Childhood Experience and the Expression of Genetic Potential
... while others will not. Again, this process appears to have genetic and environmental determinants. Neurons that make synaptic connections with others and have an adequate level of activation will survive; neurons with little activity resorb. This is one example of a general principle of activity-dep ...
... while others will not. Again, this process appears to have genetic and environmental determinants. Neurons that make synaptic connections with others and have an adequate level of activation will survive; neurons with little activity resorb. This is one example of a general principle of activity-dep ...
Untitled
... When the intact sheep brain has been thoroughly examined, cut it into right and left halves to expose the medial surfaces.To do this, place the brain on a table, ventral surface downward.Place a knife with a long thin blade in the medial longitudinalfissure. Then, with a single smooth stroke, cut th ...
... When the intact sheep brain has been thoroughly examined, cut it into right and left halves to expose the medial surfaces.To do this, place the brain on a table, ventral surface downward.Place a knife with a long thin blade in the medial longitudinalfissure. Then, with a single smooth stroke, cut th ...
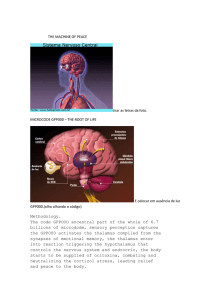
THE MACHINE OF PEACE tirar as letras da foto. MICROCODE
... stimuli from the periphery and the brain stem and also some coming from higher centers. There synapse axons of neurons located there, and then start new axons that will make connections with other higher centers, especially the cortex. Almost all signals that go upward to the cortex synapse in the n ...
... stimuli from the periphery and the brain stem and also some coming from higher centers. There synapse axons of neurons located there, and then start new axons that will make connections with other higher centers, especially the cortex. Almost all signals that go upward to the cortex synapse in the n ...
Chapter 2 - landman
... Three Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent) neurons: Carry messages from sense organs to the spinal cord or brain ...
... Three Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent) neurons: Carry messages from sense organs to the spinal cord or brain ...
The CNS Efficiency Model of the Chiropractic Subluxation
... applied to the nervous system. Neurons are born and differentiate in ways that are not conditioned by their future functions as elements of neural circuits Our understanding how functions ... can emerge from these beginnings, … is worth remembering that fundamental attributes of the nervous system s ...
... applied to the nervous system. Neurons are born and differentiate in ways that are not conditioned by their future functions as elements of neural circuits Our understanding how functions ... can emerge from these beginnings, … is worth remembering that fundamental attributes of the nervous system s ...
Module 3:Neural conduction and transmission Lecture 13
... signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at the end of the neurons. These terminal buttons contain neurotransmitters which plays important role in conduction at synapse. Synapse is the junction where one neuron ends and the other begin ...
... signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at the end of the neurons. These terminal buttons contain neurotransmitters which plays important role in conduction at synapse. Synapse is the junction where one neuron ends and the other begin ...
The Science of Psychology
... A newspaper-style web page that contains interesting articles, news reports, activities, and commentary on brain-related issues. Brain Function and Pathology: http://www.waiting.com/brainfunction.html Concise table of diagrams of brain structures, descriptions of brain functions, and descriptions of ...
... A newspaper-style web page that contains interesting articles, news reports, activities, and commentary on brain-related issues. Brain Function and Pathology: http://www.waiting.com/brainfunction.html Concise table of diagrams of brain structures, descriptions of brain functions, and descriptions of ...
BRAINSTEM - Anatomy.tv
... The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem by three tracts: Inferior cerebellar peduncle The thin inferior peduncles connect the cortex of the cerebellum to the medulla oblongata. They consist of both motor and sensory fibers; ascending and descending tracts from the spinal cord. Middle cerebellar ...
... The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem by three tracts: Inferior cerebellar peduncle The thin inferior peduncles connect the cortex of the cerebellum to the medulla oblongata. They consist of both motor and sensory fibers; ascending and descending tracts from the spinal cord. Middle cerebellar ...
The three minds of body
... childhood gut bacteria has the maximum impact on the developing brain and peters off by the age of 2-3 years just when the brain expansion also starts slowing down. Apparently the ancients knew something about the gut-brain connection. Hence the colon cleaning process of Ayurveda (including enema et ...
... childhood gut bacteria has the maximum impact on the developing brain and peters off by the age of 2-3 years just when the brain expansion also starts slowing down. Apparently the ancients knew something about the gut-brain connection. Hence the colon cleaning process of Ayurveda (including enema et ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... • Transmission of information between neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the ...
... • Transmission of information between neurons almost always occurs by chemical rather than electrical means. • Action potential causes release of specific chemical that are stored in synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic ending. • These chemicals are known as neurotransmitters and diffuse across the ...
Wisdom Qigong, opens the brain for wisdom.
... in the last century brain science really taken with PET scans, EEC 's, electron microscopes etc.. This yielded t be able to study. Living neuronal networks in the body What now appears. We not only neurons in our skull but in our entire body, especially in our belly and organs in our connective tiss ...
... in the last century brain science really taken with PET scans, EEC 's, electron microscopes etc.. This yielded t be able to study. Living neuronal networks in the body What now appears. We not only neurons in our skull but in our entire body, especially in our belly and organs in our connective tiss ...
CNS Embryology 2pptx (2)
... • Roof plate of myelencephalon consists of a single layer of ependymal cells covered by pia mater The two combined are known as tela choroidea. • Proliferation of vascular mesenchyme forms sac-like invaginations that project into the underlying ventricular cavity and form the choroid plexus, which ...
... • Roof plate of myelencephalon consists of a single layer of ependymal cells covered by pia mater The two combined are known as tela choroidea. • Proliferation of vascular mesenchyme forms sac-like invaginations that project into the underlying ventricular cavity and form the choroid plexus, which ...
The Ten-Percent Myth
... Other sources for the ubiquity of the 10-percent myth probably come from popular authors' misconstrual of scientific papers by early brain researchers. For example, in calling (for technical reasons) a huge percentage of the cerebral hemispheres the "silent cortex," early investigators may have lef ...
... Other sources for the ubiquity of the 10-percent myth probably come from popular authors' misconstrual of scientific papers by early brain researchers. For example, in calling (for technical reasons) a huge percentage of the cerebral hemispheres the "silent cortex," early investigators may have lef ...
Reflex arc ppt - bananateachersworld
... blunt pencil about 1 cm apart. 2. The blindfolded student has to say whether it was one point or two points that touched them. 3. Place a cross on the hand for each point felt. Results: Map the density of sensory receptors by drawing it into your book. Conclusion: Are the receptors in groups? Or ran ...
... blunt pencil about 1 cm apart. 2. The blindfolded student has to say whether it was one point or two points that touched them. 3. Place a cross on the hand for each point felt. Results: Map the density of sensory receptors by drawing it into your book. Conclusion: Are the receptors in groups? Or ran ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 3
... Module 3: Brain’s Building Blocks ...
... Module 3: Brain’s Building Blocks ...
Slide 1
... • Cerebellum receives impulses from the cerebral cortex of the intent to initiate voluntary muscle contraction • Signals from proprioceptors and visual and equilibrium pathways continuously “inform” the cerebellum of the body’s position and momentum • Cerebellar cortex calculates the best way to smo ...
... • Cerebellum receives impulses from the cerebral cortex of the intent to initiate voluntary muscle contraction • Signals from proprioceptors and visual and equilibrium pathways continuously “inform” the cerebellum of the body’s position and momentum • Cerebellar cortex calculates the best way to smo ...
Brainstem 10
... Its efferent fibers go to the anterior horn cells & to cranial nuclei 3, 4, 6, 7 & 11). It is responsible for the reflex movements of the eyes, head and neck in response to visual stimuli, as in following a moving object or altering the direction of the gaze. ...
... Its efferent fibers go to the anterior horn cells & to cranial nuclei 3, 4, 6, 7 & 11). It is responsible for the reflex movements of the eyes, head and neck in response to visual stimuli, as in following a moving object or altering the direction of the gaze. ...
Drug-Induced Psychosis and Schizophrenia
... neurological process), the oligodendroglia (cells that wrap, sheet-like, to form the myelin sheath), and interstitial neurons (these are cells that exist in the cortical sub-plate, which serves as a transition point for the development of the cerebral cortex. They somehow outlive the scheduled cell- ...
... neurological process), the oligodendroglia (cells that wrap, sheet-like, to form the myelin sheath), and interstitial neurons (these are cells that exist in the cortical sub-plate, which serves as a transition point for the development of the cerebral cortex. They somehow outlive the scheduled cell- ...
Enlightenment - The Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science
... individual neurons and specific patterns of activity to network dynamics, and then linking these elements to complex tasks such as perception or learning and memory, optogenetics should make it possible to understand the brain in unprecedented detail. Many other brain functions are promising candida ...
... individual neurons and specific patterns of activity to network dynamics, and then linking these elements to complex tasks such as perception or learning and memory, optogenetics should make it possible to understand the brain in unprecedented detail. Many other brain functions are promising candida ...
Chapter 2: The Biological Basis of Behavior
... A young woman recovering from a blow to her head finds she has great difficulty maintaining her balance and coordinating her movements. Injury to which part of her brain is likely to be causing her difficulties? a. cerebellum c. cerebral cortex b. medulla d. thalamus ...
... A young woman recovering from a blow to her head finds she has great difficulty maintaining her balance and coordinating her movements. Injury to which part of her brain is likely to be causing her difficulties? a. cerebellum c. cerebral cortex b. medulla d. thalamus ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.