, the memories store ...
Behavioral dopamine signals
... Figure 1. Schematics of electrophysiological responses of single dopaminergic neurons to reward-related stimuli. (a) Prediction-error coding at the time of the reward: activation following an unpredicted reward (positive-prediction error; top), no response to a fully expected reward (no prediction e ...
... Figure 1. Schematics of electrophysiological responses of single dopaminergic neurons to reward-related stimuli. (a) Prediction-error coding at the time of the reward: activation following an unpredicted reward (positive-prediction error; top), no response to a fully expected reward (no prediction e ...
Using chaotic artificial neural networks to model memory in the brain
... or recollection and involves calling back the stored information in response to some cue for use in a process or activity. In this stage, the stored memory should be located and then accessed by the brain in a state of full attention [11]. The man-made memories created to mimic the human memory are ...
... or recollection and involves calling back the stored information in response to some cue for use in a process or activity. In this stage, the stored memory should be located and then accessed by the brain in a state of full attention [11]. The man-made memories created to mimic the human memory are ...
Part 1: From Ion Channels to behavior, HT2009 Course
... Central processing of visual information Central visual pathways The visual field and the receptive field The topographic organisation of the visual cortex Neuronal mechanisms of vision in LGN and cortex The processing and analysis of various visual submodalities ...
... Central processing of visual information Central visual pathways The visual field and the receptive field The topographic organisation of the visual cortex Neuronal mechanisms of vision in LGN and cortex The processing and analysis of various visual submodalities ...
cerebral cortex - krigolson teaching
... the thalamus. Major projections from other cortical areas include those from the parietal cortex and certain frontal areas. MA: Primary motor area; SMA: supplementary motor area; PMA: premotor area. ...
... the thalamus. Major projections from other cortical areas include those from the parietal cortex and certain frontal areas. MA: Primary motor area; SMA: supplementary motor area; PMA: premotor area. ...