Narcotic analgesics
... produced in combination with opiate receptors at deep levels of the brain (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system). Opioid receptors are grouped into the following four classes: 1- Mu- found in pain-regulating areas of the brain; contribute to analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, physical dep ...
... produced in combination with opiate receptors at deep levels of the brain (thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system). Opioid receptors are grouped into the following four classes: 1- Mu- found in pain-regulating areas of the brain; contribute to analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, physical dep ...
Formulation and evaluation of ketorolac tromethamine as an anti
... Ketorolac tromethamine (KT) is considered as a member of NSAIDs that used in treatment of musculoskeletal and joint disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis , ankylosing spondilitis and acute gouty arthritis . Because KT appears to be associated with a higher incidence of adverse effects mainly irrita ...
... Ketorolac tromethamine (KT) is considered as a member of NSAIDs that used in treatment of musculoskeletal and joint disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis , ankylosing spondilitis and acute gouty arthritis . Because KT appears to be associated with a higher incidence of adverse effects mainly irrita ...
Pharmacokinetic interaction of rifapentine and
... currently recommended as one of four preferred regimens for patients who have not had previous treatment for HIV. Furthermore, raltegravir may be substituted for efavirenz in pregnant women, and there are fewer drug interactions with raltegravir than with the other preferred regimens. Therefore, it ...
... currently recommended as one of four preferred regimens for patients who have not had previous treatment for HIV. Furthermore, raltegravir may be substituted for efavirenz in pregnant women, and there are fewer drug interactions with raltegravir than with the other preferred regimens. Therefore, it ...
Modern Methods in Drug Discovery WS06/07
... The available knowledge on the human genome and the present SNPs in it allow two approaches: 1. Finding new targets (either on the genome, the mRNA, or the protein level) 2. pharmacogenomic methods will lead to personalized medicine (which drug and at what dosage), esp. for long term application of ...
... The available knowledge on the human genome and the present SNPs in it allow two approaches: 1. Finding new targets (either on the genome, the mRNA, or the protein level) 2. pharmacogenomic methods will lead to personalized medicine (which drug and at what dosage), esp. for long term application of ...
Bez nadpisu - Univerzita Karlova
... alcohol. Drug that inhibit hepatic metabolism (ketaconazole) may result in dangerously high levels of nonsedating antihistaminic drugs (e.g. terfenadine) the plasma concentration of either antihistamine may increase and precipitate lethal arrhythmias. ...
... alcohol. Drug that inhibit hepatic metabolism (ketaconazole) may result in dangerously high levels of nonsedating antihistaminic drugs (e.g. terfenadine) the plasma concentration of either antihistamine may increase and precipitate lethal arrhythmias. ...
Niosome and Proniosome – Vesicular Structured Dosage Form for
... parts of the body relative to others. Targeted drug delivery seeks to concentrate the medication in the tissues of interest while reducing the relative concentration of the medication in the remaining tissues.1This improves efficacy of the while reducing side effects. Drug targeting is the delivery ...
... parts of the body relative to others. Targeted drug delivery seeks to concentrate the medication in the tissues of interest while reducing the relative concentration of the medication in the remaining tissues.1This improves efficacy of the while reducing side effects. Drug targeting is the delivery ...
Controlled Release Softgel Drug Delivery
... form is that it is preferred by patients compared to tablets and two piece hard gelatin capsules. According to one survey2, approximately 90% of respondents strongly preferred clear softgels over other dosage forms in virtually all the areas investigated. Notably, the overall preference of softgels ...
... form is that it is preferred by patients compared to tablets and two piece hard gelatin capsules. According to one survey2, approximately 90% of respondents strongly preferred clear softgels over other dosage forms in virtually all the areas investigated. Notably, the overall preference of softgels ...
Treatment of Tuberculosis: Standard Therapy for Active Disease in
... • All patients should be initially started on a 4-drug regimen of Isoniazid (INH), Rifampin (RIF), Pyrazinamide (PZA), and Ethambutol (EMB). Following the initial 8-week phase of treatment, the continuation phase should consist of INH and RIF in pansensitive cases. • Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) ...
... • All patients should be initially started on a 4-drug regimen of Isoniazid (INH), Rifampin (RIF), Pyrazinamide (PZA), and Ethambutol (EMB). Following the initial 8-week phase of treatment, the continuation phase should consist of INH and RIF in pansensitive cases. • Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) ...
E: Psychoactive Drugs Other than Narcotics and Stimulants
... integration of sensory experiences with emotions and motivation (321). Their findings help explain the symptoms of lethargy and attention and memory problems associated with acute marijuana use. There is little evidence that marijuana produces tolerance or severe physical withdrawal symptoms, though ...
... integration of sensory experiences with emotions and motivation (321). Their findings help explain the symptoms of lethargy and attention and memory problems associated with acute marijuana use. There is little evidence that marijuana produces tolerance or severe physical withdrawal symptoms, though ...
A case of benzydamine HCL intoxication
... drops. Acute poisoning with benzydamine HCL is associated with agitation, hallucinations, seizures and rarely somnolence. In this study, we reported a rare case of benzydamine poisoning in a girl who presented with somnolence and visual hallucinations one hour after taking five benzydamine HCL drage ...
... drops. Acute poisoning with benzydamine HCL is associated with agitation, hallucinations, seizures and rarely somnolence. In this study, we reported a rare case of benzydamine poisoning in a girl who presented with somnolence and visual hallucinations one hour after taking five benzydamine HCL drage ...
Anesthesia for Geriatric Patients
... protein for acidic drugs) decreases with age. • While the level of α-1 acid glycoprotein (binding protein for basic drugs) increases. ...
... protein for acidic drugs) decreases with age. • While the level of α-1 acid glycoprotein (binding protein for basic drugs) increases. ...
Lecture : Contents : Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection
... Inhibit protein synthesis by binding reversibly (Bacteriostatic )to 30 S subunit. (Doxycycline ) must be not given with Pharmacokinetics Given orally Absorption is 90-100%(completely absorped from GIT) BUT di & tri-valent cations ( Ca, Mg, Fe, AL) impair absorption Protein binding 40-80 ...
... Inhibit protein synthesis by binding reversibly (Bacteriostatic )to 30 S subunit. (Doxycycline ) must be not given with Pharmacokinetics Given orally Absorption is 90-100%(completely absorped from GIT) BUT di & tri-valent cations ( Ca, Mg, Fe, AL) impair absorption Protein binding 40-80 ...
DBM Draft Position paper on Mood Stabilizers for
... Lithium in contrast does an extraordinary number of things in the body but no-one is clear on what are its key actions. In addition being helpful in mood disorders, it appears to have antiaggressive or anti-impulsive effects. These are very different drugs, but you’d never guess it from their market ...
... Lithium in contrast does an extraordinary number of things in the body but no-one is clear on what are its key actions. In addition being helpful in mood disorders, it appears to have antiaggressive or anti-impulsive effects. These are very different drugs, but you’d never guess it from their market ...
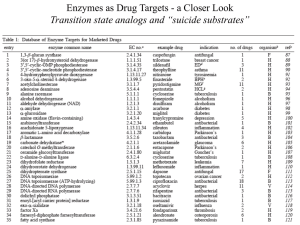
Lecture 13, Inhibitors - Cal State LA
... mimic of the substrate or the transition state. Lecture on Protein targets listed some examples of reversible inhibitors as drugs 1. Transition state mimic for adenosine deaminase (enzyme which degrades anticancer drugs) ...
... mimic of the substrate or the transition state. Lecture on Protein targets listed some examples of reversible inhibitors as drugs 1. Transition state mimic for adenosine deaminase (enzyme which degrades anticancer drugs) ...
Antiarrhythmic Drugs - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... (admin/elim) p.o. t1/2 = 3hrs hepatic elim acetylate to Nacetylprocainami de (NAPA) ...
... (admin/elim) p.o. t1/2 = 3hrs hepatic elim acetylate to Nacetylprocainami de (NAPA) ...
Metabolism and drug interactions of 3-hydroxy-3
... formation is inhibited in striated muscle. Subsequently, there is a lack of cholesterol precursors produced from mevalonic acid. These are important for several cell functions and serve, for example, glycosylation of cell surface proteins, electron transfer during mitochondrial membranes and post-tr ...
... formation is inhibited in striated muscle. Subsequently, there is a lack of cholesterol precursors produced from mevalonic acid. These are important for several cell functions and serve, for example, glycosylation of cell surface proteins, electron transfer during mitochondrial membranes and post-tr ...
Drug interaction

A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance (usually another drug) affects the activity of a drug when both are administered together. This action can be synergistic (when the drug's effect is increased) or antagonistic (when the drug's effect is decreased) or a new effect can be produced that neither produces on its own. Typically, interactions between drugs come to mind (drug-drug interaction). However, interactions may also exist between drugs and foods (drug-food interactions), as well as drugs and medicinal plants or herbs (drug-plant interactions). People taking antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take food containing tyramine as hypertensive crisis may occur (an example of a drug-food interaction). These interactions may occur out of accidental misuse or due to lack of knowledge about the active ingredients involved in the relevant substances.It is therefore easy to see the importance of these pharmacological interactions in the practice of medicine. If a patient is taking two drugs and one of them increases the effect of the other it is possible that an overdose may occur. The interaction of the two drugs may also increase the risk that side effects will occur. On the other hand, if the action of a drug is reduced it may cease to have any therapeutic use because of under dosage. Notwithstanding the above, on occasion these interactions may be sought in order to obtain an improved therapeutic effect. Examples of this include the use of codeine with paracetamol to increase its analgesic effect. Or the combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin in order to overcome bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. It should also be remembered that there are interactions that, from a theoretical standpoint, may occur but in clinical practice have no important repercussions.The pharmaceutical interactions that are of special interest to the practice of medicine are primarily those that have negative effects for an organism. The risk that a pharmacological interaction will appear increases as a function of the number of drugs administered to a patient at the same time.It is possible that an interaction will occur between a drug and another substance present in the organism (i.e. foods or alcohol). Or in certain specific situations a drug may even react with itself, such as occurs with dehydration. In other situations, the interaction does not involve any effect on the drug. In certain cases, the presence of a drug in an individual's blood may affect certain types of laboratory analysis (analytical interference).It is also possible for interactions to occur outside an organism before administration of the drugs has taken place. This can occur when two drugs are mixed, for example, in a saline solution prior to intravenous injection. Some classic examples of this type of interaction include that Thiopentone and Suxamethonium should not be placed in the same syringe and same is true for Benzylpenicillin and Heparin. These situations will all be discussed under the same heading due to their conceptual similarity.Drug interactions may be the result of various processes. These processes may include alterations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug, such as alterations in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug. Alternatively, drug interactions may be the result of the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug, e.g. the co-administration of a receptor antagonist and an agonist for the same receptor.