TSM3 - Development of the CNS and PNS
... A subsequent infolding of the plate gives rise to the neural groove and bilateral neural crests which propagate into the mesoderm The folds in the neural plate fuse together to form the neural tube which is contained within the mesoderm and fully formed by the fourth week of development The neural t ...
... A subsequent infolding of the plate gives rise to the neural groove and bilateral neural crests which propagate into the mesoderm The folds in the neural plate fuse together to form the neural tube which is contained within the mesoderm and fully formed by the fourth week of development The neural t ...
Autism And Mirror Neurons
... Humans are normally able to do this quite well once fully developed- BUT autistic people seem to have a lack of empathy. What allows us to interpret the feelings of other people? Mirror Neurons!… along with a few other structures ...
... Humans are normally able to do this quite well once fully developed- BUT autistic people seem to have a lack of empathy. What allows us to interpret the feelings of other people? Mirror Neurons!… along with a few other structures ...
Nervous System Part Five
... Controls release of hormones by the anterior pituitary and produces posterior pituitary hormones Regulation of sleep-wake cycles ...
... Controls release of hormones by the anterior pituitary and produces posterior pituitary hormones Regulation of sleep-wake cycles ...
Document
... have desires and these cause behavior • 3-year-olds can distinguish between the mental world and the physical world • 4-year-olds understand that behavior is based on beliefs and that the beliefs can be ...
... have desires and these cause behavior • 3-year-olds can distinguish between the mental world and the physical world • 4-year-olds understand that behavior is based on beliefs and that the beliefs can be ...
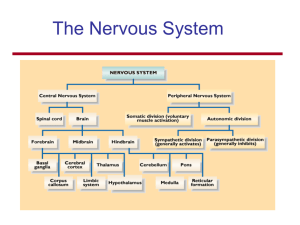
Nervous System 1
... – Dorsal and ventral roots of spinal nerves join insdte the vertebral column. – Each dorsal root joins at the same level as the corresponding ventral root, rather than posterior to it. – Usually all visceral motor fibers exit from the cord in the ventral root. So the shift is complete – leaving the ...
... – Dorsal and ventral roots of spinal nerves join insdte the vertebral column. – Each dorsal root joins at the same level as the corresponding ventral root, rather than posterior to it. – Usually all visceral motor fibers exit from the cord in the ventral root. So the shift is complete – leaving the ...
Brain
... increases heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate, blood flow to skeletal muscles, glucose metabolism decreases the activities that are not essential at the moment (digestive system organs are subdued- decreased blood flow to that system ...
... increases heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate, blood flow to skeletal muscles, glucose metabolism decreases the activities that are not essential at the moment (digestive system organs are subdued- decreased blood flow to that system ...
12-2cut
... • Recall that there are two types of neurotransmitters: excitatory and inhibitory • So, synapses can be either excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the neurotransmitter produced • CNS neurons often receive input from many other neurons ...
... • Recall that there are two types of neurotransmitters: excitatory and inhibitory • So, synapses can be either excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the neurotransmitter produced • CNS neurons often receive input from many other neurons ...
The Central Nervous System
... – Commisures connect corresponding gray areas of two hemispheres enabling them to function as a whole • The largest is the corpus collosum – Association fibers connect different parts of the same hemisphere – Projection fibers connects the cerebrum and lower brain areas • Sensory information reaches ...
... – Commisures connect corresponding gray areas of two hemispheres enabling them to function as a whole • The largest is the corpus collosum – Association fibers connect different parts of the same hemisphere – Projection fibers connects the cerebrum and lower brain areas • Sensory information reaches ...
Problems of the Nervous System
... The brain coordinates and controls the activities of the nervous system. Your brain helps you to receive and process messages; to think, remember, reason, and feel emotions; and to coordinate muscle movements. ...
... The brain coordinates and controls the activities of the nervous system. Your brain helps you to receive and process messages; to think, remember, reason, and feel emotions; and to coordinate muscle movements. ...
Brain Development
... In addition to its calming effects, sugar is known to make babies more alert and to encourage their hand-to-mouth coordination ...
... In addition to its calming effects, sugar is known to make babies more alert and to encourage their hand-to-mouth coordination ...
Problems of the Nervous System
... The brain coordinates and controls the activities of the nervous system. Your brain helps you to receive and process messages; to think, remember, reason, and feel emotions; and to coordinate muscle movements. ...
... The brain coordinates and controls the activities of the nervous system. Your brain helps you to receive and process messages; to think, remember, reason, and feel emotions; and to coordinate muscle movements. ...
Integrate and Fire Neural Network
... • What would this device need to do for it to be useful in your work ? ...
... • What would this device need to do for it to be useful in your work ? ...
Slide 1
... the heart and diaphragm • Some cranial nerves carry only sensory fibers, others carry only motor fibers, and others carry both types of fibers. ...
... the heart and diaphragm • Some cranial nerves carry only sensory fibers, others carry only motor fibers, and others carry both types of fibers. ...
Biology and behavior
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its energy. ...
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its energy. ...
Continuing Education Independent Study Series
... The somatic system, which is voluntary, conveys impulses to skeletal muscle tissue and produces movement. ...
... The somatic system, which is voluntary, conveys impulses to skeletal muscle tissue and produces movement. ...
Gross anatomy, and terms for directions and sections
... – System referenced to anatomical neuraxis, which is straight in many animals, and curved in humans. • Rostral / caudal; ventral / dorsal ...
... – System referenced to anatomical neuraxis, which is straight in many animals, and curved in humans. • Rostral / caudal; ventral / dorsal ...
The Nervous System
... another neuron (or specialized cell). • Firing neurons release neurotransmitters that cross the synapse. ...
... another neuron (or specialized cell). • Firing neurons release neurotransmitters that cross the synapse. ...
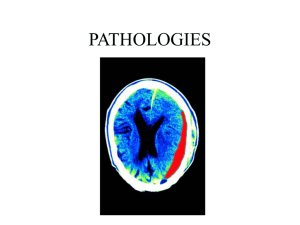
Abnormal Brain Wiring as a Pathogenetic Mechanism in
... brain regions, each having their own task or function, interact through thousands of structural connections, continuously processing, sharing, and integrating information. Driven by advances in neuroimaging techniques and mathematics, it has now become increasingly feasible to examine large scale br ...
... brain regions, each having their own task or function, interact through thousands of structural connections, continuously processing, sharing, and integrating information. Driven by advances in neuroimaging techniques and mathematics, it has now become increasingly feasible to examine large scale br ...
IT`S ALL IN YOUR MIND - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... of these smaller lobes has a specific job to help the body and brain communicate. The frontal lobes think and create (#1). The parietal lobes (#4) help us with directions and to recognize objects and their uses. At the back of the head are the occipital lobes (#5) where messages from the eyes are re ...
... of these smaller lobes has a specific job to help the body and brain communicate. The frontal lobes think and create (#1). The parietal lobes (#4) help us with directions and to recognize objects and their uses. At the back of the head are the occipital lobes (#5) where messages from the eyes are re ...
Brain stem-External Features
... MID BRAIN – DORSAL SURFACE Marked by 4 elevations: 1. Two superior colliculi: concerned with visual reflexes. 2. Two inferior colliculi: forms part of auditory pathway. Nerve emerging from Midbrain (one): • Trochlear (4th): just caudal to inferior colliculus (The only cranial nerve emerging fro ...
... MID BRAIN – DORSAL SURFACE Marked by 4 elevations: 1. Two superior colliculi: concerned with visual reflexes. 2. Two inferior colliculi: forms part of auditory pathway. Nerve emerging from Midbrain (one): • Trochlear (4th): just caudal to inferior colliculus (The only cranial nerve emerging fro ...
HEAD , FACIAL BONES, SINUSES, AND ORBITS
... Astrocytomas are glial cell tumors that are derived from connective tissue cells called astrocytes. These cells can be found anywhere in the brain or spinal cord. Astrocytomas are the most common type of childhood brain tumor. ...
... Astrocytomas are glial cell tumors that are derived from connective tissue cells called astrocytes. These cells can be found anywhere in the brain or spinal cord. Astrocytomas are the most common type of childhood brain tumor. ...
Your Brain
... When Gage’s coworkers reached him, he was conscious and able to tell them what had happened. He was rushed to a physician who was able to stop the bleeding and save his life, but the destruction of such a large amount of brain tissue took a terrible toll on his emotions and intelligence. Gage became ...
... When Gage’s coworkers reached him, he was conscious and able to tell them what had happened. He was rushed to a physician who was able to stop the bleeding and save his life, but the destruction of such a large amount of brain tissue took a terrible toll on his emotions and intelligence. Gage became ...
The Nervous System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Disorders of the nervous system are numerous and often very difficult to diagnose and treat because of the complexity of this system. ...
... Disorders of the nervous system are numerous and often very difficult to diagnose and treat because of the complexity of this system. ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.