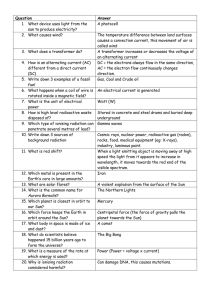
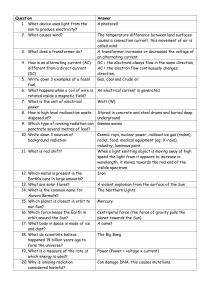
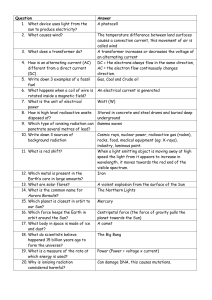
Question Answer What device uses light from the sun to produce
... A transformer increases or decreases the voltage of an alternating current Gas, Coal and Crude oil Watt (W) Gamma waves When a light emitting object is moving away at high speed the light from it appears to increase in wavelength, it moves towards the red end of the visible spectrum. A violent explo ...
... A transformer increases or decreases the voltage of an alternating current Gas, Coal and Crude oil Watt (W) Gamma waves When a light emitting object is moving away at high speed the light from it appears to increase in wavelength, it moves towards the red end of the visible spectrum. A violent explo ...
Magnetism guided reading
... Chapter 18.2 Magnetism from Electrical Currents (use the information starting on page 626 to answer the following questions) 23. What observations suggested a relationship between electricity and magnetism? ...
... Chapter 18.2 Magnetism from Electrical Currents (use the information starting on page 626 to answer the following questions) 23. What observations suggested a relationship between electricity and magnetism? ...
Physics 121 Lab: Finding the horizontal component of the magnetic
... surface of earth dips to align with the total field. In the northern hemisphere, the north-end of the compass directs downward at some inclination angle, θ, depending on its latitude. The magnetic field in the vicinity of your lab station comes mainly from the earth, but it is sometimes significantl ...
... surface of earth dips to align with the total field. In the northern hemisphere, the north-end of the compass directs downward at some inclination angle, θ, depending on its latitude. The magnetic field in the vicinity of your lab station comes mainly from the earth, but it is sometimes significantl ...
Physical origin
... field declines and any concentrations of field spread out. If the Earth's dynamo shut off, the dipole part would disappear in a few tens of thousands of years.[] In a perfect conductor (á=Ñ), there would be no diffusion. By Lenz's law, any change in the magnetic field would be immediately opposed by ...
... field declines and any concentrations of field spread out. If the Earth's dynamo shut off, the dipole part would disappear in a few tens of thousands of years.[] In a perfect conductor (á=Ñ), there would be no diffusion. By Lenz's law, any change in the magnetic field would be immediately opposed by ...
Earthlike planets
... d.convection does not extend all the way to the center of the core. e.Earth initially formed from solid particles in the solar nebula. 4. Earth's magnetic field is generated by the dynamo effect in the a. molten metallic core. b.solid central core. c.plastic mantle. d.the crust. e.aurora. 5. The oxy ...
... d.convection does not extend all the way to the center of the core. e.Earth initially formed from solid particles in the solar nebula. 4. Earth's magnetic field is generated by the dynamo effect in the a. molten metallic core. b.solid central core. c.plastic mantle. d.the crust. e.aurora. 5. The oxy ...
Physics 1 notes 4-11-13 NOVA earth`s magnetic field
... magnetic field at that time. It’s possible to plot a graph of the field strength over time. In the past 300 years, the field strength has declined. Scientists model the earth’s core with liquid sodium, which is highly conductive, like molten iron. Magnetic field generates electric current that g ...
... magnetic field at that time. It’s possible to plot a graph of the field strength over time. In the past 300 years, the field strength has declined. Scientists model the earth’s core with liquid sodium, which is highly conductive, like molten iron. Magnetic field generates electric current that g ...
ElectroMagnet - Arbor Scientific
... coils have soft iron inserted into the middle of them. By following the wire closely with your eye, you can also see that the coils are wrapped around in opposite directions. The coils, when carrying a current, induce two magnetic fields and force the iron to become magnetized. Each coil, because th ...
... coils have soft iron inserted into the middle of them. By following the wire closely with your eye, you can also see that the coils are wrapped around in opposite directions. The coils, when carrying a current, induce two magnetic fields and force the iron to become magnetized. Each coil, because th ...
The Sun and Our Earth - Rochester Community Schools
... Magnetic fields causes the convection to slow in the convection zone. Slower convection causes a decrease in the amount of gas that is transferring energy from the core to the photosphere. Because less energy is transferred, some regions of the photosphere are cooler than the surrounding region ...
... Magnetic fields causes the convection to slow in the convection zone. Slower convection causes a decrease in the amount of gas that is transferring energy from the core to the photosphere. Because less energy is transferred, some regions of the photosphere are cooler than the surrounding region ...
Comp Quest 22 SPI 0807.12.3
... not as high. As Earth rotates, the liquid in the core flows. Charged particles move, which makes a magnetic field. The strength of a magnetic field decreases rapidly with distance from the magnet. On the surface of the planet, Earth’s magnetic field is not very strong compared to that of a nearby el ...
... not as high. As Earth rotates, the liquid in the core flows. Charged particles move, which makes a magnetic field. The strength of a magnetic field decreases rapidly with distance from the magnet. On the surface of the planet, Earth’s magnetic field is not very strong compared to that of a nearby el ...
PPT
... Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later…maybe. ...
... Morley looked and looked, and decided it wasn’t there. How do waves travel??? Electricity and magnetism are “relative”: Whether charges move or not depends on which frame we use… This was how Einstein began thinking about his “theory of special relativity”… We’ll leave that theory for later…maybe. ...
Chapter 6 Part1: Multiple choices
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
Aurora

An aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere), where their energy is lost. The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emits light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration imparted to the precipitating particles. Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes. Different aspects of an aurora are elaborated in various sections below.